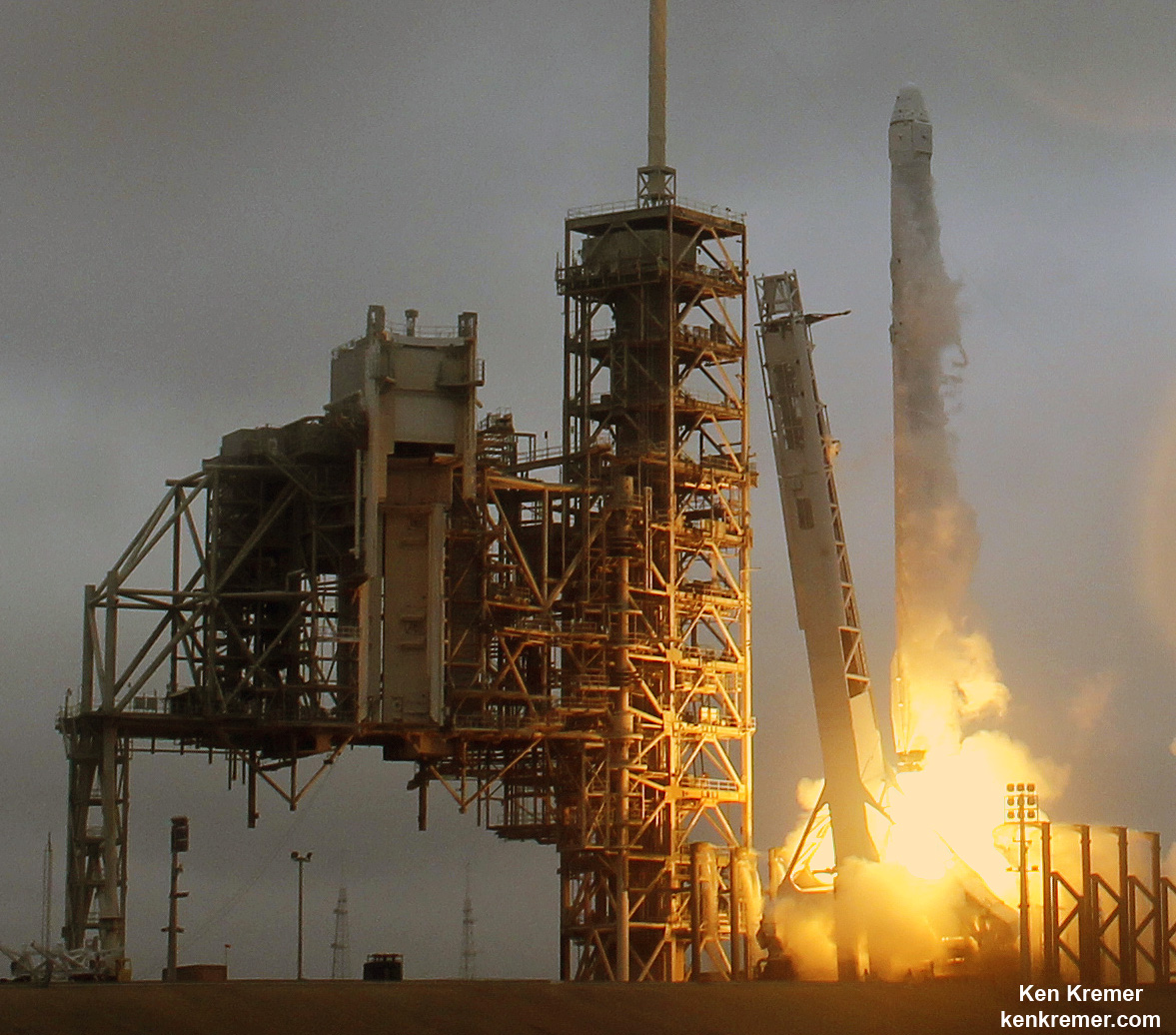
SpaceX is targeting a June 1 blastoff for the firms next cargo delivery mission to the International Space Station (ISS) for NASA following today’s (May 28) successful test firing of the Falcon 9 booster’s main engines on the Florida Space Coast under sunny skies.
Liftoff of the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the unmanned Dragon cargo freighter from seaside pad 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida is slated for 5:55 p.m. EDT Thursday, June 1.
“Static fire test of Falcon 9 complete,” SpaceX confirmed via Twitter soon after completion of the test at noon today 12 p.m. EDT.
“Targeting June 1 launch from historic Pad 39A for Dragon’s next resupply mission to the @Space_Station.”
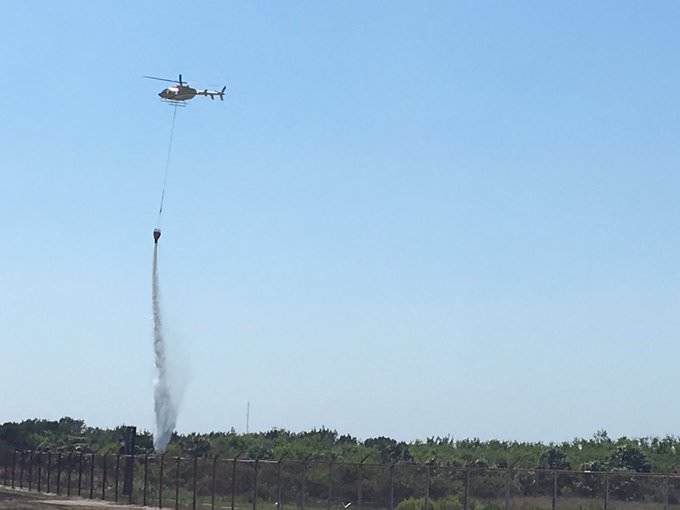
The static fire test also apparently set off a brush fire near the pad which required a response from firefighters to douse the blaze with water bucket drops from helicopters.
“#USFWS firefighters are responding to a new wildfire at Merritt Island NWR caused by a static rocket test fire #FLfire,” tweeted the US Fish and Wildlife Service.
The wildfire stretched to 4 acres on Merritt Island and was successfully contained, the US Fish and Wildlife Service said.

With the launch conveniently coinciding with dinnertime, it will offer prime time viewing thrills for spectators and space enthusiasts coming from near and far.
The weather outlook for Thursday is currently promising with mostly sunny conditions but can change at a moments notice.
And to top that off SpaceX will attempt a land landing of the first stage back at the Cape at Landing Zone 1 some 9 minutes after liftoff.
The Dragon resupply ship dubbed Dragon CRS-11 counts as SpaceX’s eleventh contracted commercial resupply services (CRS) mission to the International Space Station for NASA since 2012.
It is carrying almost 6,000 pounds of science research, crew supplies and hardware to the orbiting laboratory in support of Expedition 52 and 53 crew members. The unpressurized trunk of the spacecraft also will transport solar panels, tools for Earth-observation and equipment to study neutron stars.
Dragon CRS-11 will be the second SpaceX resupply mission to launch this year.
The prior SpaceX cargo ship launched on Feb 19, 2017 on the CRS-10 mission to the space station. It was also the first SpaceX launch of a Falcon 9 from NASA’s historic pad 39A.
Another significant milestone for this flight is that it features the first reuse of a previously launched Dragon. It previously launched on the CRS-4 resupply mission.
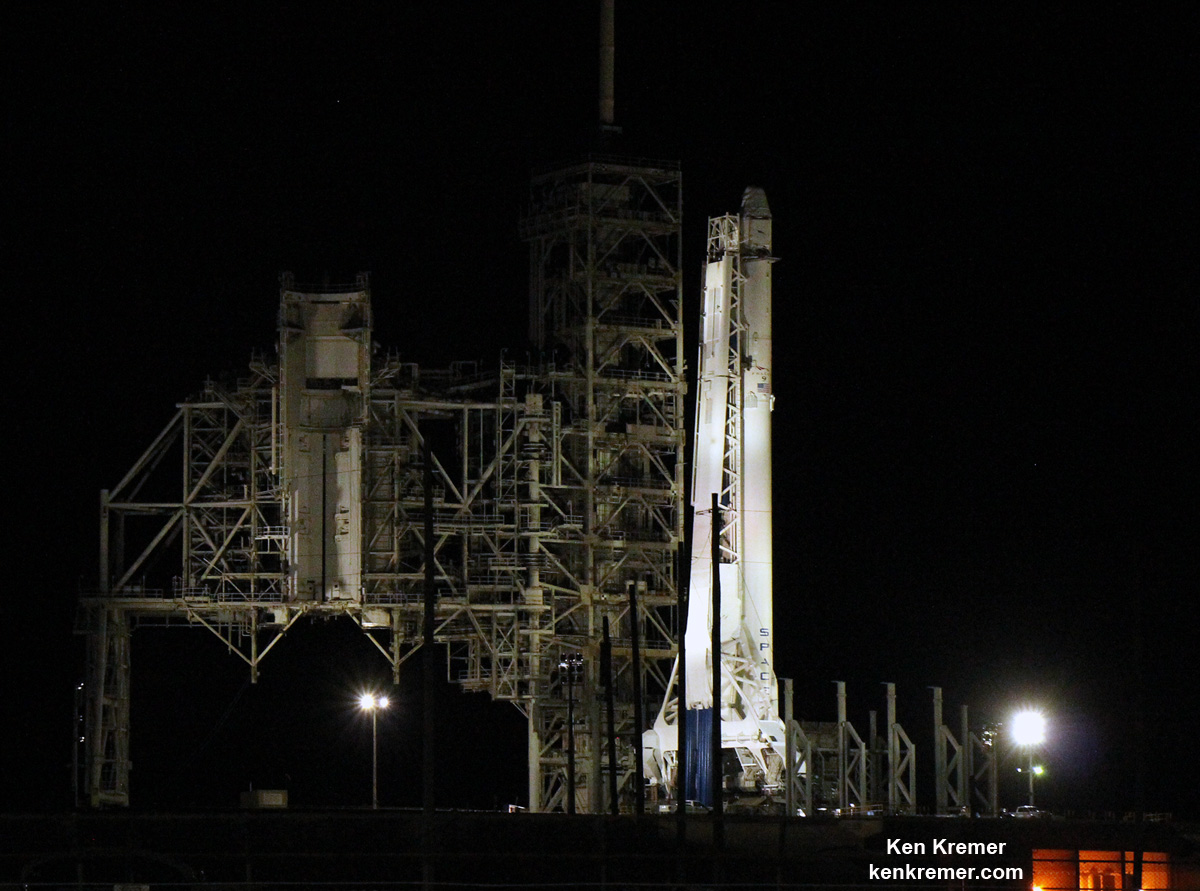

Sunday’s brief static fire test involved a successful hot fire ignition test of the two stage rocket and all nine first stage Merlin 1D engines Sunday afternoon while the rocket was firmly held down at the pad.
The hold down engine test is routinely conducted to confirm the readiness of the engines and rocket for flight.
The nine Merlin 1D engines generate 1.7 million pounds of thrust for approximately three seconds.
The test simulates all the conditions of flight except liftoff, and involves loading of the densified liquid oxygen and RP-1 propellants into the first and second stages starting about 70 minutes prior to ignition.
The engine test was run without the Dragon cargo ship bolted on top.
The rocket was rolled out of the SpaceX processing hangar at the perimeter fence early this morning and then up the slight incline to the top of pad 39A. It was erected vertical to launch position using a dedicated transporter-erector.
With the successful completion of the static fire test, the booster will be rolled back to the big processing hangar and Dragon CRS-11 will be integrated on top.
NASA will offer live launch coverage on NASA Television and the agency’s website at beginning 5:15 p.m. on June 1.
In case of a delay for any reason, the next launch opportunity is 5:07 p.m. Saturday, June 3, with NASA TV coverage starting at 4:30 p.m.

Watch for Ken’s onsite CRS-10 mission reports direct from the Kennedy Space Center and Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.

………….
Learn more about the SpaceX Dragon CRS-11 resupply launch to ISS, NASA missions and more at Ken’s upcoming outreach events at Kennedy Space Center Quality Inn, Titusville, FL:
May 30/31: “SpaceX CRS-11 and CRS-10 resupply launches to the ISS, Inmarsat 5 and NRO Spysat, EchoStar 23, SLS, Orion, Commercial crew capsules from Boeing and SpaceX , Heroes and Legends at KSCVC, ULA Atlas/John Glenn Cygnus launch to ISS, SBIRS GEO 3 launch, GOES-R weather satellite launch, OSIRIS-Rex, Juno at Jupiter, InSight Mars lander, SpaceX and Orbital ATK cargo missions to the ISS, ULA Delta 4 Heavy spy satellite, Curiosity explores Mars, Pluto and more,” Kennedy Space Center Quality Inn, Titusville, FL, evenings