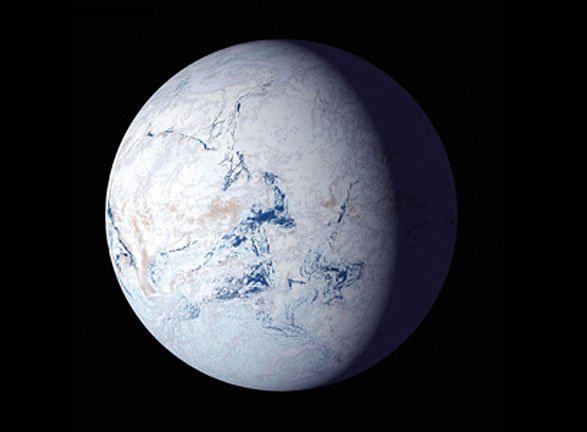
Hundreds of millions of years ago, Earth went through two episodes of severe glaciation. These two episodes—the Sturtian and the Marinoan glaciations—occured during the Earth’s Cryogenian Period. The Cryogenian lasted from about 720 million to 635 million years ago.
The phenomenon is called “Snowball Earth” and both instances of it happened in pretty quick succession. And while a planet encased in ice and snow sounds devastating, these episodes may have paved the way for the development of complex life.
The question is, what caused the Earth to freeze over like that?
Continue reading “Did Snowball Earth Happen Because of a Sudden Drop in Sunlight?”