Universe Today has had the incredible opportunity of exploring various scientific fields, including impact craters, planetary surfaces, exoplanets, astrobiology, solar physics, comets, planetary atmospheres, planetary geophysics, cosmochemistry, meteorites, radio astronomy, extremophiles, organic chemistry, black holes, cryovolcanism, planetary protection, dark matter, supernovae, neutron stars, and exomoons, and how these separate but unique all form the basis for helping us better understand our place in the universe.
Continue reading “Evolutionary Biology: Why study it? What can it teach us about finding life beyond Earth?”Plate Tectonics Might Only Occur on 0.003% of Planets. That Makes Earth Very Special Indeed.
Plate tectonics, oceans, and continents might just be the secret ingredients for complex life on Earth. And if these geological features are rare elsewhere in the universe, then perhaps that explains why we haven’t yet discovered intelligent alien life. New research from American and Swiss Earth scientists suggests that these ingredients represent missing variables in the famous Drake equation, devised more than half a century ago to estimate the chances of finding advanced civilizations in our galaxy. Including these new variables could completely rewrite the probability of detecting intelligent life in the Milky Way.
Continue reading “Plate Tectonics Might Only Occur on 0.003% of Planets. That Makes Earth Very Special Indeed.”Greenland’s ice Loss is Worse Than We Thought
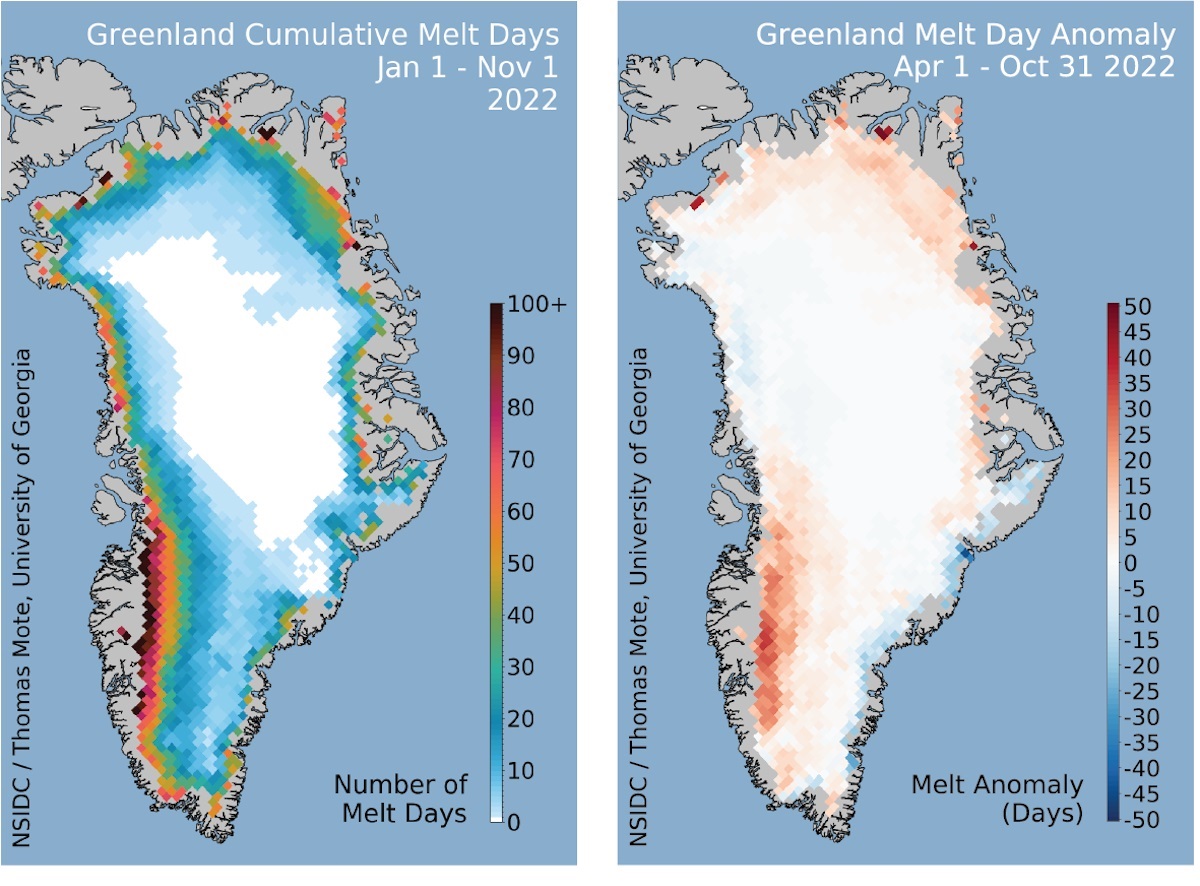
Climate change is the single greatest threat facing our planet today. Thanks to excess carbon emissions that have been growing steadily since the mid-20th century, average temperatures continue to rise worldwide. This leads to feedback mechanisms, such as rising sea levels, extreme weather, drought, wildfires, and glacial melting. This includes the Arctic Ice Pack, the East Antarctic glacier, and the Greenland Ice Sheet (GrIS), which are rapidly melting and increasing global sea levels.
Worse than that, the disappearance of the world’s ice sheets means that Earth’s surface and oceans absorb more heat, driving global temperatures even further. According to a new NASA-supported study by an international team of Earth scientists and glaciologists, the Greenland Ice Sheet is melting at an accelerating rate, much faster than existing models predict. According to these findings, far more ice will be lost from Greenland during the 21st century, which means its contribution to sea-level rise will be significantly higher.
Continue reading “Greenland’s ice Loss is Worse Than We Thought”The Rapid Changes We’re Seeing With the Earth’s Magnetic Field Don’t Mean the Poles are About to Flip. This is Normal
One of the most interesting discoveries about Earth in the past few decades concerns the Earth’s magnetic poles. Paleomagnetic records show that the poles have flipped places 183 times in the last 83 million years. That’s about every 450,000 years on average, though there were ten million years between flips in at least two cases.
The Earth’s magnetic field is experiencing some rapid changes right now, but scientists say that has no relation to pole flipping.
Continue reading “The Rapid Changes We’re Seeing With the Earth’s Magnetic Field Don’t Mean the Poles are About to Flip. This is Normal”The IPCC Releases its 2022 Report on Climate Change, in Case you Needed Something Else to Worry About
Since 1988, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) was formed and tasked with advancing knowledge of humanity’s impact on the natural environment. Beginning in 1990, they have issued multiple reports on the natural, political, and economic impacts Climate Change will have, as well as possible options for mitigation and adaptation. On Feb. 27th, the IPCC released the second part of its Sixth Assessment Report (AR6) – “Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability” – and the outlook isn’t good!
Continue reading “The IPCC Releases its 2022 Report on Climate Change, in Case you Needed Something Else to Worry About”NASA has 4 new Earth Science Missions Launching in 2022
Outer space is a great place to go if you want to study the Earth. Although outward-looking spacecraft like Hubble and the highly anticipated James Webb Space Telescope garner most of the attention from the public – understandably, given their spectacular imagery of distant astronomical phenomena – the large majority of satellite infrastructure in orbit is actually focused back on our home planet. The unparalleled view of the planet from space offers unique advantages to scientists hoping to measure changes and patterns here on Earth that just aren’t possible from the ground. In 2022, NASA will launch four new Earth science missions, each offering something unique, and adding a new way to understand, and protect, our home.
let’s take a look at the four missions, and what they hope to achieve in the coming years.
Continue reading “NASA has 4 new Earth Science Missions Launching in 2022”Animals Could Have Been Around Hundreds of Millions of Years Earlier Than Previously Believed
According to the most widely accepted theories, evolutionary biologists assert that life on Earth began roughly 4 billion years ago, beginning with single-celled bacteria and gradually giving way to more complex organisms. According to this same evolutionary timetable, the first complex organisms emerged during the Neoproterozoic era (ca. 800 million years ago), which took the form of fungi, algae, cyanobacteria, and sponges.
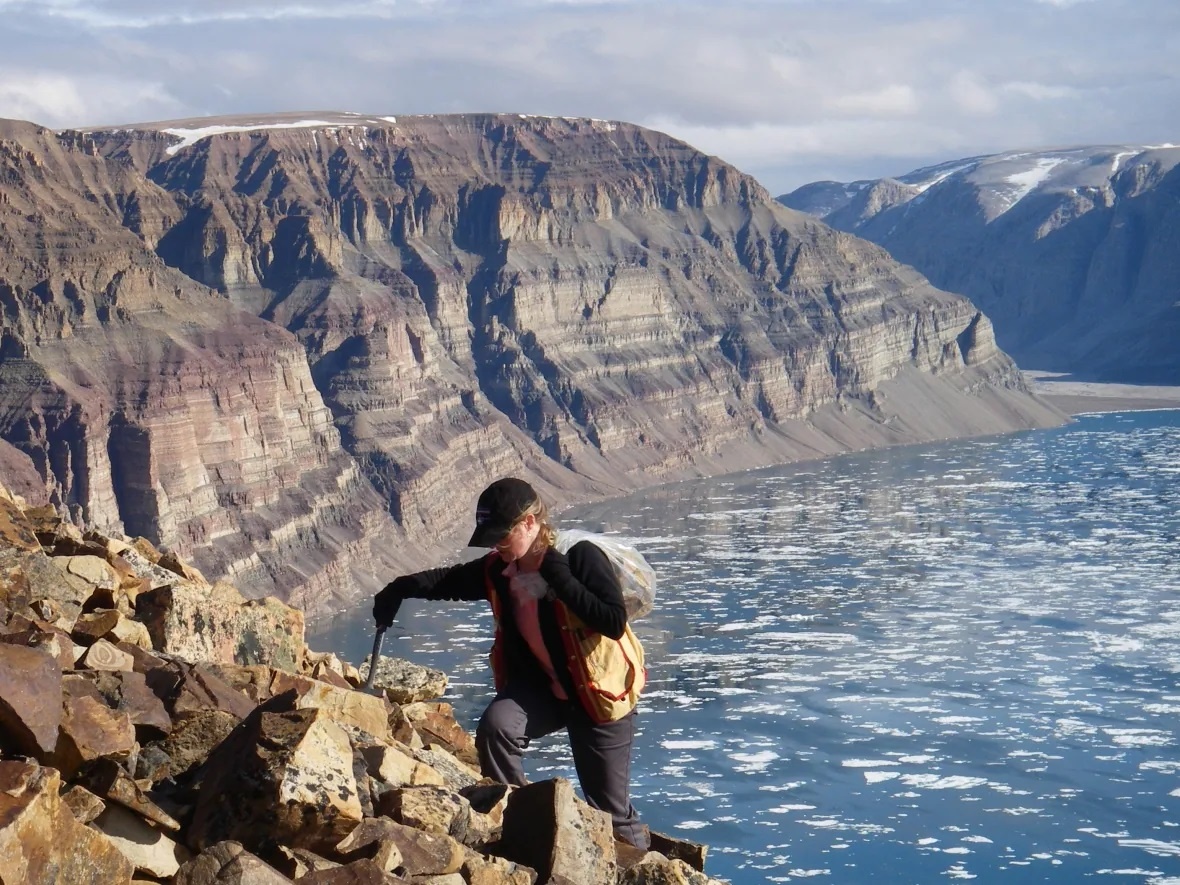
However, due to recent findings made in the Arctic Circle, it appears that sponges may have existed in Earth’s oceans hundreds of millions of years earlier than we thought! These findings were made by Prof. Elizabeth Turner of Laurentian University, who unearthed what could be the fossilized remains of sponges that are 890 million years old. If confirmed, these samples would predate the oldest fossilized sponges by around 350 million years.
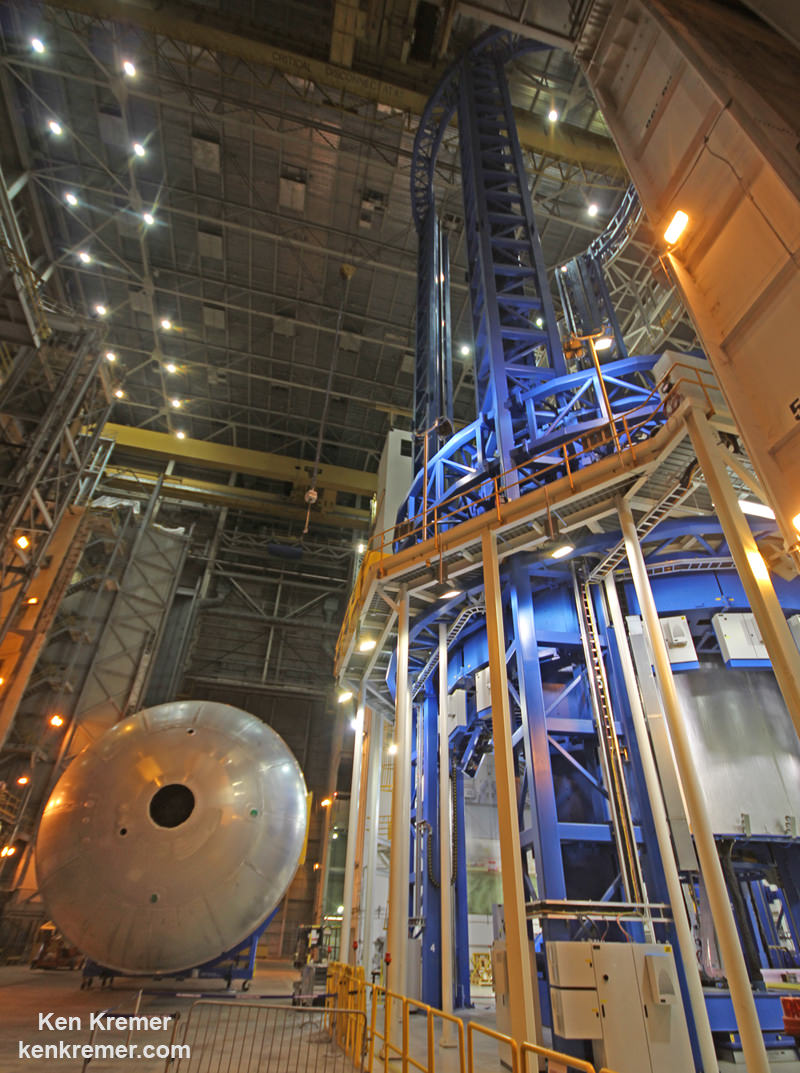
Continue reading “Animals Could Have Been Around Hundreds of Millions of Years Earlier Than Previously Believed”Clean Room Tour with NASA’s Next Gen Tracking Data Relay Satellite TDRS-M, Closeout Incident Under Review – Photos


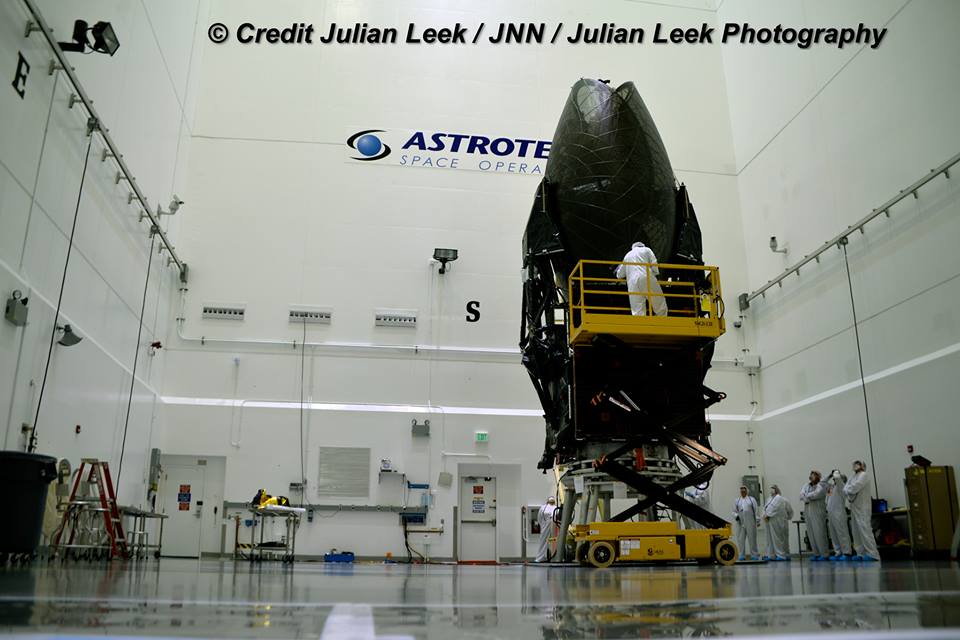
ASTROTECH SPACE OPERATIONS/KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FL – The last of NASA’s next generation Tracking and Data Relay Satellites (TRDS) designed to relay critical science data and research observations gathered by the International Space Station (ISS), Hubble and dozens of Earth-orbiting Earth science missions is undergoing final prelaunch clean room preparations on the Florida Space Coast while targeting an early August launch – even as the agency reviews the scheduling impact of a weekend “closeout incident” that “damaged” a key component.
Liftoff of NASA’s $408 million eerily insectoid-looking TDRS-M science relay comsat atop a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket currently scheduled for August 3 may be in doubt following a July 14 work related incident causing damage to the satellite’s Omni S-band antenna while inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida.
“The satellite’s Omni S-band antenna was damaged during final spacecraft closeout activities,” NASA said in an updated status statement provided to Universe Today earlier today, July 16. NASA did not provide any further details when asked.
Everything had been perfectly on track as of Thursday, July 13 as Universe Today participated in an up close media tour and briefing about the massive probe inside the clean room processing facility at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fl.
On July 13, technicians were busily working to complete final spacecraft processing activities before its encapsulation inside the nose cone of the ULA Atlas V rocket she will ride to space, planned for the next day on July 14. The satellite and pair of payload fairings were stacked in separate high bays at Astrotech on July 13.
Alas the unspecified “damage” to the TDRS-M Omni S-band antenna unfortunately took place on July 14.
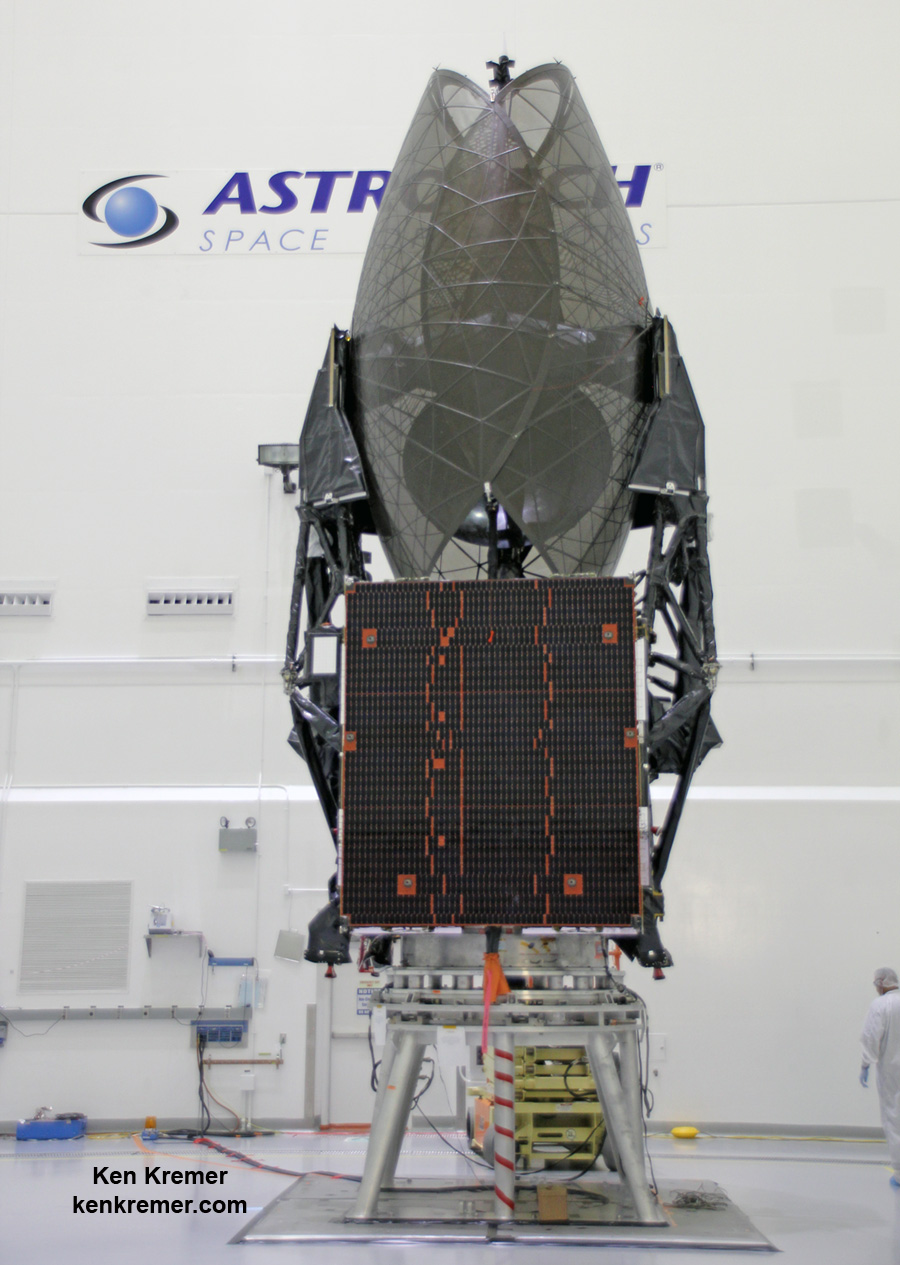

TDRS-M was built by Boeing and engineers are now analyzing the damage in a team effort with NASA. However it’s not known exactly during which closeout activity or by whom the damage occurred.
ULA CEO Tory Bruno tweeted that his company is not responsible and referred all questions to NASA. This may indicate that the antennae was not damaged during the encapsulation procedures inside the ULA payload fairing halves.
“NASA and Boeing are reviewing an incident that occurred with the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS-M) on July 14 at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida. The satellite’s Omni S-band antenna was damaged during final spacecraft closeout activities” stated NASA.
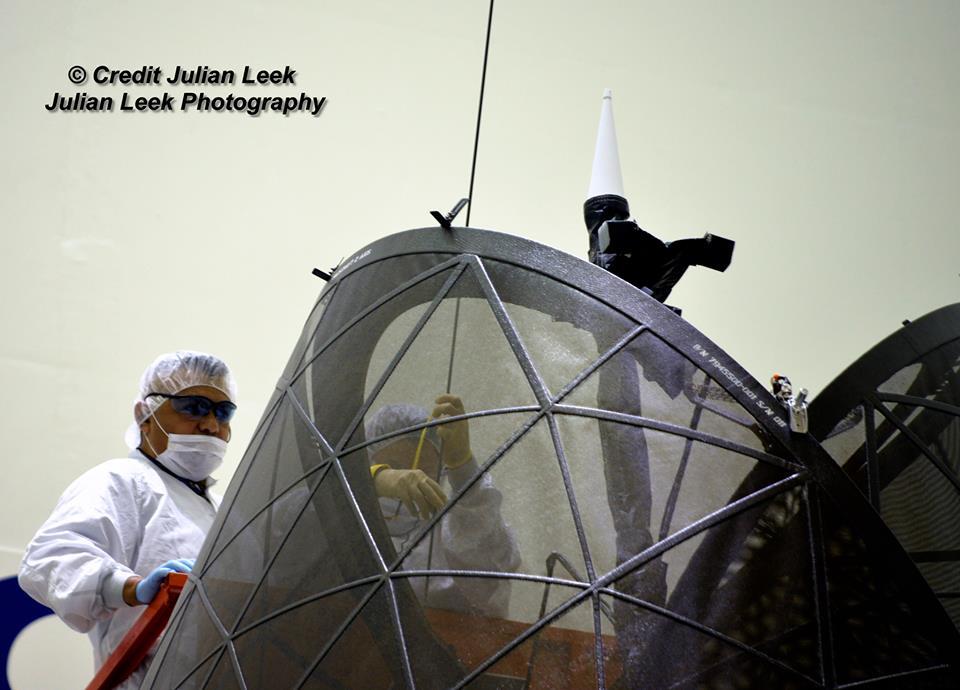

TDRS-M looks like a giant insect – or a fish depending on your point of view. It was folded into flight configuration for encapsulation in the clean room and the huge pair of single access antennas resembled a cocoon or a cicada. The 15 foot diameter single access antennas are large parabolic-style antennas and are mechanically steerable.
What does TDRS do? Why is it important? How does it operate?
“The existing Space Network of satellites like TDRS provide constant communications from other NASA satellites like the ISS or Earth observing satellites like Aura, Aqua, Landsat that have high bandwidth data that needs to be transmitted to the ground,” TDRS Deputy Project Manager Robert Buchanan explained to Universe Today during an interview in the Astrotech clean room.
“TRDS tracks those satellites using antennas that articulate. Those user satellites send the data to TDRS, like TDRS-M we see here and nine other TDRS satellites on orbit now tracking those satellites.”
“That data acquired is then transmitted to a ground station complex at White Sands, New Mexico. Then the data is sent to wherever those user satellites want the data to be sent is needed, such as a science data ops center or analysis center.”
Once launched and deployed in space they will “take about 30 to 40 days to fully unfurl,” Buchanan told me in the Astrotech clean room.
Astrotech is located just a few miles down the road from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center and the KSC Visitor Complex housing the finest exhibits of numerous spaceships, hardware items and space artifacts.

At this time, the TDRS-M website countdown clock is still ticking down towards a ULA Atlas V blastoff on August 3 at 9:02 a.m. EDT (1302 GMT) from Space Launch Complex 41 (SLC-41) on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, for a late breakfast delight.
The Aug. 3 launch window spans 40 minutes from 9:02 to 9:42 a.m. EDT.
Whether or not the launch date will change depends on the results of the review of the spacecraft’s health by NASA and Boeing. Several other satellites are also competing for launch slots in August.
“The mission team is currently assessing flight acceptance and schedule. TDRS-M is planned to launch Aug. 3, 2017, on an United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida,” NASA explained.
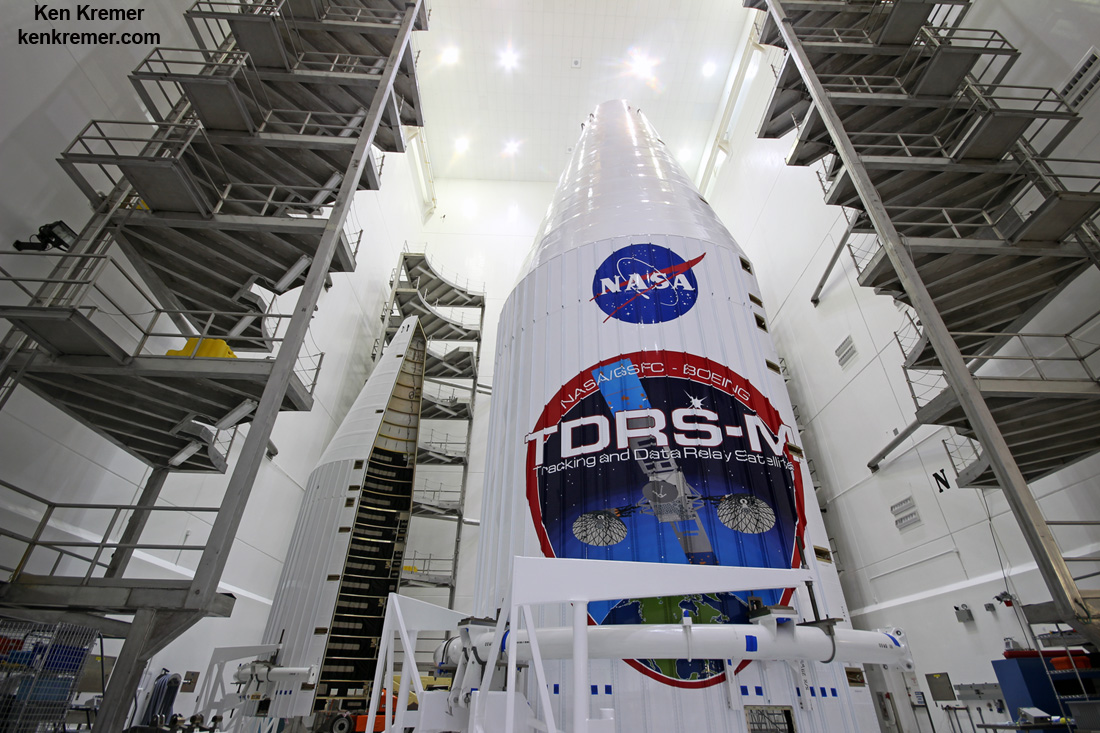

TDRS-M, spacecraft, which stands for Tracking and Data Relay Satellite – M is NASA’s new and advanced science data relay communications satellite that will transmit research measurements and analysis gathered by the astronaut crews and instruments flying abroad the International Space Station (ISS), Hubble Space Telescope and over 35 NASA Earth science missions including MMS, GPM, Aura, Aqua, Landsat, Jason 2 and 3 and more.
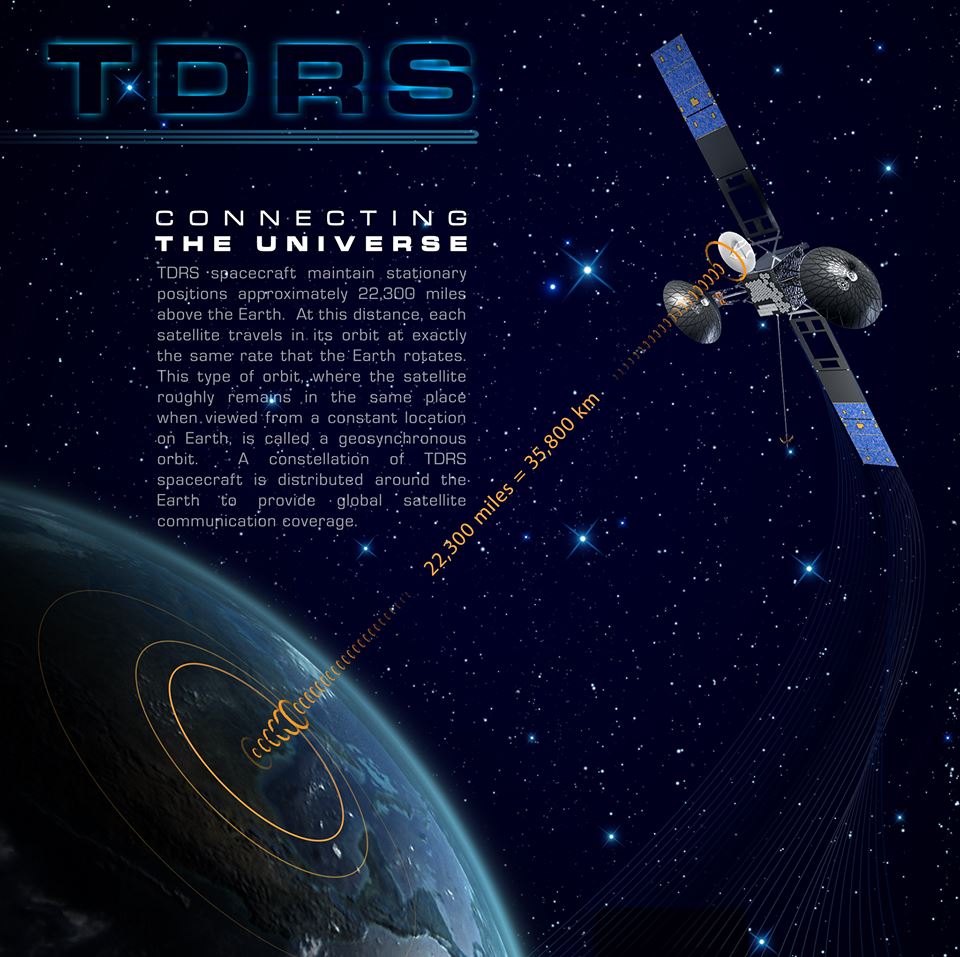
The TDRS constellation orbits 22,300 miles above Earth and provide near-constant communication links between the ground and the orbiting satellites.

TRDS-M will have S-, Ku- and Ka-band capabilities. Ka has the capability to transmit as much as six-gigabytes of data per minute. That’s the equivalent of downloading almost 14,000 songs per minute says NASA.
The TDRS program is managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland.
TDRS-M is the third satellite in the third series of NASA’s American’s most powerful and most advanced Tracking and Data Relay Satellites. It is designed to last for a 15 year orbital lifetime.
The first TDRS satellite was deployed from the Space Shuttle Challenger in 1983 as TDRS-A.
TDRS-M was built by prime contractor Boeing in El Segundo, California and is the third of a three satellite series – comprising TDRS -K, L, and M. They are based on the Boeing 601 series satellite bus and will be keep the TDRS satellite system operational through the 2020s.
TDSR-K and TDRS-L were launched in 2013 and 2014.
The Tracking and Data Relay Satellite project is managed at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center.
TDRS-M was built as a follow on and replacement satellite necessary to maintain and expand NASA’s Space Network, according to a NASA description.
The gigantic satellite is about as long as two school buses and measures 21 meters in length by 13.1 meters wide.
It has a dry mass of 1800 kg (4000 lbs) and a fueled mass of 3,454 kilogram (7,615 lb) at launch.
TDRS-M will blastoff on a ULA Atlas V in the baseline 401 configuration, with no augmentation of solid rocket boosters on the first stage. The payload fairing is 4 meters (13.1 feet) in diameter and the upper stage is powered by a single-engine Centaur.
TDRS-M will be launched to a Geostationary orbit some 22,300 miles (35,800 km) above Earth.
“The final orbital location for TDRS-M has not yet been determined,” Buchanen told me.
The Atlas V booster is being assembled inside the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at SLC-41 and will be rolled out to the launch pad the day before liftoff with the TDRS-M science relay comsat comfortably encapsulated inside the nose cone.

Carefully secured inside its shipping container, the TDRS-M satellite was transported on June 23 by a US Air Force cargo aircraft from Boeing’s El Segundo, California facility to Space Coast Regional Airport in Titusville, Florida, for preflight processing at Astrotech.
Watch for Ken’s onsite TDRS-M and space mission reports direct from the Kennedy Space Center and Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.
Trump Proposes $19.1 Billion 2018 NASA Budget, Cuts Earth Science and Education


The Trump Administration has proposed a $19.1 Billion NASA budget request for Fiscal Year 2018, which amounts to a $0.5 Billion reduction compared to the recently enacted FY 2017 NASA Budget. Although it maintains many programs such as human spaceflight, planetary science and the Webb telescope, the budget also specifies significant cuts and terminations to NASA’s Earth Science and manned Asteroid redirect mission as well as the complete elimination of the Education Office.
Overall NASA’s FY 2018 budget is cut approximately 3%, or $560 million, for the upcoming fiscal year starting in October 2017 as part of the Trump Administration’s US Federal Budget proposal rolled out on May 23, and quite similar to the initial outline released in March.
The cuts to NASA are smaller compared to other Federal science agencies also absolutely vital to the health of US scientific research – such as the NIH, the NSF, the EPA, DOE and NIST which suffer unconscionable double digit slashes of 10 to 20% or more.
The highlights of NASA’s FY 2018 Budget were announced by NASA acting administrator Robert Lightfoot during a ‘State of NASA’ speech to agency employees held at NASA HQ, Washington, D.C. and broadcast to the public live on NASA TV.
Lightfoot’s message to NASA and space enthusiasts was upbeat overall.
“What this budget tells us to do is to keep going!” NASA acting administrator Robert Lightfoot said.
“Keep doing what we’ve been doing. It’s very important for us to maintain that course and move forward as an agency with all the great things we’re doing.”
“I want to reiterate how proud I am of all of you for your hard work – which is making a real difference around the world. NASA is leading the world in space exploration, and that is only possible through all of your efforts, every day.”
“We’re pleased by our top line number of $19.1 billion, which reflects the President’s confidence in our direction and the importance of everything we’ve been achieving.”
Lightfoot recalled the recent White House phone call from President Trump to NASA astronaut & ISS Station Commander Peggy Whitson marking her record breaking flight for the longest cumulative time in space by an American astronaut.
Thus Lightfoot’s vision for NASA has three great purposes – Discover, Explore, and Develop.
“NASA has a historic and enduring purpose. It can be summarized in three major strategic thrusts: Discover, Explore, and Develop. These correspond to our missions of scientific discovery, missions of exploration, and missions of new technology development in aeronautics and space systems.”
Lightfoot further recounted the outstanding scientific accomplishments of NASA’s Mars rover and orbiters paving the path for the agencies plans to send humans on a ‘Journey to Mars’ in the 2030s.
“We’ve had a horizon goal for some time now of reaching Mars, and this budget sustains that work and also provides the resources to keep exploring our solar system and look beyond it.”
Lightfoot also pointed to upcoming near term science missions- highlighting a pair of Mars landers – InSIGHT launching next year as well as the Mars 2020 rover. Also NASA’s next great astronomical observatory – the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST).
“In science, this budget supports approximately 100 missions: 40 missions currently preparing for launch & 60 operating missions.”
“The James Webb Space Telescope is built!” Lightfoot gleefully announced.
“It’s done testing at Goddard and now has moved to Johnson for tests to simulate the vacuum of space.”
JWST is the scientific successor to the Hubble Space Telescope and slated for launch in Oct. 2018. The budget maintains steady support for Webb.

The Planetary Sciences division receives excellent support with a $1.9 Billion budget request. It includes solid support for the two flagship missions – Mars 2020 and Europa Clipper as well as the two new Discovery class missions selected -Lucy and Psyche.
“The budget keeps us on track for the next selection for the New Frontiers program, and includes formulation of a mission to Jupiter’s moon Europa.”
“SLS and Orion are making great progress. They are far beyond concepts, and as I mentioned, components are being tested in multiple ways right now as we move toward the first flight of that integrated system.”
NASA is currently targeting the first integrated launch of SLS and Orion on the uncrewed Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) for sometime in 2019.
Top NASA managers recently decided against adding a crew of two astronauts to the flight after conducting detailed agency wide studies at the request of the Trump Administration.
NASA would have needed an additional $600 to $900 to upgrade EM-1 with humans.
Unfortunately Trump’s FY 2018 NASA budget calls for a slight reduction in development funding for both SLS and Orion – thus making a crewed EM-1 flight fiscally unviable.
The budget request does maintain full funding for both of NASA’s commercial crew vehicles planned to restore launching astronauts to low Earth orbit (LEO) and the ISS from US soil on US rockets – namely the crewed Dragon and CST-100 Starliner – currently under development by SpaceX and Boeing – thus ending our sole reliance on Russian Soyuz for manned launches.
“Working with commercial partners, NASA will fly astronauts from American soil on the first new crew transportation systems in a generation in the next couple of years.”
“We need commercial partners to succeed in low-Earth orbit, and we also need the SLS and Orion to take us deeper into space than ever before.”

However the Trump Administration has terminated NASA’s somewhat controversial plans for the Asteroid Redirect Mission (ARM) – initiated under the Obama Administration – to robotically retrieve a near Earth asteroid and redirect it to lunar orbit for a visit by a crewed Orion to gather unique asteroidal samples.
“While we are ending formulation of a mission to an asteroid, known as the Asteroid Redirect Mission, many of the central technologies in development for that mission will continue, as they constitute vital capabilities needed for future human deep space missions.”
Key among those vital capabilities to be retained and funded going forward is Solar Electric Propulsion (SEP).
“Solar electric propulsion (SEP) for our deep space missions is moving ahead as a key lynchpin.”
The Trump Administration’s well known dislike for Earth science and disdain of climate change has manifested itself in the form of the termination of 5 current and upcoming science missions.
NASA’s FY 2018 Earth Science budget suffers a $171 million cut to $1.8 Billion.
“While we are not proposing to move forward with Orbiting Carbon Observatory-3 (OCO-3), Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE), Climate Absolute Radiance and Refractivity Observatory Pathfinder (CLARREO PF), and the Radiation Budget Instrument (RBI), this budget still includes significant Earth Science efforts, including 18 Earth observing missions in space as well as airborne missions.”
The DSCOVR Earth-viewing instruments will also be shut down.
NASA’s Office of Education will also be terminated completely under the proposed FY 2018 budget and the $115 million of funding excised.
“While this budget no longer supports the formal Office of Education, NASA will continue to inspire the next generation through its missions and the many ways that our work excites and encourages discovery by learners and educators. Let me tell you, we are as committed to inspiring the next generation as ever.”
Congress will now have its say and a number of Senators, including Republicans says Trumps budget is DOA.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.
Early Earth Was Almost Entirely Underwater, With Just A Few Islands

It might seem unlikely, but tiny grains of minerals can help tell the story of early Earth. And researchers studying those grains say that 4.4 billion years ago, Earth was a barren, mountainless place, and almost everything was under water. Only a handful of islands poked above the surface.
Continue reading “Early Earth Was Almost Entirely Underwater, With Just A Few Islands”