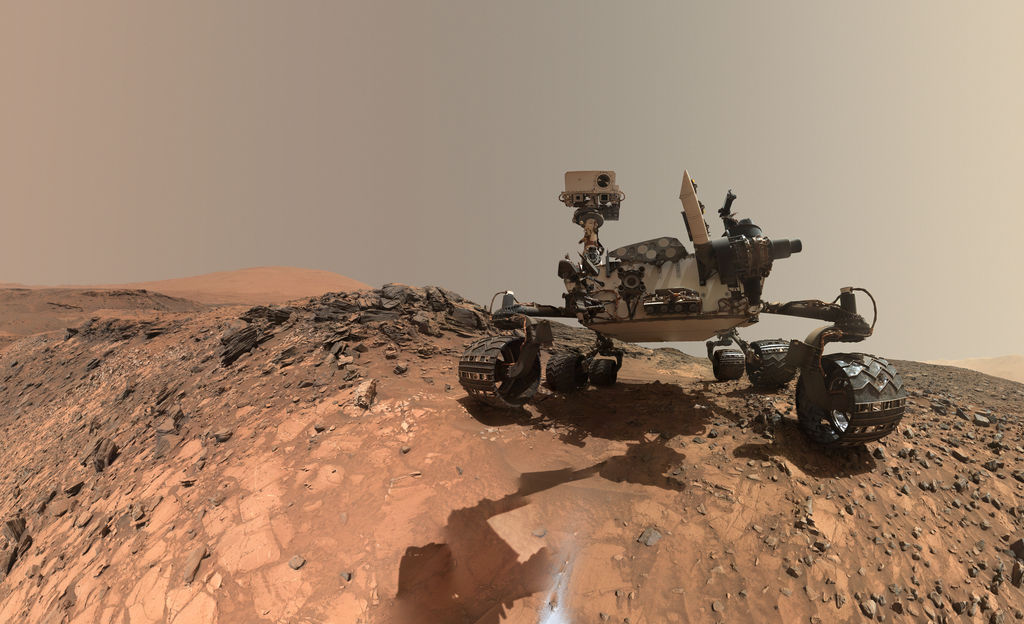
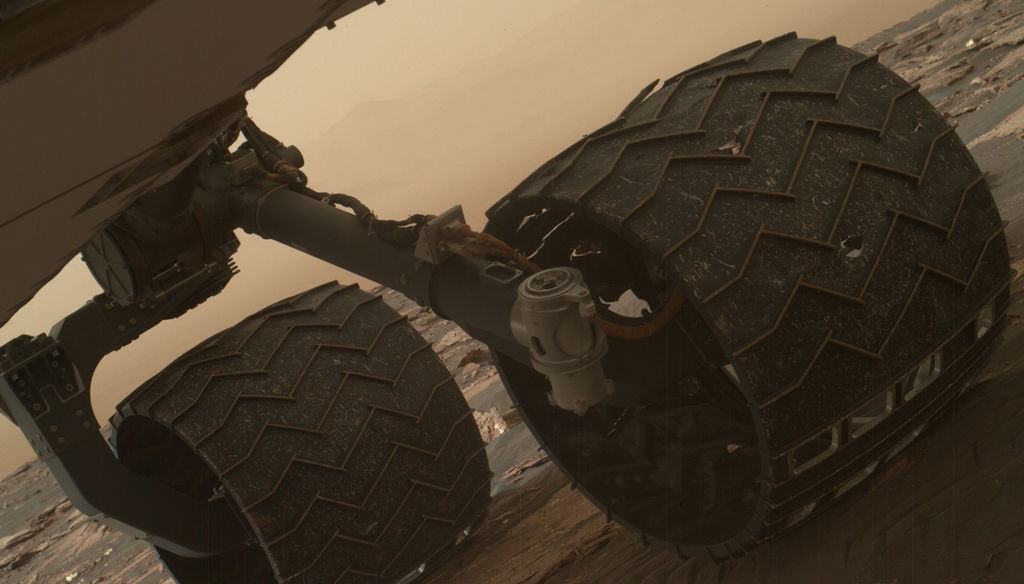
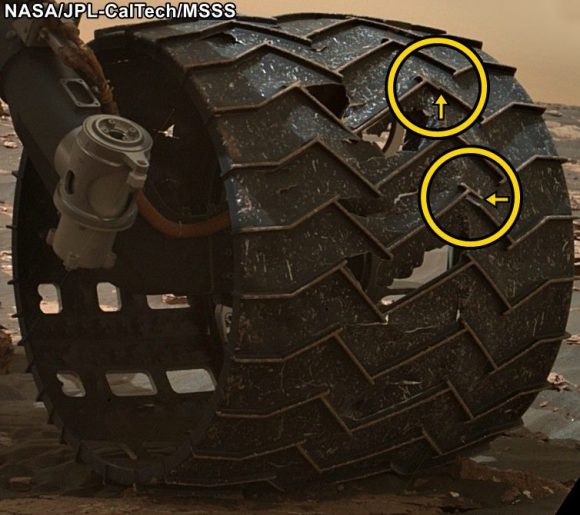
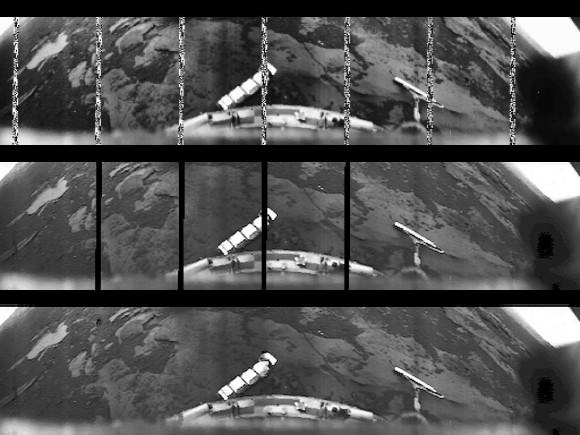
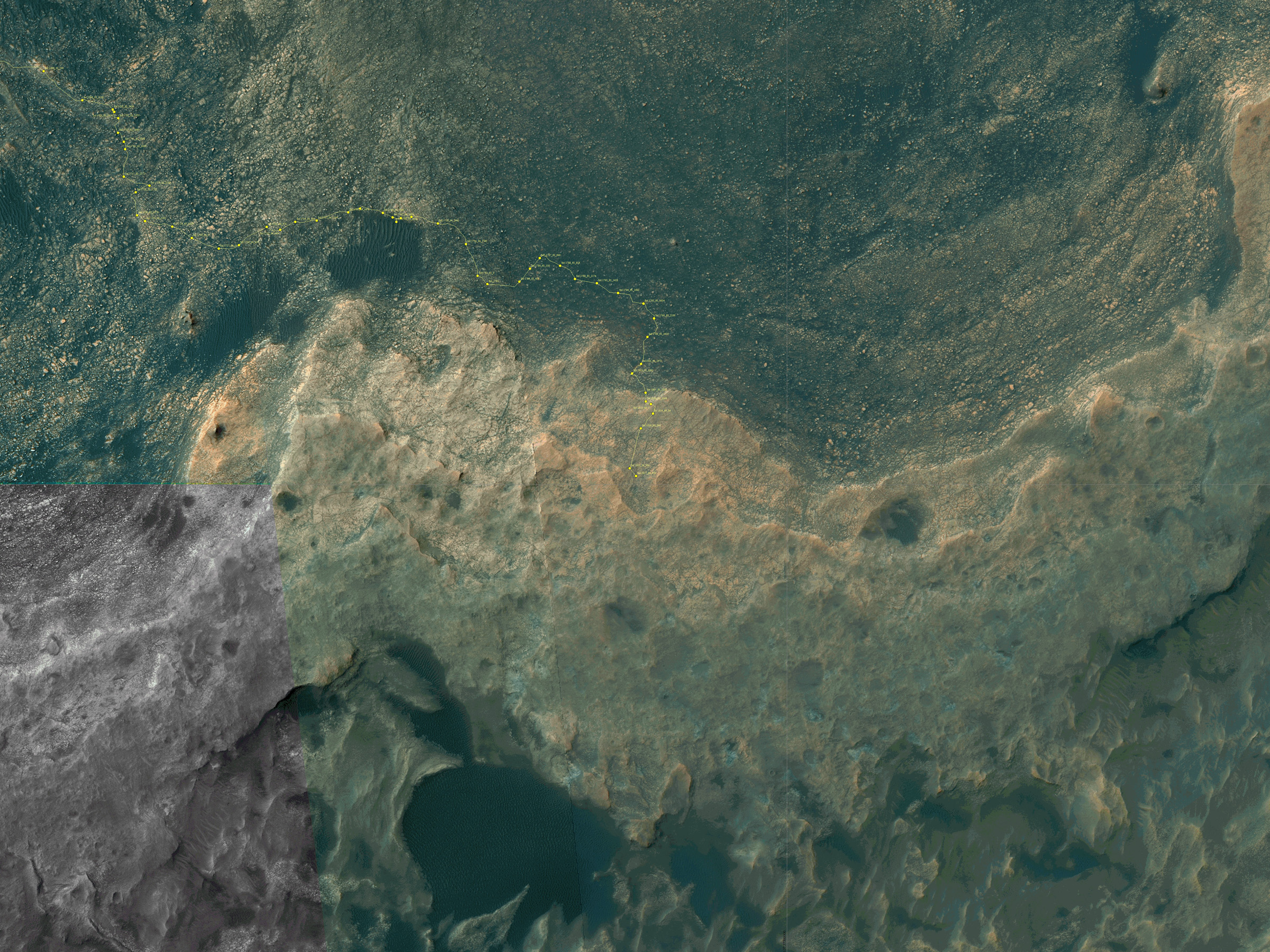
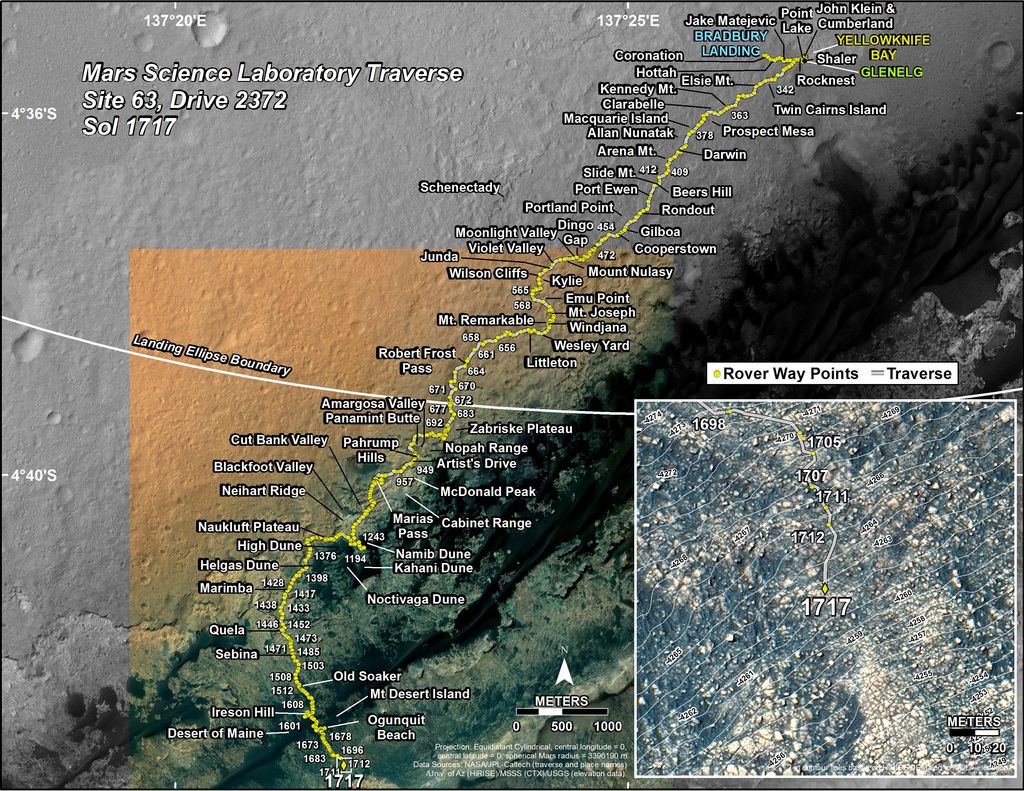
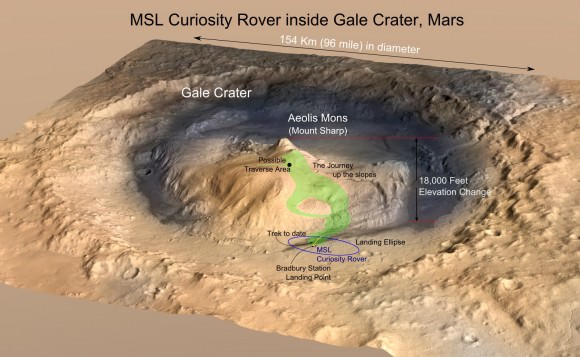
The Curiosity Rover has made some incredible discoveries during the five years it has been operating on the surface of Mars. And in the course of conducting its research, the rover has also accrued some serious mileage. However, it certainly came as a surprise when during a routine examinations in 2013, members of the Curiosity science team noted that its wheels had suffered rips in their treads (followed by breaks reported in 2017).
Looking to the future, researchers at NASA’s Glenn Research Center hope to equip next-generation rovers with a new wheel. It is based on the “Spring Tire“, which NASA developed with Goodyear back in the mid-2000s. However, rather than using coiled steel wires woven into a mesh pattern (which was part of the original design) a team of NASA scientists has created a more durable and flexible version which could revolution space exploration.
When it comes right down to it, the Moon, Mars, and other bodies in the Solar System have harsh, punishing terrain. In the case of the Moon, the main issue is the regolith (aka. Moon dust) which covers the majority of its surface. This fine dust is essentially jagged bits of lunar rock which play havoc with engines and machine components. On Mars, the situation is slightly different, with regolith and sharp rocks covering most of the terrain.
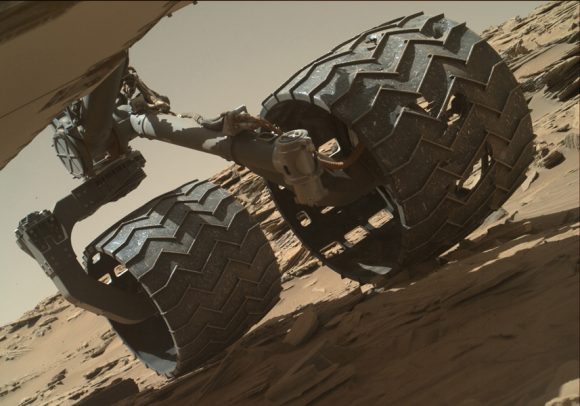

In 2013, after just a year on the surface, the Curiosity rover’s wheels began to show signs of wear and tear due it traversing unexpectedly harsh terrain. This led many to worry that the rover might not be able to complete its mission. It also led many at NASA’s Glenn Research Center to reconsider a design they had been working on almost a decade prior, which was intended for renewed missions to the Moon.
For NASA Glenn, tire development has been a focus of research for about a decade now. In this respect, they are returning to a time-honored tradition of NASA engineers and scientists, which began back in the Apollo era. At the time, both the American and Russian space programs were evaluating multiple tires designs for use on the lunar surface. Overall, three major designs were proposed.
First, you had the wheels specially designed for Lunokhod rover, a Russian vehicle whose name literally translates to “Moon Walker”. The wheel design for this rover consisted of eight rigid-rim, wire-mesh tires that were connected to their axles by bicycle-type spokes. Metal cleats were also mounted on the outside of the tire to ensure better traction in the lunar dust.
Then there was NASA’s concept for a Modularized Equipment Transporter (MET), which was developed with the support of Goodyear. This unpowered cart came with two nitrogen-filled, smooth rubber tires to make it easier to pull the cart through lunar soil and over rocks. And then there was the design for the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), which was the last NASA vehicle to visit the Moon.
This crewed vehicle, which Apollo astronauts used to drive around on the challenging lunar surface, relied on four large, flexible wire-mesh wheels with stiff inner frames. During the mid-2000s, when NASA began planning on mounting new missions to the Moon (and future missions to Mars), they began reevaluating the LRV tire and incorporating new materials and technologies into the design.
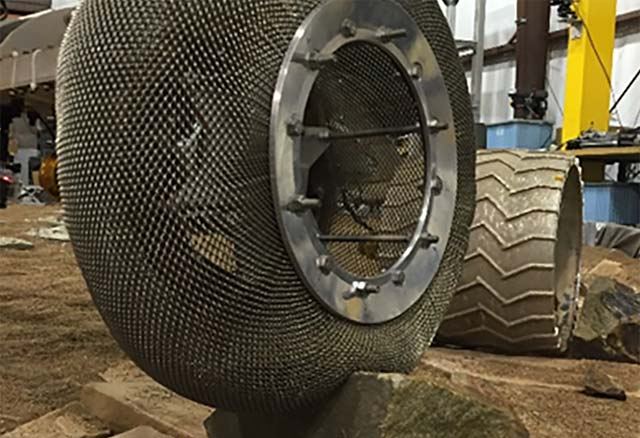
The fruit of this renewed research was the Spring Tire, which was the work of mechanical research engineer Vivake Asnani, who worked closely with Goodyear to develop it. The design called for an airless, compliant tire made up of hundreds of coiled steel wires, which were then woven into a flexible mesh. This not only ensured light weight, but also gave the tires the ability to support high loads while conforming to the terrain.
To see how the Spring Tire would fare on Mars, engineers at NASA’s Glenn Research Center began testing them in the Slope lab, where they ran them through an obstacle course that simulated the Martian environment. While the tires performed generally well in simulated sand, they experienced problems when the wire mesh deformed after passing over jagged rocks.
To address this, Colin Creager and Santo Padua (a NASA engineer and materials scientist, respectively) discussed possible alternatives. In time, they agreed the steel wires should be replaced with nickel titanium, a shape memory alloy that is capable of retaining its shape under tough conditions. As Padua explained in a NASA Glenn video segment, the inspiration to use this alloy was very serendipitous:
“I just happened to be over in the building here, where the Slope lab is. And I was over here for a different meeting for the work that I do in shape memory alloys, and I happen to run into Colin in the hall. And I was like ‘what are you doing back and why aren’t you over in the impact lab?’ – because I knew him as a student. He said, ‘well, I’ve graduated, and I’ve been working out here full-time for awhile… I work in Slope.”
Despite working at JPL for ten years, Padua had not seen the Slope lab before and accepted an invitation to see what they were working on. After entering the lab and looking at the Spring Tires they were testing, Padua asked if they were experiencing problems with deformation. When Creager admitted that they were, Padua proposed a solution which just happened to be his field of expertise.
“I had never even heard of the term shape memory alloys before, but I knew [Padua] was a materials science engineer,” said Creager. “And so, since then we’ve been collaborating on these tires using his materials expertise, especially in shape memory alloys, to come up with this new tire that we think is really going to revolutionize planetary rover tires and potentially even tires for Earth too.”
The key to shape memory alloys is their atomic structure, which is assembled in such a way that the material “remember” its original shape and is able to return to it after being subjected to deformation and strain. After building the shape memory alloy tire, the Glenn engineers sent it to the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, where it was tested in the Mars Life Test Facility.
Overall, the tires not only performed well in simulated Martian sand, but were able to withstand going over punishing rocky outcroppings without difficulty. Even after the tires were deformed all the way down to their axles, they were able to retain their original shape. They also managed to do this while carrying a significant payload, which is another prerequisite when developing tires for exploration vehicles and rovers.
The priorities for the Mars Spring Tire (MST) are to offer greater durability, better traction in soft sand, and lighter weight. As NASA indicates on the MST website (part of the Glenn Research Center’s website), there are three major benefits to developing high performing compliant tires like the Spring Wheel:
“First, they would allow rovers to explore greater regions of the surface than currently possible. Secondly, because they conform to the terrain and do not sink as much as rigid wheels, they can carry heavier payloads for the same given mass and volume. Lastly, because the compliant tires can absorb energy from impacts at moderate to high speeds, they can be used on crewed exploration vehicles which are expected to move at speeds significantly higher than the current Mars rovers.”
The first available opportunity to test these tires out is just a few years away, when NASA’s Mars 2020 Rover will be sent to the surface of the Red Planet. Once there, the rover will pick up where Curiosity and other rovers have left off, searching for signs of life in Mars’ harsh environment. The rover is also tasked with preparing samples that will eventually be returned to Earth by a crewed mission, which is expected to take place sometime in the 2030s.