KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FL – An unmanned Russian Progress resupply ship bound for the International Space Station (ISS) was lost shortly after launch from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan on Thursday when its Soyuz booster suffered a catastrophic anomaly in the third stage, and the craft and its contents were totally destroyed.
The Russian launch failure deals somewhat of a setback to the ever ongoing efforts by all the space station partners to keep the orbiting outpost well stocked with critical supplies of food and provisions for the multinational six person crew and science experiments to carry out the research activities for which the station was assembled.
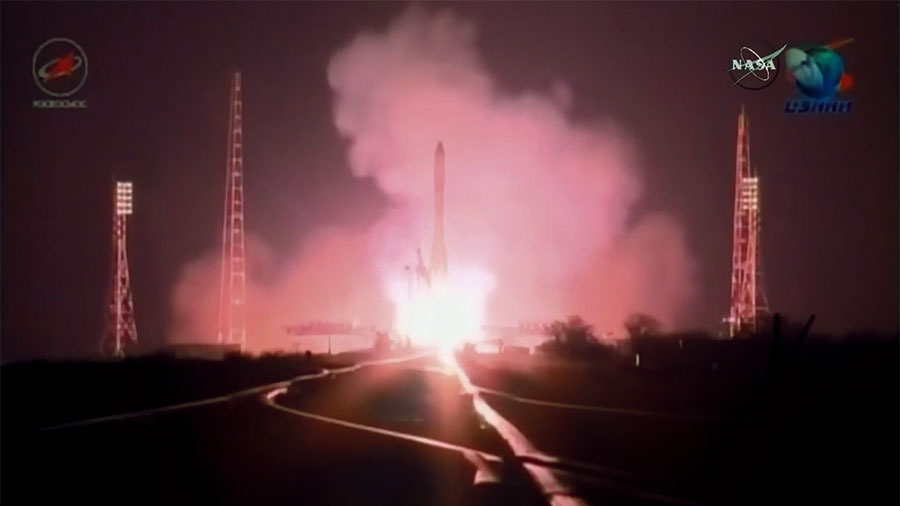
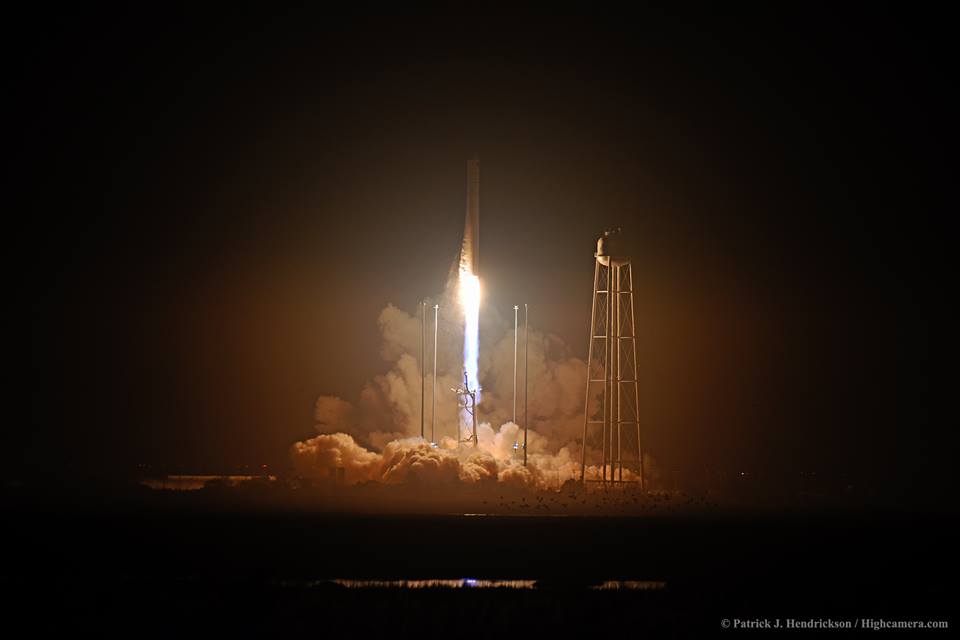
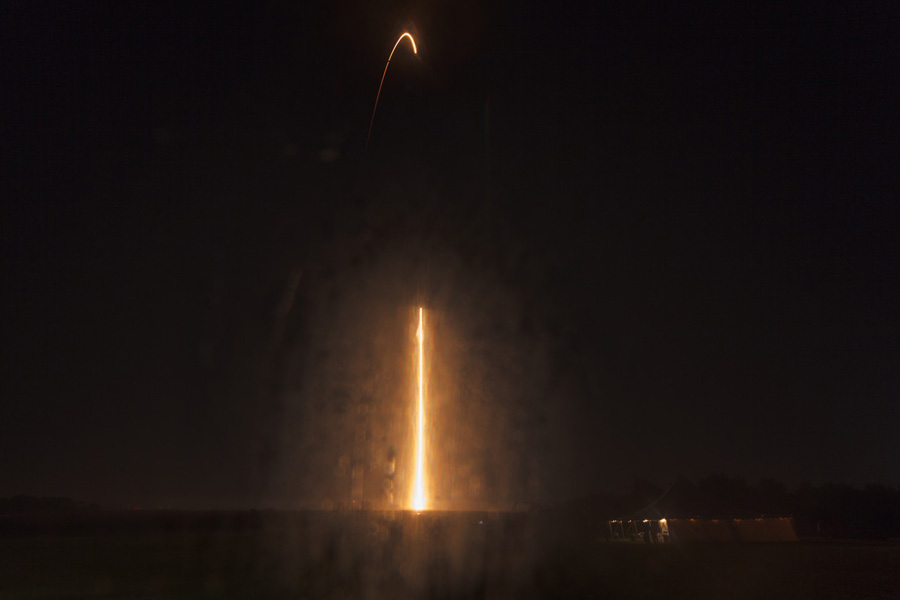
The three stage Soyuz-U rocket failed in flight around six and a half minutes after what had been an otherwise flawless nighttime liftoff from the Baikonur Cosmodrome at 9:51 a.m. EST (8:51 p.m. Baikonur time), Thursday, Dec. 1.
Telemetry from the Progress 65 vehicle, also known as Progress MS-04, stopped after 382 seconds of flight while soaring about 190 km over the southern Russian Republic of Tyva.
“The Russian space agency Roscosmos has confirmed a Progress cargo resupply spacecraft bound for the International Space Station and her six person crew has lost shortly after launch,” said NASA.
“According to preliminary information, the contingency took place at an altitude of about 190 km over remote and unpopulated mountainous area of the Republic of Tyva,” said Roscosmos in a statement.
The Progress vehicle burned up during the resulting and unplanned fiery plummet through the Earth’s atmosphere.
This was the second failure of a Russian Progress launch in the past two years. The last failure took place in April 2015 when the third stage separation failed – sending the vehicle spinning wildly out of control and destroying the Progress 59 freighter.
Per protocol, the Russian space agency Roscosmos has formed a state commission to investigate the accident, seek out the root cause and implement measures to prevent such failures in the future.
“The first few minutes of flight were normal, but Russian flight controllers reported telemetry data indicating a problem during third stage operation. The Russians have formed a State Commission and are the source for details on the specific failure cause,” NASA said.
Crew launches on a different version of the Soyuz rocket were delayed and put on hold several months following last year’s Progress 59 failure and accident investigation.
Despite the failure there was no immediate impact on the current Expedition 50 crew and life goes on.
“The loss of the cargo ship will not affect the normal operations of the ISS and the life of the station crew,” said Roscosmos.
“The spacecraft was not carrying any supplies critical for the United States Operating Segment (USOS) of the station,” NASA reported.
Currently there is a satisfactory level of supplies.
“Six crew members living aboard the space station are safe and have been informed of the mission’s status. Both the Russian and U.S. segments of the station continue to operate normally with onboard supplies at good levels.”
However the continued useful utilization of the million pound station is totally dependent on receiving a steady train of supplies from Earth – comprising Russian, US and Japanese cargo freighters launching multiple times per year.
The Progress 65 cargo freighter was jam packed with 2.6 tons of food, fuel, and supplies for the space station crew, including approximately 1,400 pounds of propellant, 112 pounds of oxygen, 925 pounds of water, and 2,750 pounds of spare parts, supplies and scientific experiment hardware.
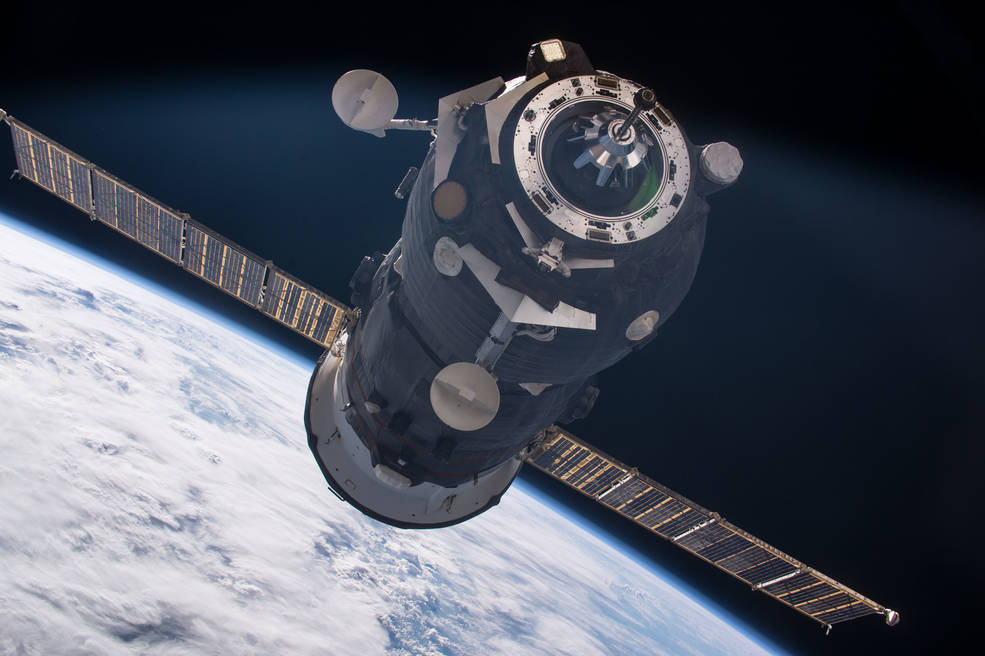

The Progress was carrying a few items from NASA but they are all replaceable, says NASA. The US items packed on board included spare parts for the station’s environmental control and life support system, research hardware, crew supplies and crew clothing.
Had all gone well, Progress 65 would have docked to the rear port of the space station’s Russian Zvezda Service Module at 11:43 a.m. Saturday, Dec. 3.
Japan is all set to launch the next cargo flight to the ISS on Friday, Dec. 9 when the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) HTV-6 resupply ship will blast off atop the H-II rocket.
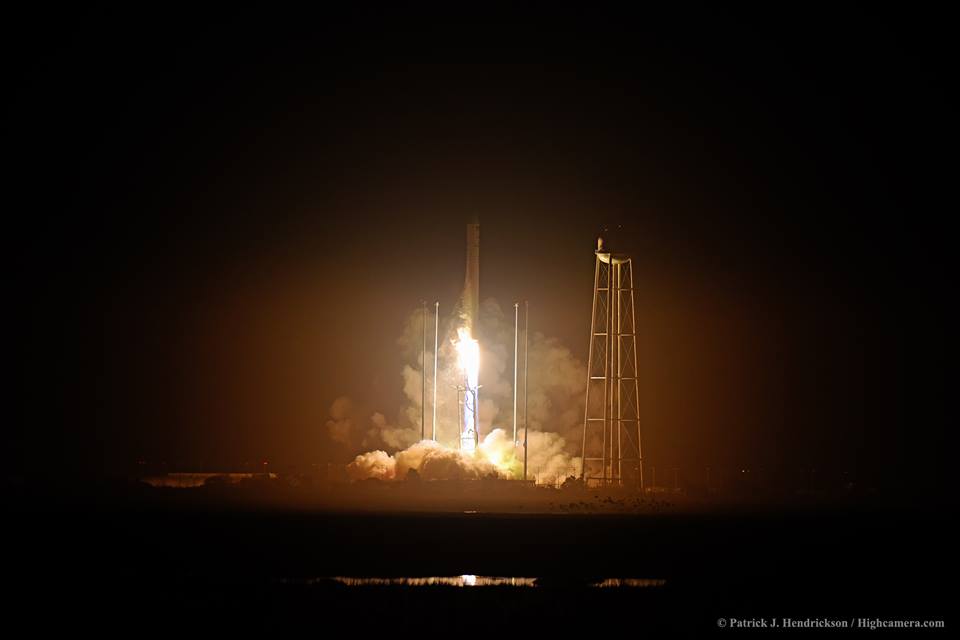
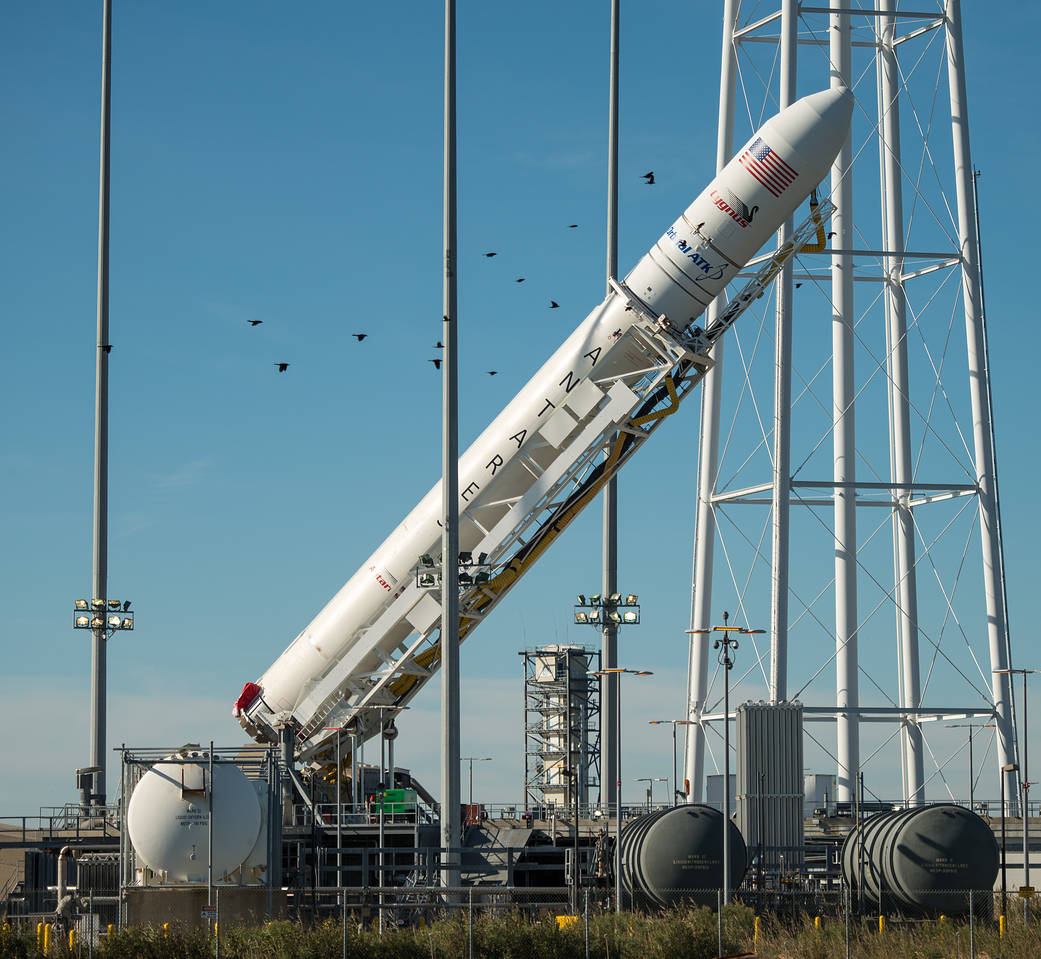
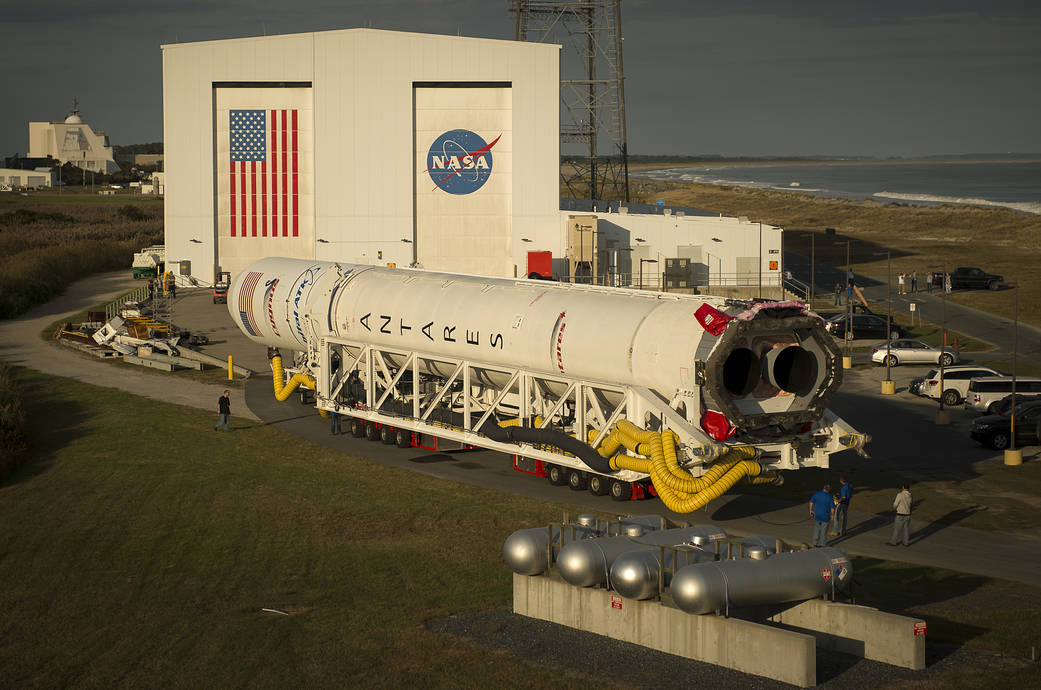
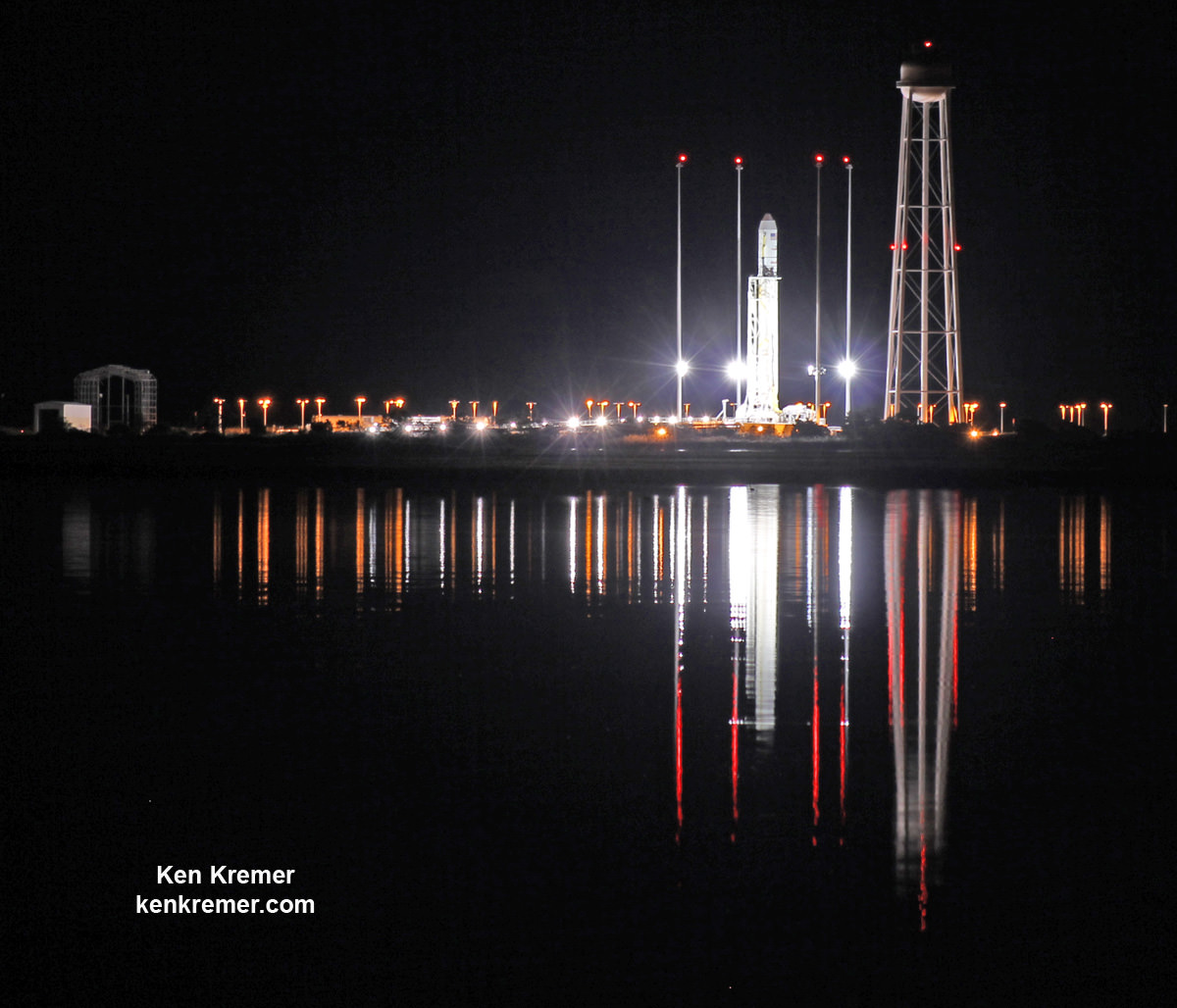
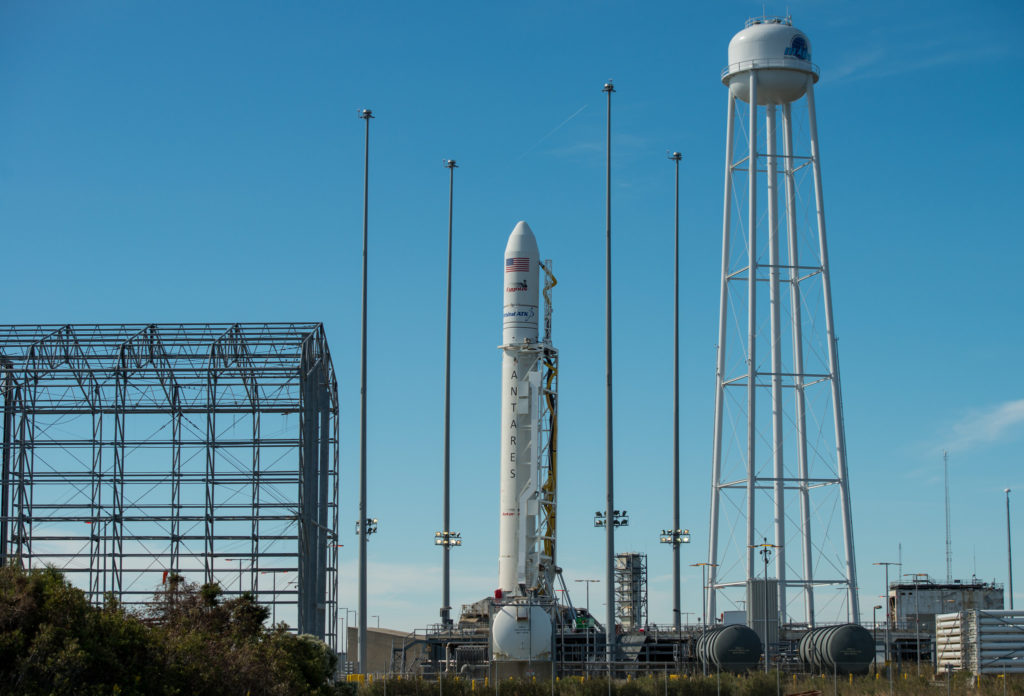
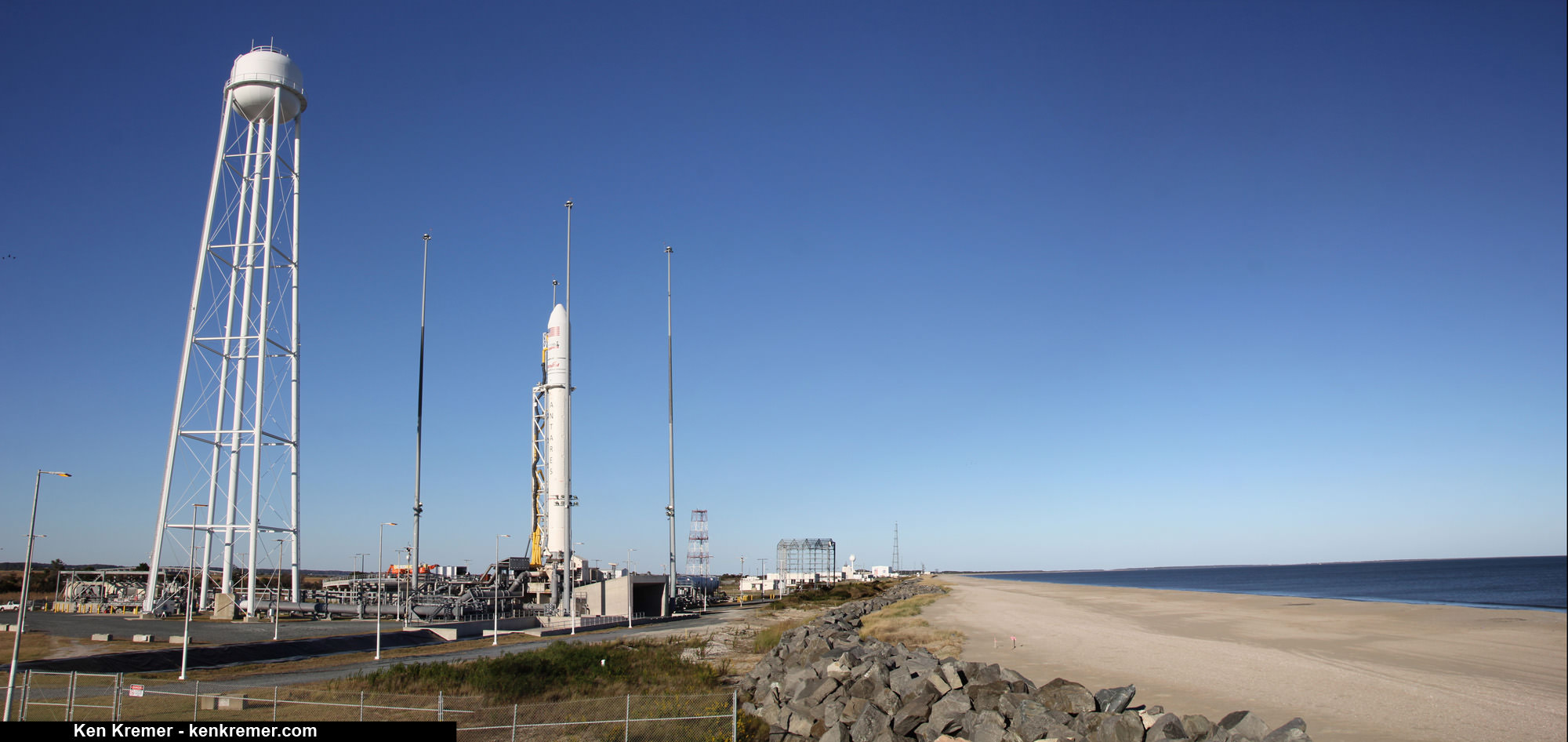
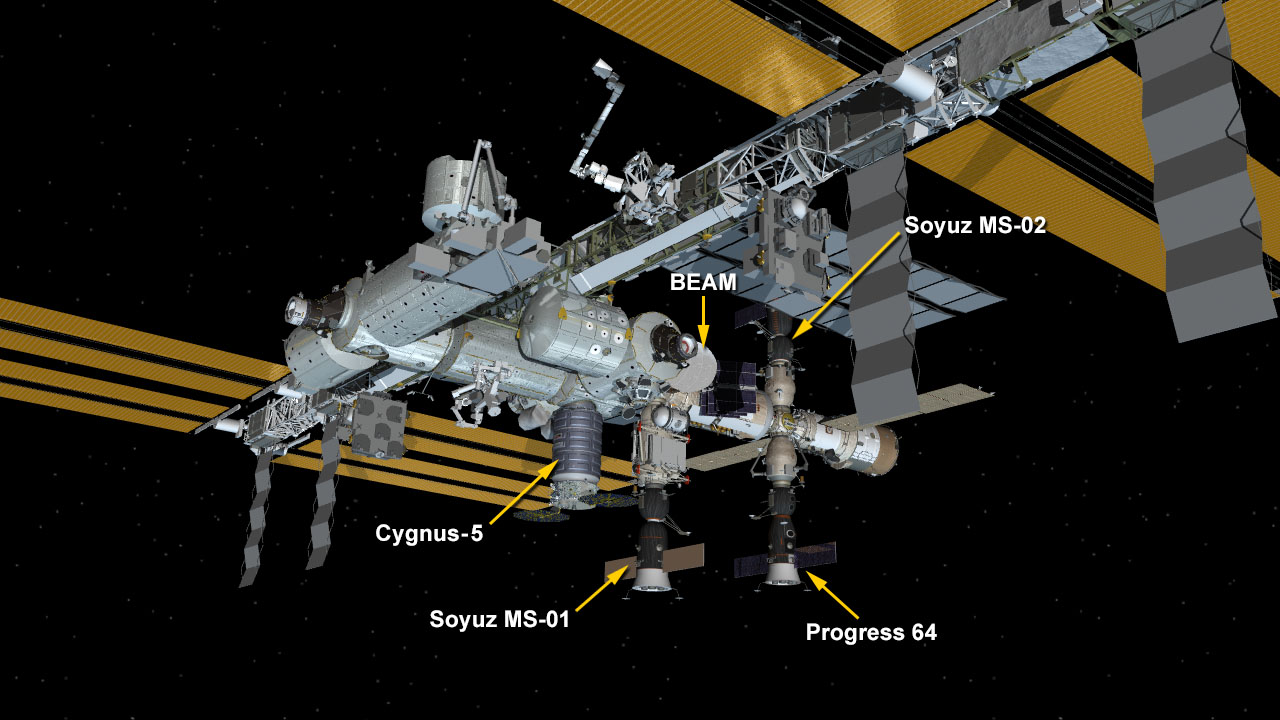
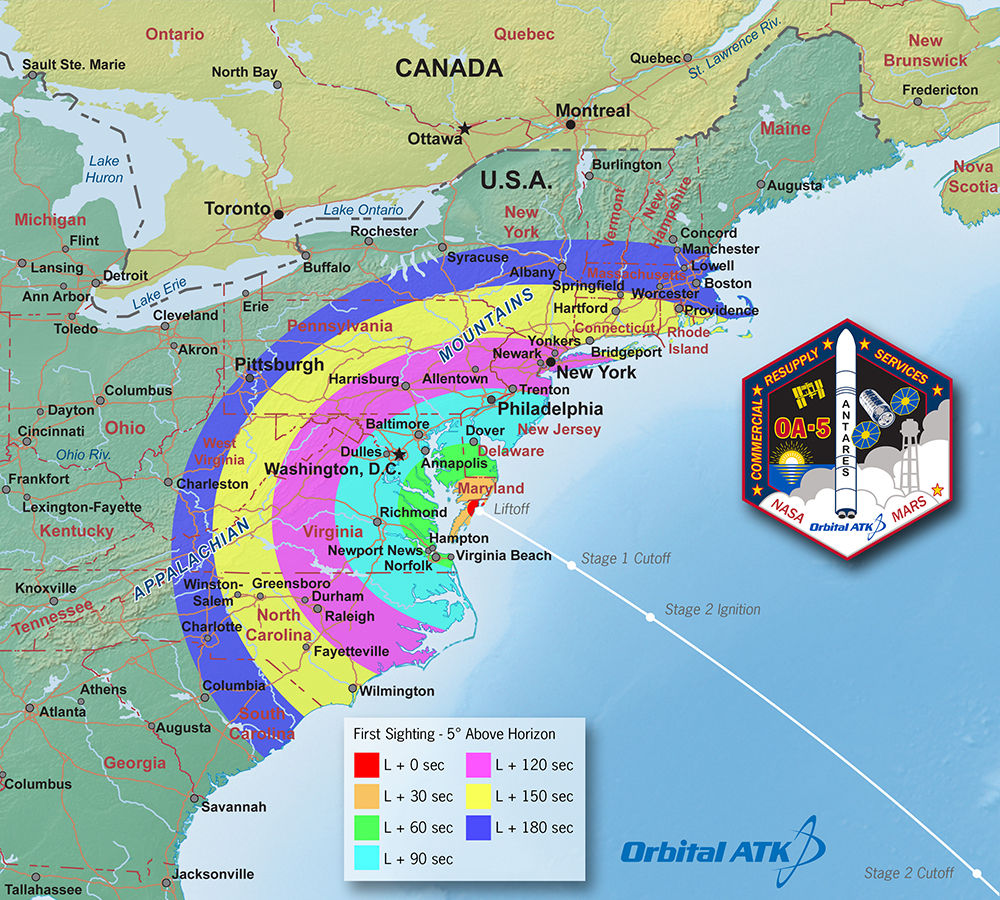
The most recent US commercial cargo launch to the ISS took place on Oct. 17 with blastoff of the Orbital ATK Antares rocket from NASA Wallops in Virginia, which delivered the Cygnus OA-5 resupply freighter to orbit. It docked to the ISS on Oct 23.
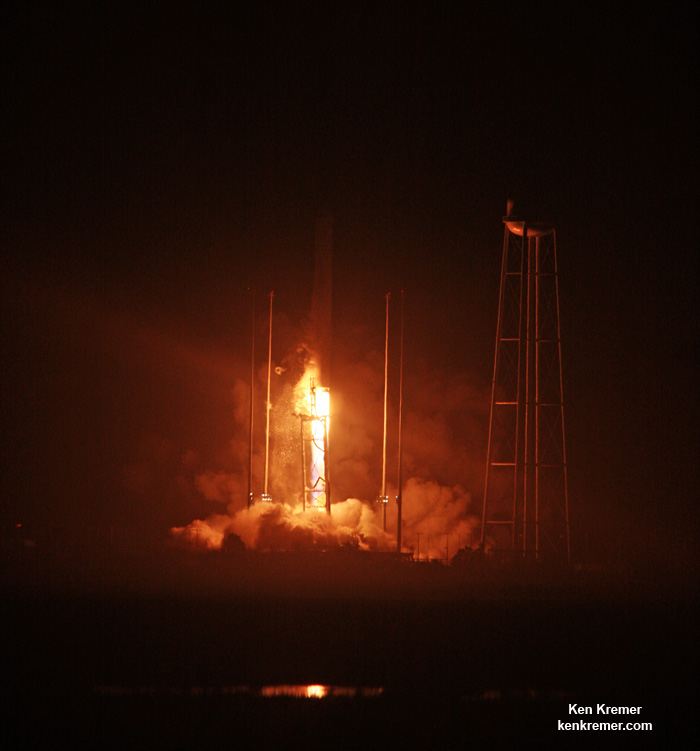

The next US cargo launch could be either an Orbital ATK Cygnus launch atop a ULA Atlas V in March 2017 or a SpaceX Dragon launch perhaps in Jan 2017.
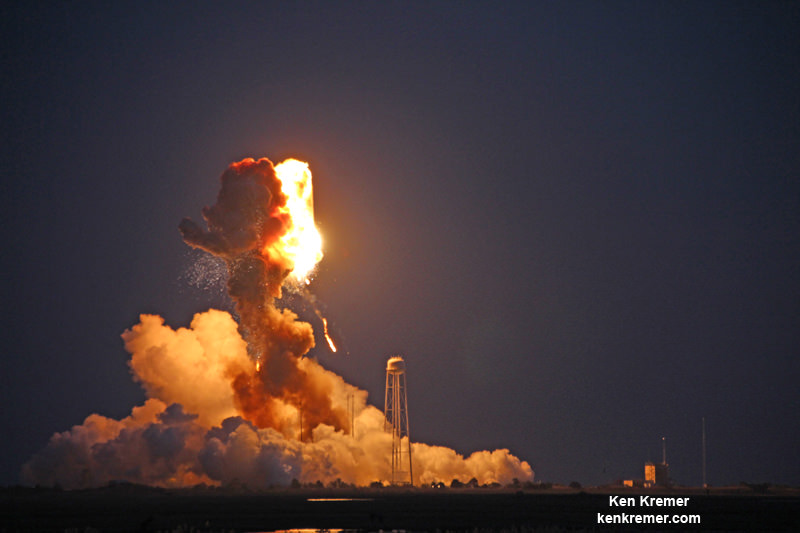
The US has also suffered ISS cargo launch failures from both of the commercial resupply providers; SpaceX on the Dragon CRS-7 mission in Jun 2015 and Orbital ATK on the Cygnus Orb-3 mission in October 2014.
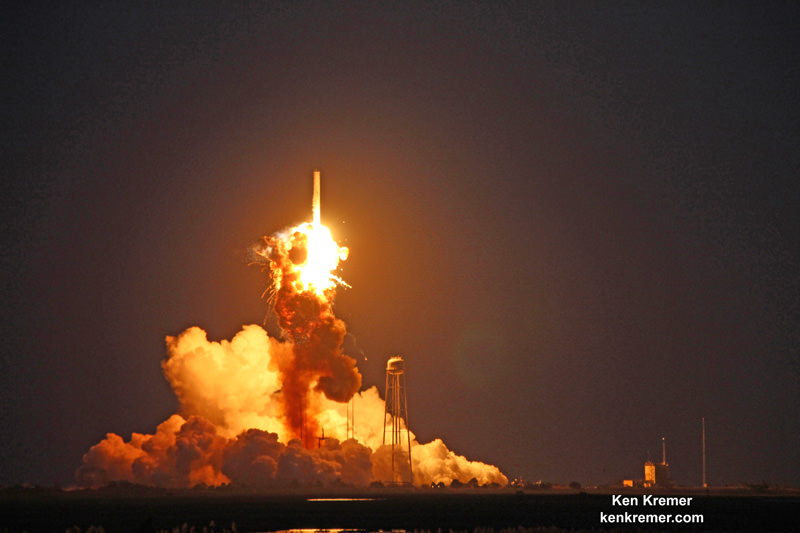

The cargo ships function as a railroad to space and function as the lifeline to keep the station continuously crewed and functioning. Without periodic resupply by visiting vehicles from the partner nations the ISS cannot continue to operate.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.