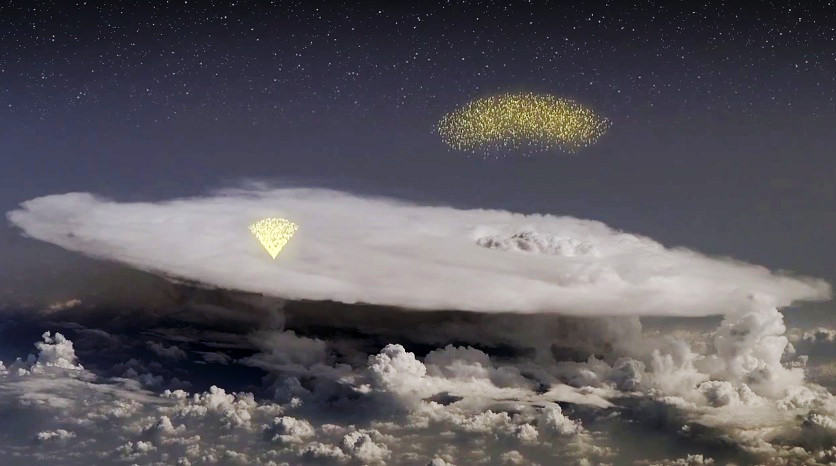
Discovered “by accident” by NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope in 2010, dark lightning is a surprisingly powerful — yet invisible — by-product of thunderstorms in Earth’s atmosphere. Like regular lightning, dark lightning is the result of a natural process of charged particles within storm clouds trying to cancel out opposing charges. Unlike normal lightning, though, dark lightning is invisible to our eyes and doesn’t radiate heat or light — instead, it releases bursts of gamma radiation.
What’s more, these gamma-ray outbursts originate at relatively low altitudes well within the storm clouds themselves. This means that airplane pilots and passengers flying through thunderstorms may be getting exposed to gamma rays from dark lightning, which are energetic enough to pass through the hull of an aircraft… as well as anything or anyone inside it. To find out how such exposure to dark lightning could affect air travelers, the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) is conducting computer modeling tests using their SoftWare for the Optimization of Radiation Detectors — SWORD, for short.
Terrestrial Gamma-ray Flashes (TGFs) are extremely intense, sub-millisecond bursts of gamma rays and particle beams of matter and anti-matter. First identified in 1994, they are associated with strong thunderstorms and lightning, although scientists do not fully understand the details of the relationship to lightning. The latest theoretical models of TGFs suggest that the particle accelerator that creates the gamma rays is located deep within the atmosphere, at altitudes between six and ten miles, inside thunderclouds and within reach of civilian and military aircraft.
These models also suggest that the particle beams are intense enough to distort and collapse the electric field within thunderstorms and may, therefore, play an important role in regulating the production of visible lightning. Unlike visible lightning, TGF beams are sufficiently broad — perhaps about half a mile wide at the top of the thunderstorm — that they do not create a hot plasma channel and optical flash; hence the name, “dark lightning.”
A team of NRL Space Science Division researchers, led by Dr. J. Eric Grove of the High Energy Space Environment (HESE) Branch, is studying the radiation environment in the vicinity of thunderstorms and dark lightning flashes. Using the Calorimeter built by NRL on NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope they are measuring the energy content of dark lightning and, for the first time, using gamma rays to geolocate the flashes.
As a next step, Dr. Chul Gwon of the HESE Branch is using NRL’s SoftWare for the Optimization of Radiation Detectors (SWORD) to create the first-ever simulations of a dark lightning flash striking a Boeing 737. He can calculate the radiation dosage to the passengers and crew from these Monte Carlo simulations. Previous estimates have indicated it could be as high as the equivalent of hundreds of chest X-rays, depending on the intensity of the flash and the distance to the source.
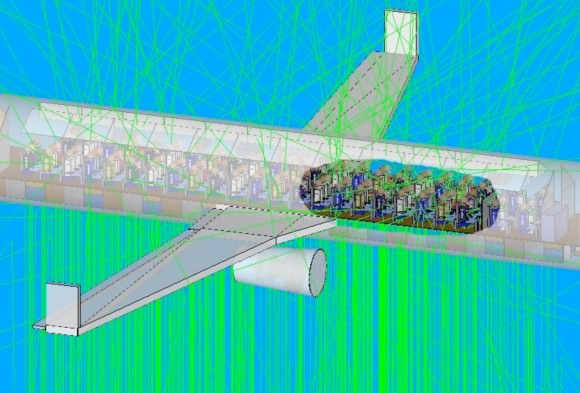
(Credit: U.S. Naval Research Laboratory)
SWORD simulations allow researchers to study in detail the effects of variation in intensity, spectrum, and geometry of the flash. Dr. Grover’s team is now assembling detectors that will be flown on balloons and specialized aircraft into thunderstorms to measure the gamma ray flux in situ. The first balloon flights are scheduled to take place this summer.
Source: NRL News

