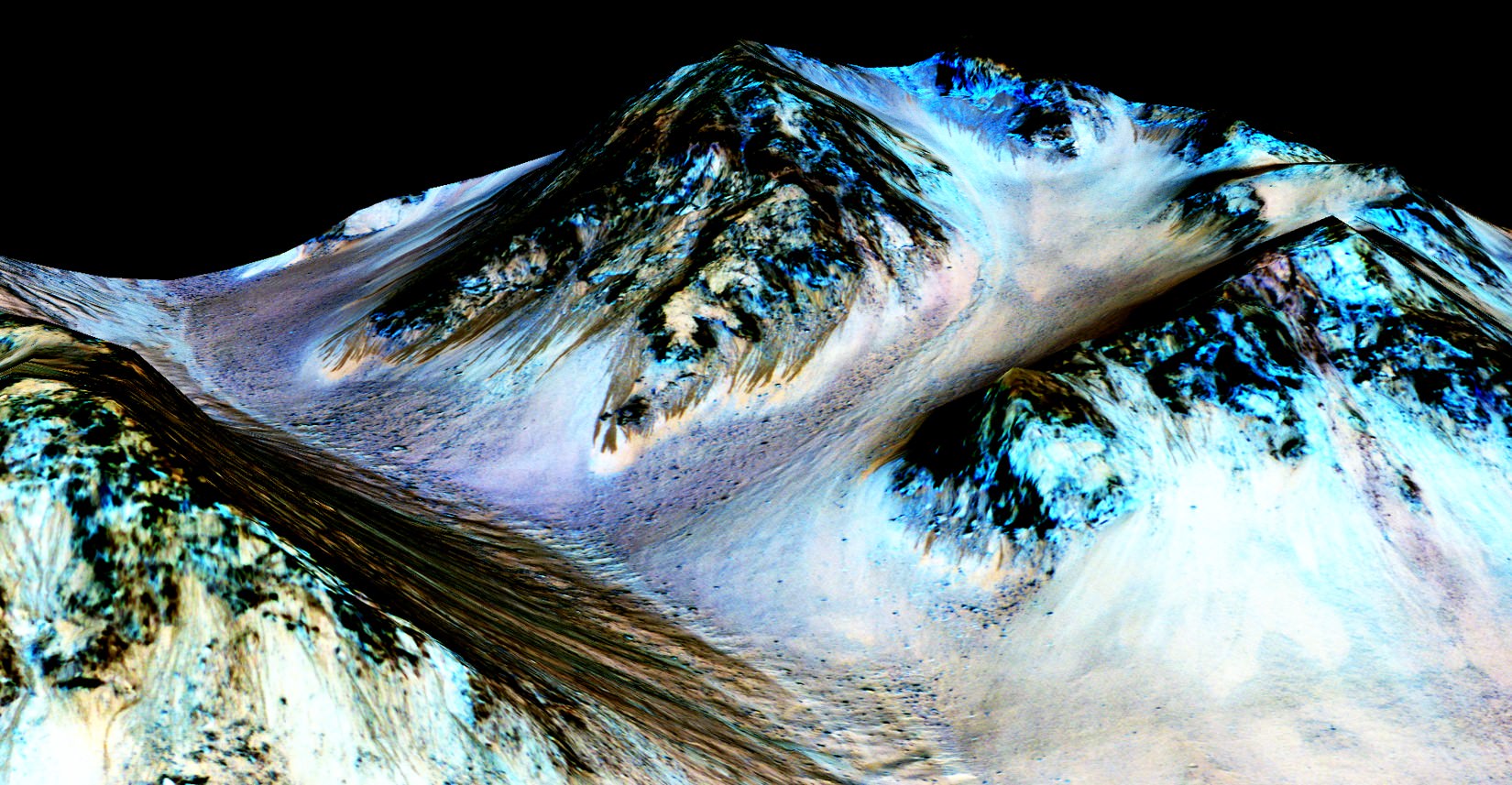
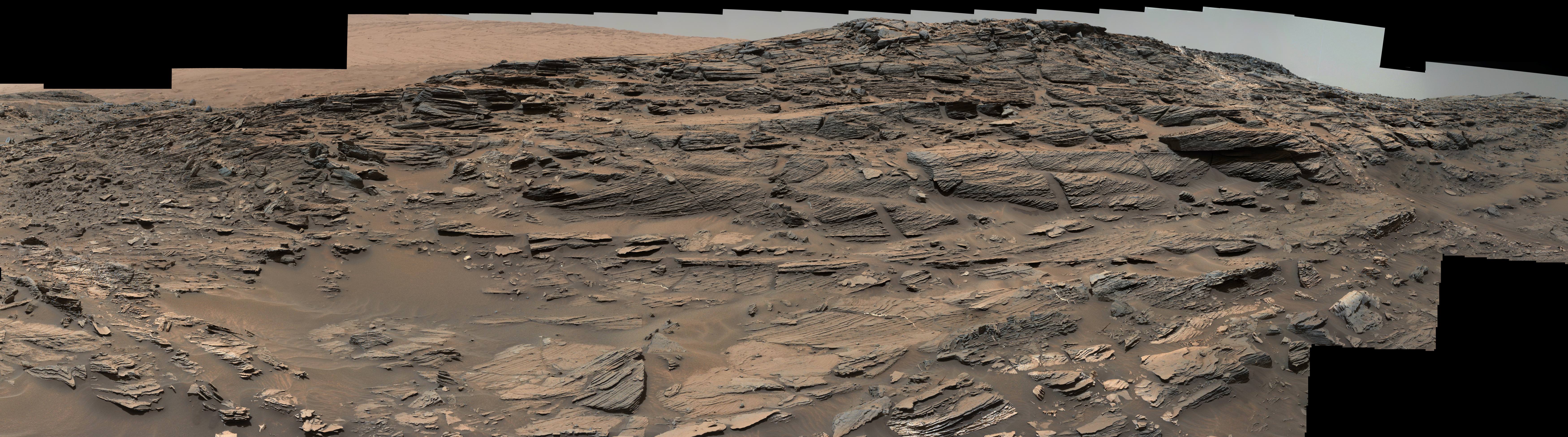
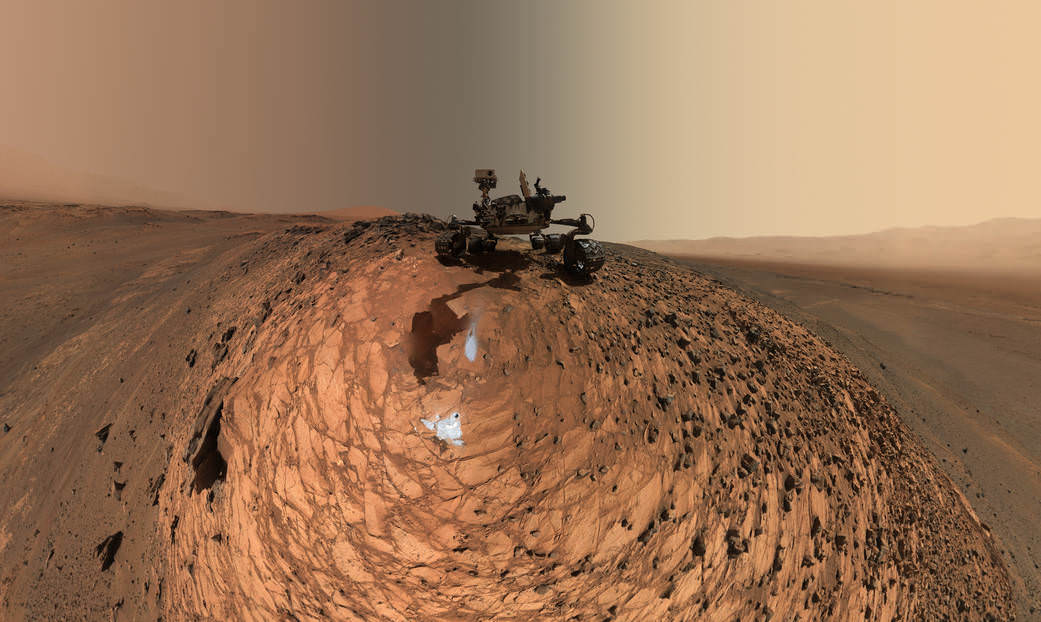
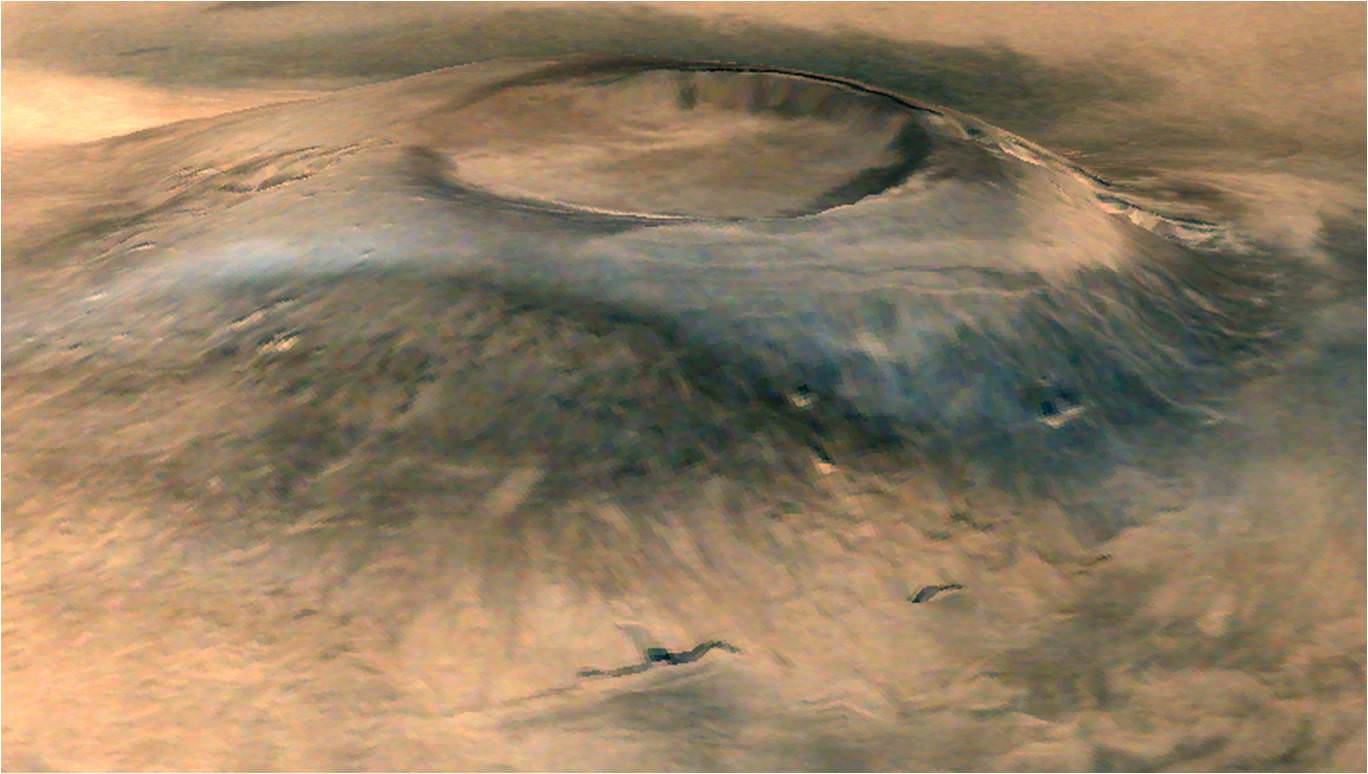
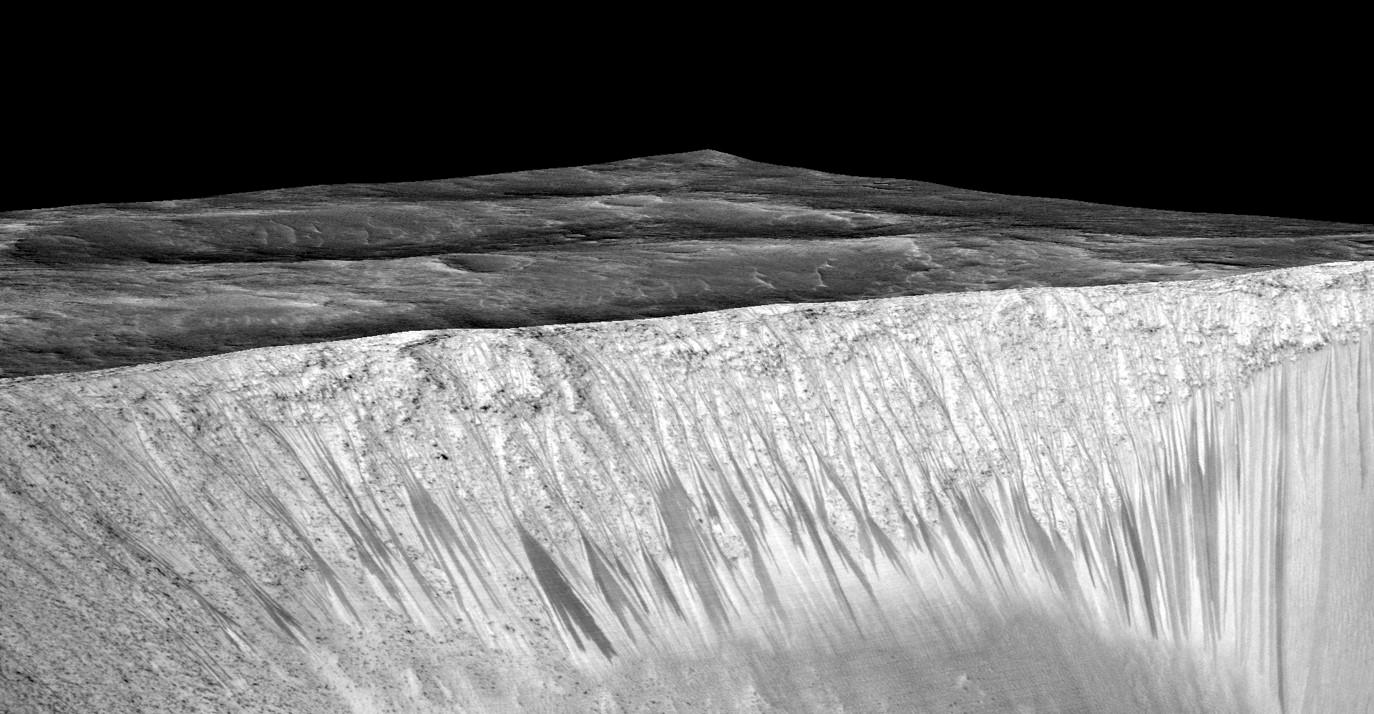
These dark, narrow, 100 meter-long streaks called recurring slope lineae flowing downhill on Mars are inferred to have been formed by contemporary flowing water. Recently, planetary scientists detected hydrated salts on these slopes at Hale crater, corroborating their original hypothesis that the streaks are indeed formed by liquid water. The blue color seen upslope of the dark streaks are thought not to be related to their formation, but instead are from the presence of the mineral pyroxene.
The image is produced by draping an orthorectified Infrared-Red-Blue/Green(IRB)) false color image on a Digital Terrain Model (DTM). This model was produced by researchers at the University of Arizona, much like the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (University of Arizona). The vertical exaggeration is 1.5.
NASA and Mars planetary scientists announced today (Sept. 28) that salty “liquid water flows intermittently” across multiple spots on the surface of today’s Mars – trumpeting a major scientific discovery with far reaching implications regarding the search for life beyond Earth and bolstering the chances for the possible existence of present day Martian microbes.
Utilizing spectroscopic measurements and imaging gathered by NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO), researchers found the first strong evidence confirming that briny water flows on the Red Planet today along dark streaks moving downhill on crater slopes and mountain sides, during warmer seasons.
“Mars is not the dry, arid planet that we thought of in the past. Today we announce that under certain circumstances, liquid water has been found on Mars,” said Jim Green, NASA Planetary Science Director at NASA Headquarters, at a media briefing held today, Sept 28.
“When you look at Earth, water is an essential ingredient. Everywhere we go where there’s liquid water, whether its deep in the Earth or in the arid regions, we find life. This is tremendously exciting.”
“We haven’t been able to answer the question – does life exist beyond Earth? But following the water is a critical element of that. We now have great opportunities to be in the right locations on Mars to thoroughly investigate that,” Green elaborated.
“Water! Strong evidence that liquid water flows on present-day Mars,” NASA officials tweeted about the discovery.
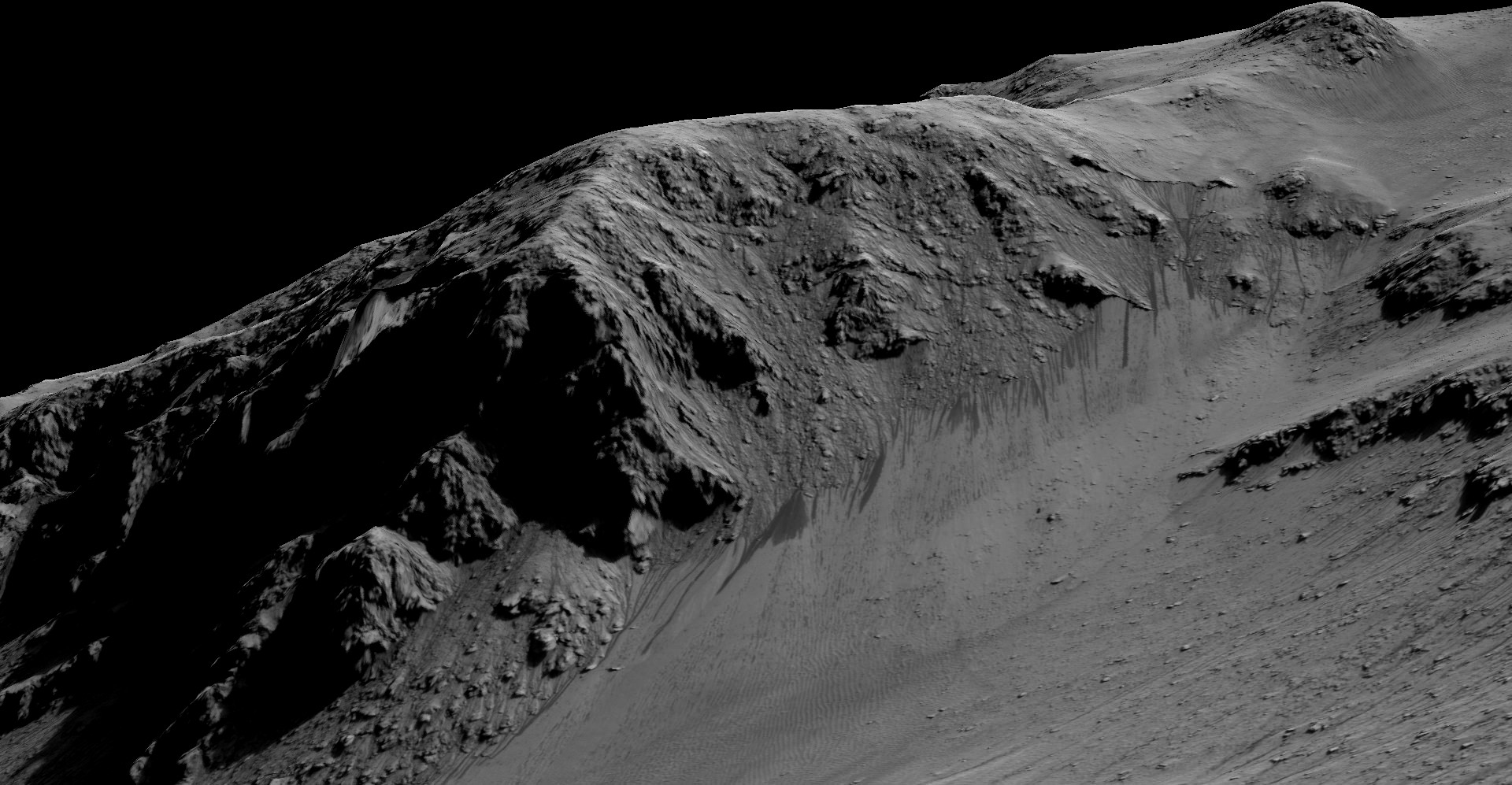
The evidence comes in the form of the detection of mysterious dark streaks, as long as 100 meters, showing signatures of hydrated salt minerals periodically flowing in liquid water down steep slopes on the Red Planet that “appear to ebb and flow over time.”
The source of the water is likely from the shallow subsurface or possibly absorbed from the atmosphere.

Water is a key prerequisite for the formation and evolution of life as we know it. So the new finding significantly bolsters the chances that present day extant life could exist on the Red Planet.
“Our quest on Mars has been to ‘follow the water,’ in our search for life in the universe, and now we have convincing science that validates what we’ve long suspected,” said John Grunsfeld, astronaut and associate administrator of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington.
“This is a significant development, as it appears to confirm that water — albeit briny — is flowing today on the surface of Mars.”
“This increases the chance that life could exist on Mars today,” noted Grunsfeld.
The data were gathered by and the conclusions are based on using two scientific instruments – the high resolution imaging spectrometer on MRO known as High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE), as well as MRO’s mineral mapping Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars (CRISM).
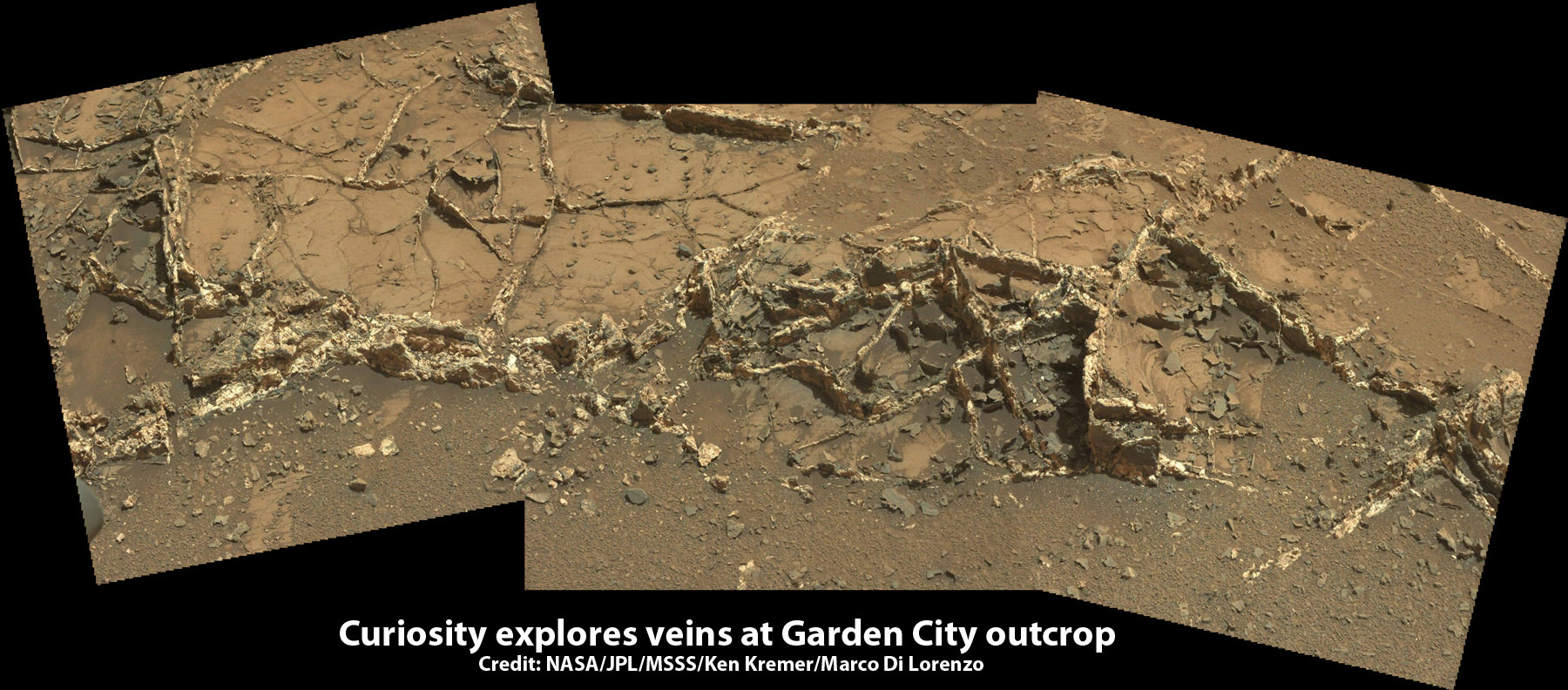
The mysterious dark streaks of downhill flows are known as recurring slope lineae (RSL).
They were first detected in 2010 at dozens of sites on the sun facing slopes of deep craters by Lujendra Ojha, then a University of Arizona undergraduate student.
The new finding is highly significant because until today’s announcement, there was no strong evidence that liquid water could actually exist on the Martian surface because the atmospheric pressure was thought to be far too low – its less than one percent of Earth’s.
The flow of water is occasional and not permanent, seasonally variable and dependent on having just the right mix of atmospheric, temperature and surface conditions with salt deposits on Mars.
Portions of Mars were covered with an ocean of water billions of years ago when the planet was far warmer and more hospitable to life. But it underwent a dramatic climate change some 3 billion years ago and lost most of that water.
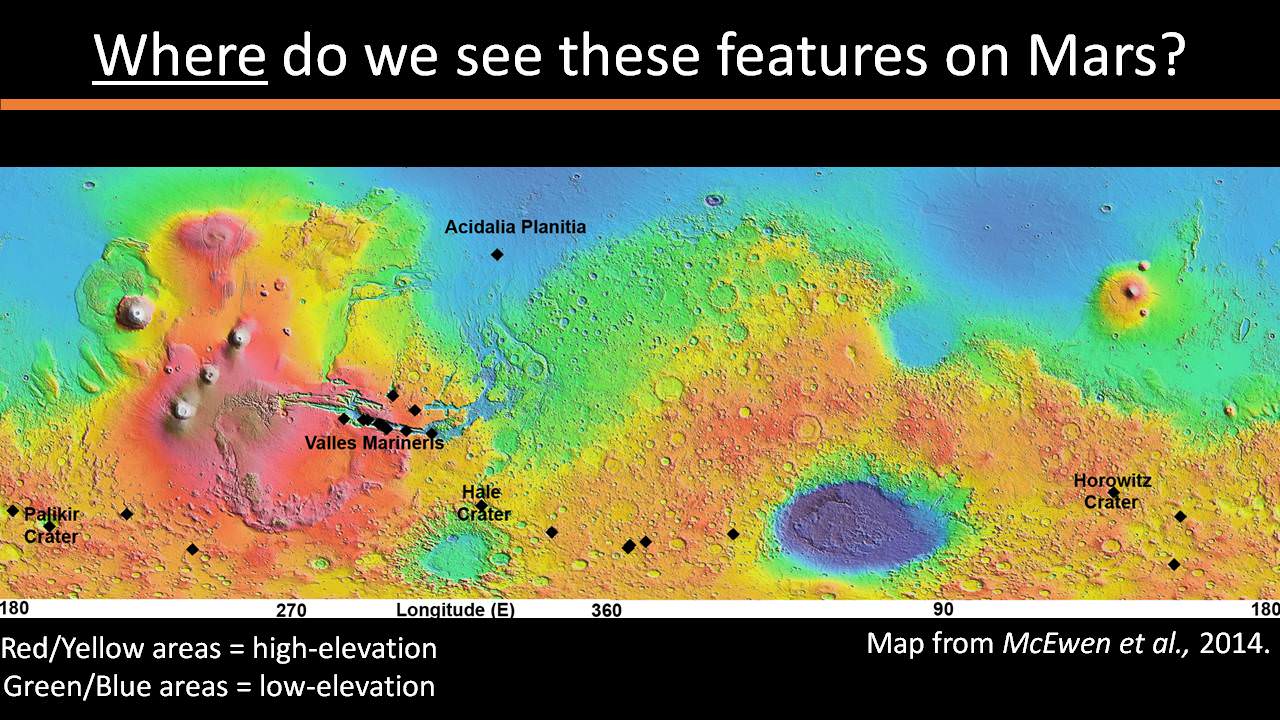
The RSL with flowing water appear in at least three different locations on Mars – including Hale crater, Horowitz crater and Palikir crater – when temperatures are above minus 10 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 23 Celsius). They appear during warm seasons, fade in cooler seasons and disappear during colder times.
Pure surface water ice would simply sublimate and evaporate away as the temperature rises. Mixing in surface salts lowers the melting point of ice, thereby allowing the water to potentially liquefy on Mars surface for a certain period of time rather than sublimating rapidly away.
“These are dark streaks that form in late spring, grow through the summer and then disappear in the fall,” said Michael Meyer lead scientist for the Mars Exploration Program at NASA Headquarters, at the media briefing.
Years of painstaking effort and laboratory work was required to verify and corroborate the finding of flowing liquid water.
“It took multiple spacecraft over several years to solve this mystery, and now we know there is liquid water on the surface of this cold, desert planet,” said Meyer. “It seems that the more we study Mars, the more we learn how life could be supported and where there are resources to support life in the future.”

Along with the media announcement, the researchers published their findings today in a refereed scientific paper in the Sept. 28 issue of Nature Geoscience.
“We found the hydrated salts only when the seasonal features were widest, which suggests that either the dark streaks themselves or a process that forms them is the source of the hydration. In either case, the detection of hydrated salts on these slopes means that water plays a vital role in the formation of these streaks,” said Lujendra Ojha, now at the Georgia Institute of Technology (Georgia Tech) in Atlanta, and lead author of the Sept. 28 publication in Nature Geoscience.
The scientists “interpret the spectral signatures as caused by hydrated minerals called perchlorates.”
Ojha said the chemical signatures from CRISM were most consistent with the detection of mixtures of magnesium perchlorate, magnesium chlorate and sodium perchlorate, based on lab experiments.
“Some perchlorates have been shown to keep liquids from freezing even when conditions are as cold as minus 94 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 70 Celsius).”
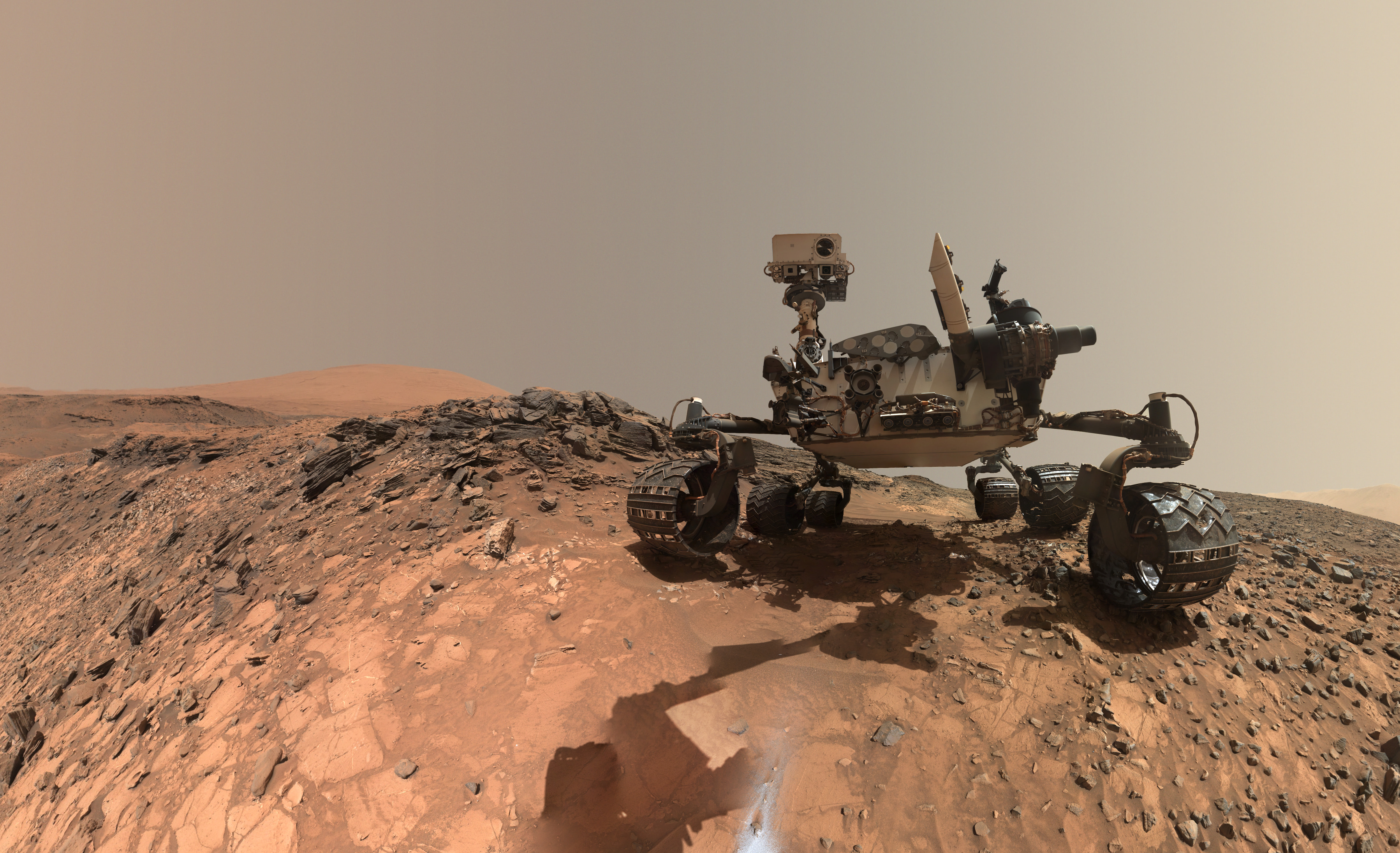
Perchlorates have previously been detected in Martian soil by two of NASA’s surface missions – the Phoenix lander and the Curiosity rover. There is also some evidence that NASA’s Viking missions in the 1970s measured signatures of these salts.
On Earth concentration of perchlorates are found in deserts.
This also marks the first time perchlorates have been identified from Mars orbit.
NASA’s overriding agency wide goal is to send humans on a ‘Journey to Mars’ in the 2030s.
So NASA astronaut Mark Kelly exclaimed that he was also super excited about the findings, from his perch serving as Commander aboard the International Space Station (ISS), where he is a member of the first ever “1 Year ISS Mission Crew” aimed at learning how the human body will adapt to the long term missions required to send astronauts to Mars and back.
“One reason why NASA’s discovery of liquid water on #Mars is so exciting: we know anywhere there’s water on Earth, there’s some form of life,” Kelly tweeted today from on board the ISS, upon hearing today’s news.
The discovery of liquid water on Mars could also be a boon to future astronauts who could use it as a natural resource to ‘live off the land’ for sustenance and to make rocket fuel.
“If going to Mars on my Year In Space, I’d arrive soon to find water! H20 > rocket fuel, which means I could find my way back home too!,” Kelly wrote on his Facebook page.
“When most people talk about water on Mars, they’re usually talking about ancient water or frozen water,” Ojha explained.
“Now we know there’s more to the story. This is the first spectral detection that unambiguously supports our liquid water-formation hypotheses for RSL.”
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.