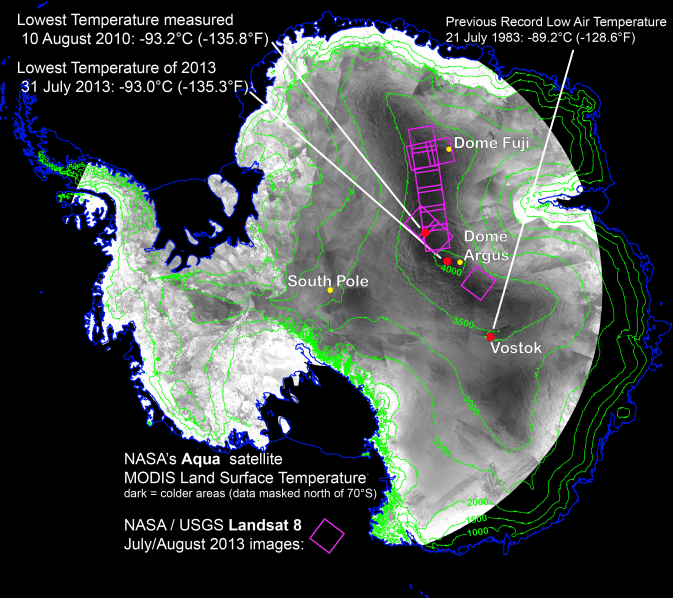
What is the coldest place on Earth? Scientists say it’s a place so cold that ordinary mercury or alcohol thermometers won’t work there. If you were there, every breath would be painful, your clothing would crackle every time you moved, and if you threw hot water into the air, it would fall to the ground as tiny shards of ice. At this place, the new record of minus 136 F (minus 93.2 C) was set on Aug. 10, 2010. Researchers analyzed data from several satellite instruments and found the coldest place on Earth in the past 32 years is … a high ridge in Antarctica between Dome Argus and Dome Fuji, two summits on the ice sheet known as the East Antarctic Plateau. Temperatures in several hollows were found to dip to the new record.
“We had a suspicion this Antarctic ridge was likely to be extremely cold,” said Ted Scambos, from the National Snow and Ice Data Center in Boulder, Colorado. “With the launch of Landsat 8, we finally had a sensor capable of really investigating this area in more detail.”
This beats out the previous low of minus 128.6 F (minus 89.2 C), set in 1983 at the Russian Vostok Research Station in East Antarctica. The coldest permanently inhabited place on Earth is northeastern Siberia, where temperatures in the towns of Verkhoyansk and Oimekon dropped to a bone-chilling 90 degrees below zero Fahrenheit (minus 67.8 C) in 1892 and 1933, respectively.
Scambos and his team made the discovery while analyzing the most detailed global surface temperature maps to date, developed with data from remote sensing satellites. The new findings were reported at the American Geophysical Union meeting in San Francisco.
The pursuit to find the coldest place on Earth started when the researchers were studying large snow dunes, sculpted and polished by the wind, on the East Antarctic Plateau. When the scientists looked closer, they noticed cracks in the snow surface between the dunes, possibly created when wintertime temperatures got so low the top snow layer shrunk. This led scientists to wonder what the temperature range was, and prompted them to hunt for the coldest places using data from two types of satellite sensors.
They used data from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instruments on NASA’s Terra and Aqua satellites and the Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer (AVHRR) on several National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration satellites. These sensitive instruments can pick up thermal radiation emitted from Earth’s surface, even in areas lacking much heat.
Using these sensors to scan the East Antarctic Plateau, Scambos detected extremely cold temperatures on a 620-mile stretch of the ridge at high elevations between Argus and Fuji, and even colder temperatures lower elevations in pockets off the ridge. Then, with the higher resolution of the Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS) aboard Landsat 8, the research team pinpointed the record-setting pockets.
The team compared the sites to topographic maps to explore how it gets so cold. Already cold temperatures fall rapidly when the sky clears. If clear skies persist for a few days, the ground chills as it radiates its remaining heat into space. This creates a layer of super-chilled air above the surface of the snow and ice. This layer of air is denser than the relatively warmer air above it, which causes it to slide down the shallow slope of domes on the Antarctic plateau. As it flows into the pockets, it can be trapped, and the cooling continues.
“By causing the air to be stationary for extended periods, while continuing to radiate more heat away into space, you get the absolute lowest temperatures we’re able to find,” Scambos said. “We suspected that we would be looking for one magical site that got extremely cold, but what we found was a large strip of Antarctica at high altitude that regularly reached these record low temperatures.”
Source: NASA