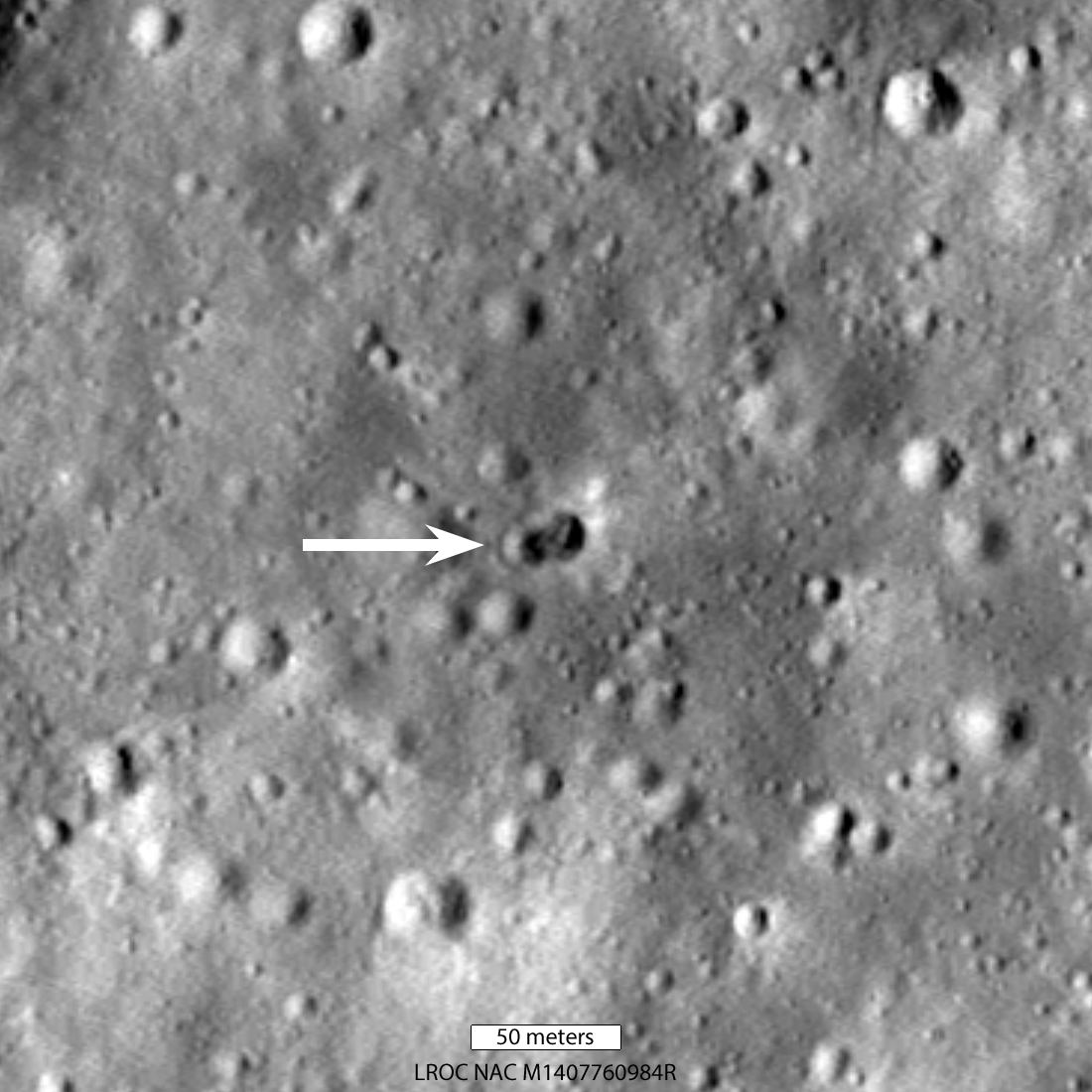
The Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) – NASA’s eye-in-the-sky in orbit around the Moon – has found the crash site of the mystery rocket booster that slammed into the far side of the Moon back on March 4th, 2022. The LRO images, taken May 25th, revealed not just a single crater, but a double crater formed by the rocket’s impact, posing a new mystery for astronomers to unravel.
Continue reading “Remember That Rocket That was Going to Crash Into the Moon? Scientists Think They've Found the Crater”The Object About to Hit the Moon isn’t a SpaceX Booster After All
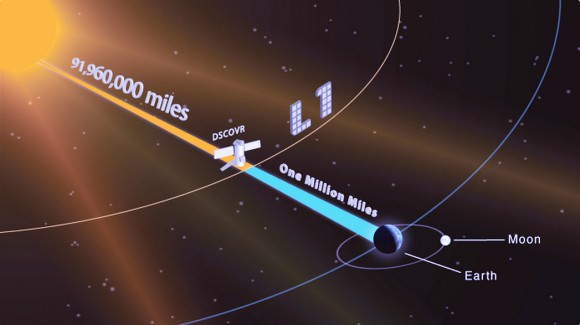
Last month, astronomers reported that a discarded upper stage of a Falcon 9 rocket, launched 7 years ago, was on a collision course with the Moon. The rocket in question carried NASA’s Deep Space Climate Observatory (DSCOVR) to the Sun-Earth L1 Lagrange point, where the still-operating observatory provides advance warning on solar wind activities. The leftover rocket stage, meanwhile, became a floating piece of space junk orbiting the Sun. Its ultimate fate was unknown, until last month, when astronomer Bill Gray predicted that it was bound for an impact with the Moon sometime on March 4th, 2022.
This week, Gray, who has been tracking the object ever since, released an update on the situation. He confirmed that there is indeed a rocket stage on course to crash into the far side of the Moon, but it’s not a SpaceX rocket at all. Instead, it’s a Chinese booster: the upper stage of the rocket that carried China’s Chang’e 5-T1 mission to the Moon in 2014.
Continue reading “The Object About to Hit the Moon isn’t a SpaceX Booster After All”Phew, Earth-Watching DSCOVR is Operational Again

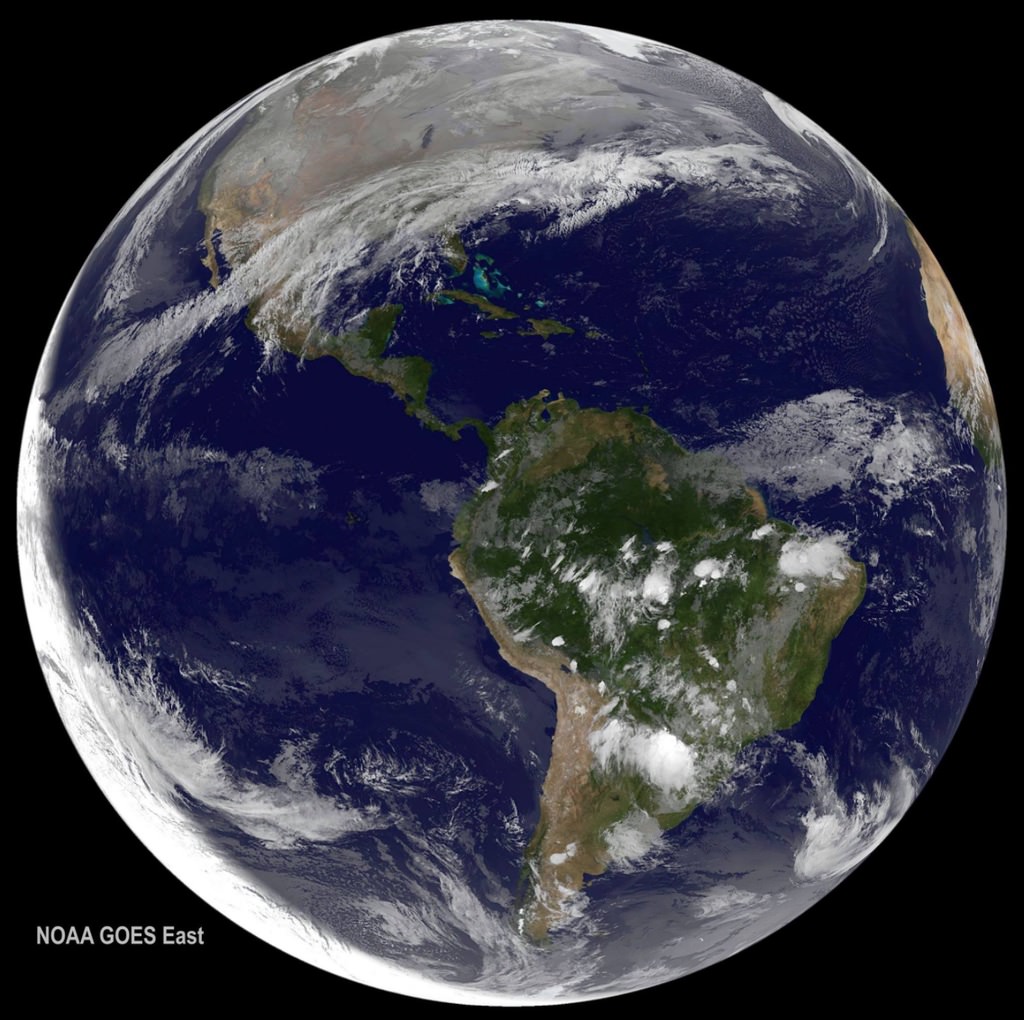
Rejoice! If you’ve missed your daily fix of seeing views of our rotating Earth from space, NOAA announced that its Deep Space Climate Observatory (DSCOVR) is now back in action. The deep space satellite, which produces incredible full-disk images of our Blue Marble, has been offline since June 27, 2019 because of a problem with the spacecraft’s attitude control system. But NOAA and NASA engineers developed and uploaded a software patch to restore DSCOVR’s operations.
Continue reading “Phew, Earth-Watching DSCOVR is Operational Again”DSCOVR Captures EPIC Views of the March 2016 Eclipse
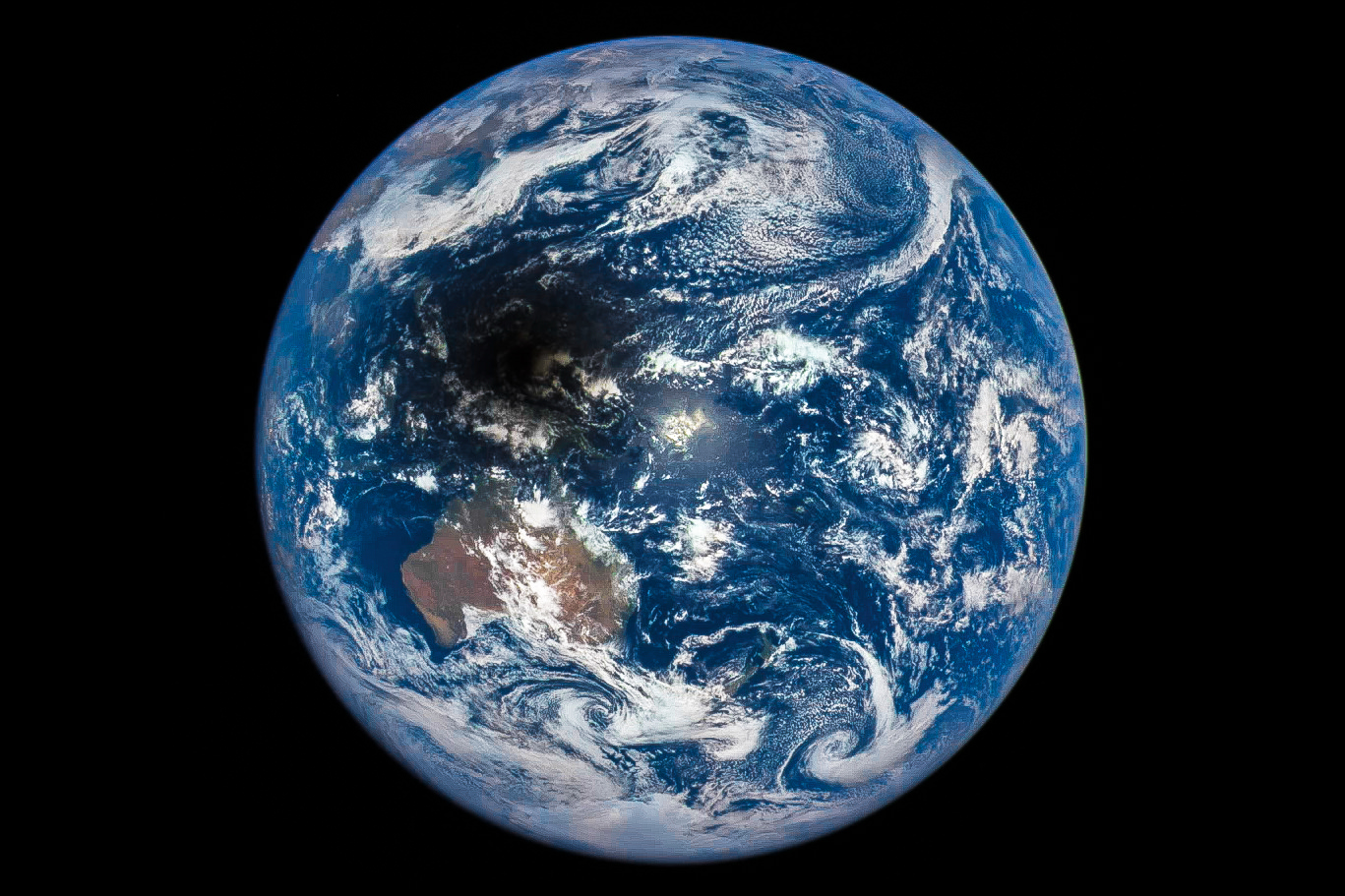

On March 8, 2016 (March 9 local time) the Moon briefly blocked the light from the Sun in what was the only total solar eclipse of the year. The event was visible across portions of southeast Asia, Indonesia, and Micronesia, and was observed by both skywatchers on the ground in person and those watching live online around the world. While to most the view was of a silhouetted Moon slowly carving away the disk of the Sun before totality revealed a shimmering corona, the view from space looking back at Earth showed the Moon’s dark shadow passing over islands, clouds, and sea.
Continue reading “DSCOVR Captures EPIC Views of the March 2016 Eclipse”
Gorgeous Views of Earth from Space Ring in New Year 2016 From the Space Station and Beyond
Happy New Year 2016 from the International Space Station (ISS) and Beyond!
Behold Earth ! Courtesy of our Human and Robotic emissaries to the High Frontier we can ring in the New Year by reveling in gorgeous new views of our beautiful Home Planet taken from the space station and beyond. Continue reading “Gorgeous Views of Earth from Space Ring in New Year 2016 From the Space Station and Beyond”
Space Weather Storm Monitoring Satellite Blasts off for Deep Space on SpaceX Rocket
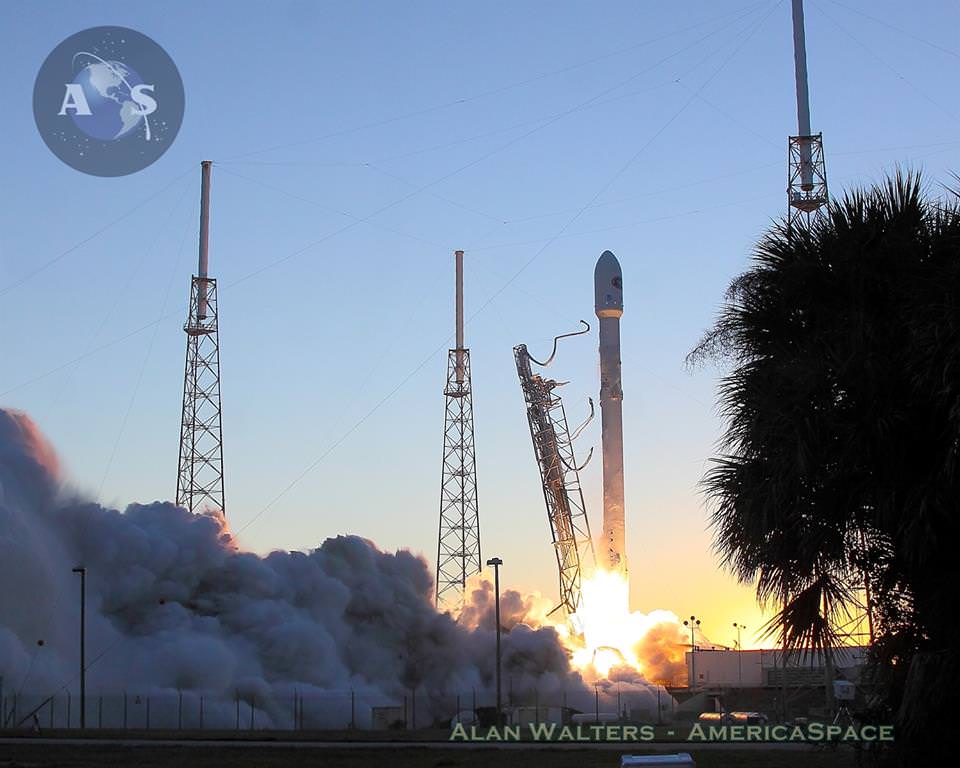

After a 17 year long wait, a new American mission to monitor intense solar storms and warn of impeding space weather disruptions to vital power grids, telecommunications satellites and public infrastructure was launched atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 on Wednesday, Feb. 11, from Cape Canaveral, Florida, to start a million mile journey to its deep space observation post.
The third time proved to be the charm when the Deep Space Climate Observatory, or DSCOVR science satellite lifted off at 6:03 p.m. EST Wednesday from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
The spectacular sunset blastoff came after two scrubs this week forced by a technical problem with the Air Force tracking radar and adverse weather on Sunday and Tuesday.
The $340 million DSCOVR has a critical mission to monitor the solar wind and aid very important forecasts of space weather at Earth at an observation point nearly a million miles from Earth. It will also take full disk color images of the sunlit side of Earth at least six times per day that will be publicly available and “wow” viewers.

The couch sized probe was targeted to the L1 Lagrange Point, a neutral gravity point that lies on the direct line between Earth and the sun located 1.5 million kilometers (932,000 miles) sunward from Earth. At L1 the gravity between the sun and Earth is perfectly balanced and the satellite will orbit about that spot just like a planet.
L1 is a perfect place for the science because it lies outside Earth’s magnetic environment. The probe will measure the constant stream of solar wind particles from the sun as they pass by.
DSCOVR is a joint mission between NOAA, NASA, and the U.S Air Force (USAF) that will be managed by NOAA. The satellite and science instruments are provided by NASA and NOAA. The rocket was funded by the USAF.
The mission is vital because its solar wind observations are crucial to maintaining accurate space weather forecasts to protect US infrastructure such as power grids, aviation, planes in flight, all types of Earth orbiting satellites for civilian and military needs, telecommunications, ISS astronauts and GPS systems.
It will take about 150 days to reach the L1 point and complete satellite and instrument checkouts.
DSCOVR will then become the first operational space weather mission to deep space and function as America’s primary warning system for solar magnetic storms.
It will replace NASA’s aging Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) satellite which is nearly 20 years old and far beyond its original design lifetime.
“DSCOVR is the latest example of how NASA and NOAA work together to leverage the vantage point of space to both understand the science of space weather and provide direct practical benefits to us here on Earth,” said John Grunsfeld, associate administrator of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington.
DSCOVR was first proposed in 1998 by then US Vice President Al Gore as the low cost ‘Triana’ satellite to take near continuous views of the Earth’s entire globe to feed to the internet as a means of motivating students to study math and science. It was eventually built as a much more capable Earth science satellite that would also conduct the space weather observations.
But Triana was shelved for purely partisan political reasons and the satellite was placed into storage at NASA Goddard and the science was lost until now.

DSCOVR is equipped with a suite of four continuously operating solar science and Earth science instruments from NASA and NOAA.
It will make simultaneous scientific observations of the solar wind and the entire sunlit side of Earth.
The 750-kilogram (1250 pound) DSCOVR probe measures 54 inches by 72 inches.

The two Earth science instruments from NASA are the Earth Polychromatic Imaging Camera (EPIC) and the National Institute of Standards and Technology Advanced Radiometer (NISTAR).
EPIC will provide true color spectral images of the entire sunlit face of Earth at least six times per day, as viewed from an orbit around L1. They will be publically available within 24 hours via NASA Langley.
It will view the full disk of the entire sunlit Earth from sunrise to sunset and collect a variety of science measurements including on ozone, aerosols, dust and volcanic ash, vegetation properties, cloud heights and more.
Listen to my post launch interview with the BBC about DSCOVR and ESA’s successful IXV launch on Feb. 11.
A secondary objective by SpaceX to recover the Falcon 9 first stage booster on an ocean going barge had to be skipped due to very poor weather and very high waves in the Atlantic Ocean making a safe landing impossible. The stage did successfully complete a soft landing in the ocean.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.



Weekly Space Hangout – Feb. 6, 2015: Astronaut Ron Garan’s “Orbital Perspective”
Host: Fraser Cain (@fcain)
Guests:
Morgan Rehnberg (cosmicchatter.org / @MorganRehnberg )
Special Guest: Astronaut Ron Garan (orbitalpersepctive.com / @Astro_Ron)
Ron will talk about his new book The Orbital Perspective: Lessons in Seeing the Big Picture from a Journey of 71 Million Miles.
This Week’s Stories:
Obama’s NASA budget request
Black Holes Do Not Exist Where Space and Time Do Not Exist, Says New Theory
SES Rethinking Being First to Fly on a Full-Throttle Falcon 9
5 Lunar X-Prize Teams Land Payday; Only 2 Landed Hardware
Moroccan Meteorite May Be a 4.4-Billion-Year-Old Chunk of Martian Crust
After Canceling NRO Launch Competition, USAF Dangles More Plums for SpaceX
Where is Saturn? VLBA Used to Accurately Measure Position of Saturn and its 62 Moons
SpaceX Nears Pad Abort Test for Human-Rated Dragon Capsule
Closer Look at the IXV Intermediate eXperimental Vehicle
Skylon Spaceplane’s Inventor Sees Busy Spaceports Coming Soon
SpaceX Conducts Static Fire Test Ahead of DSCOVR Mission
Supernova Mystery Found at the Bottom of the Sea
NASA Does an About Face on SOFIA: Requests Full Funding
LightSail Test Flight Scheduled for May 2015
Mining the Moon Becomes a Serious Prospect
TWiM: NASA Presses Congress for More Commercial Crew Funding
A Second Ringed Centaur? Centaurs with Rings Could Be Common
Rosetta Swoops In for a Close Encounter
Super Sizing Pegasus for SLS Core Transport
TWiM: SpaceX Drone Boats Named After Sci-Fi Legend’s Spaceships
It’s Official: We’re On the Way to Europa
McCain Accuses USAF of “Actively Keeping Out” SpaceX
Europe Tired of Playing “Simon Says” with SpaceX
Business on the Moon: FAA Backs Bigelow Aerospace
Mystery of the Universe’s Gamma-Ray Glow May Be Solved
New Infrared View of the Trifid Nebula Reveals New Variable Stars Far Beyond
Gap Reveals Potential Exomoon
We record the Weekly Space Hangout every Friday at 12:00 pm Pacific / 3:00 pm Eastern. You can watch us live on Google+, Universe Today, or the Universe Today YouTube page.
You can join in the discussion between episodes over at our Weekly Space Hangout Crew group in G+, and suggest your ideas for stories we can discuss each week!
Weekly Space Hangout – Jan. 23, 2015: SpaceX, Rosetta, and Asteroid Updates!
Host: Fraser Cain (@fcain)
Guests:
Morgan Rehnberg (cosmicchatter.org / @MorganRehnberg )
Ramin Skibba (@raminskibba)
Dave Dickinson (@astroguyz / www.astroguyz.com)
Continue reading “Weekly Space Hangout – Jan. 23, 2015: SpaceX, Rosetta, and Asteroid Updates!”




