[/caption]
The first student selected photos of the Moon’s surface snapped by NASA’s new pair of student named Lunar Mapping orbiters – Ebb & Flow – have just been beamed back and show an eerie view looking back to the Home Planet – and all of Humanity – barely rising above the pockmarked terrain of the mysterious far side of our nearest neighbor in space.
Congratulations to Americas’ Youth on an outstanding and inspiring choice !!
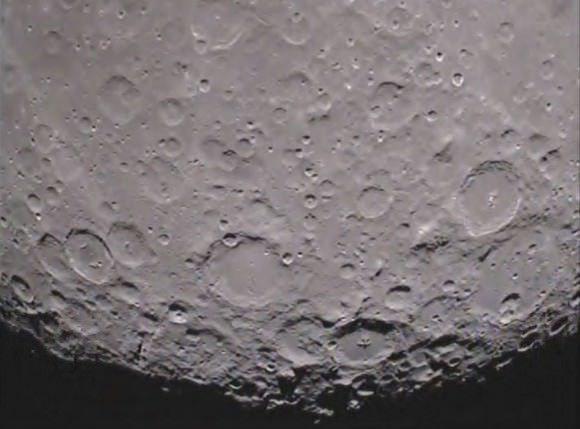
The student photo is reminiscent of one of the iconic images of Space Exploration – the first full view of the Earth from the Moon taken by NASA’s Lunar Orbiter 1 back in August 1966 (see below).
The images were taken in the past few days by the MoonKAM camera system aboard NASA’s twin GRAIL spacecraft currently circling overhead in polar lunar orbit, and previously known as GRAIL A and B. The formation-flying probes are soaring over the Moon’s north and south poles.
The nearly identical ships were rechristened as Ebb and Flow after Fourth grade students from the Emily Dickinson Elementary School in Bozeman, Mont., won the honor to rename both spacecraft by submitting the winning entries in a nationwide essay competition sponsored by NASA.
“The Bozeman 4th graders had the opportunity to target the first images soon after our science operations began,” said Maria Zuber, GRAIL principal investigator of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in Cambridge, Mass., to Universe Today.
“It is impossible to overstate how thrilled and excited we are !”
The initial packet of some 66 student-requested digital images from the Bozeman kids were taken by the Ebb spacecraft from March 15-17 and downlinked to Earth March 20. They sure have lots of exciting classwork ahead analyzing all those lunar features !
“GRAIL’s science mapping phase officially began on March 6 and we are collecting science data,” Zuber stated.
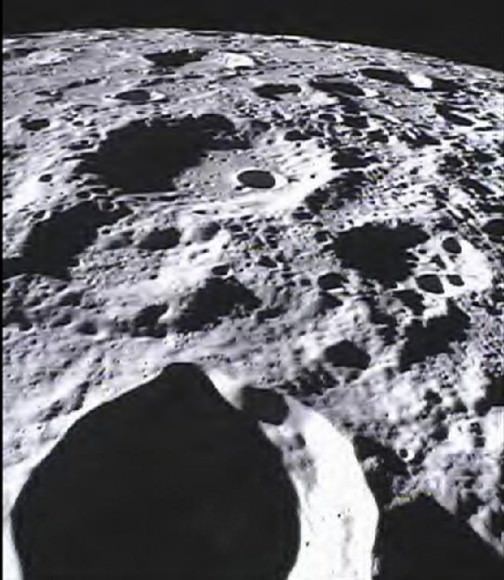

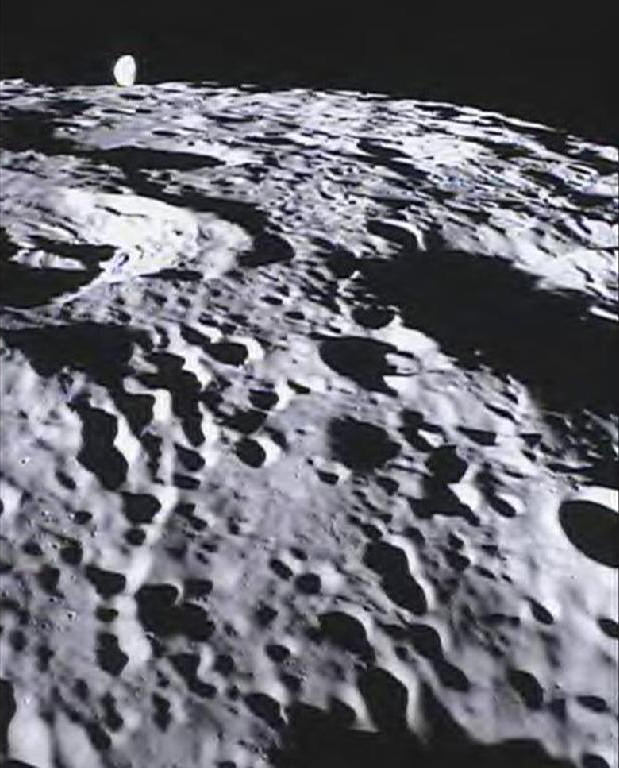
This image of the lunar surface was taken by the MoonKAM system onboard NASA’s Ebb spacecraft on March 15, 2012. The 42.3-mile-wide (68-kilometer-wide) crater in the middle of the image (with the smaller crater inside) is Poinsot. Crater Poinsot, named for the French mathematician Louis Poinsot, is located on the northern part of the moon's far side. The target was selected by 4th grade students at Emily Dickinson Elementary School in Montana who had the honor of choosing the first MoonKAM images after winning a nationwide contest. NASA/Caltech-JPL/MIT/SRS
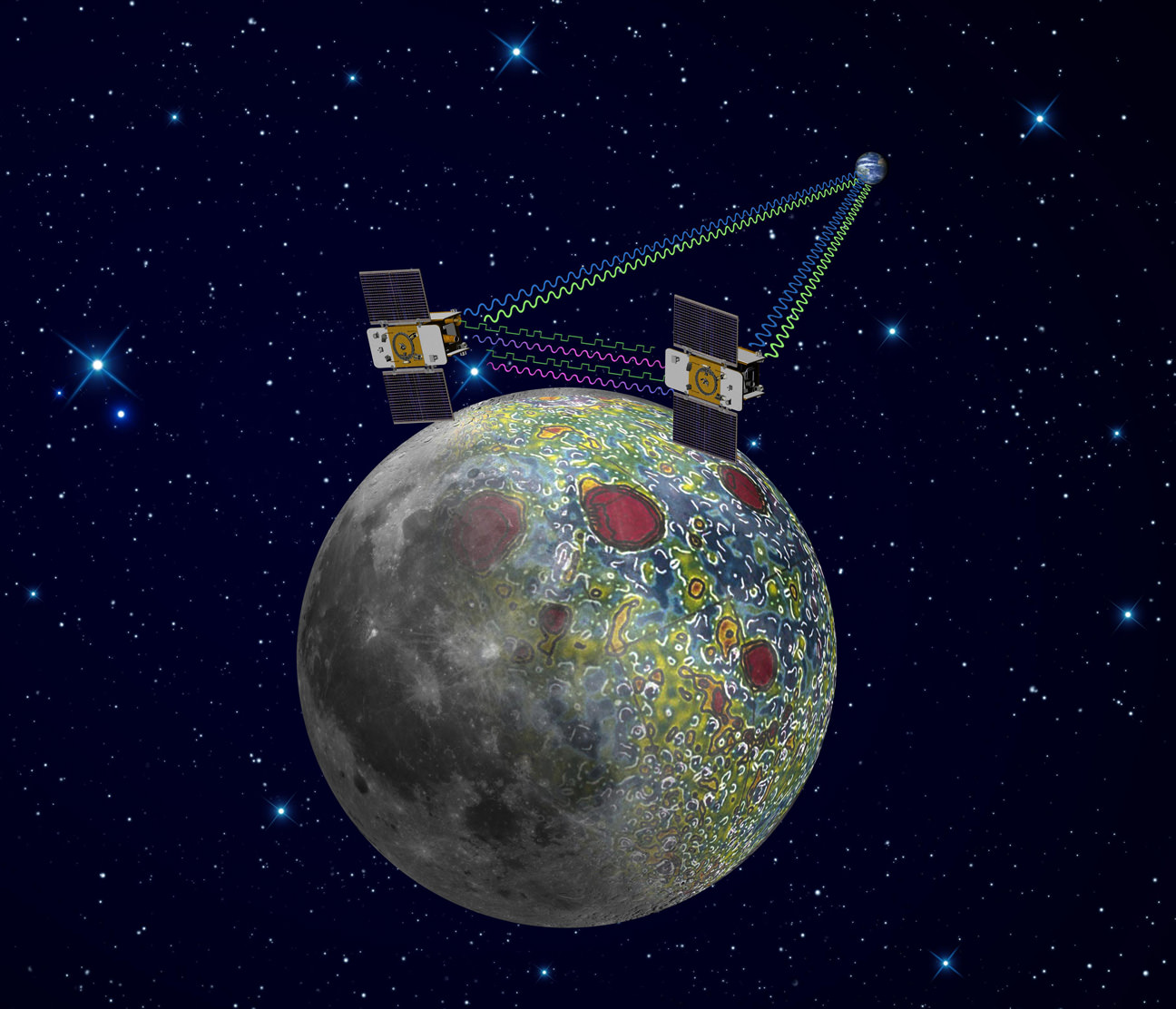
GRAIL’s science goal is to map our Moon’s gravity field to the highest precision ever. This will help deduce the deep interior composition, formation and evolution of the Moon and other rocky bodies such as Earth and also determine the nature of the Moon’s hidden core.
Engaging students and the public in science and space exploration plays a premier role in the GRAIL project. GRAIL is NASA’s first planetary mission to carry instruments – in the form of cameras – fully dedicated to education and public outreach.
Over 2,700 schools in 52 countries have signed up to participate in MoonKAM.
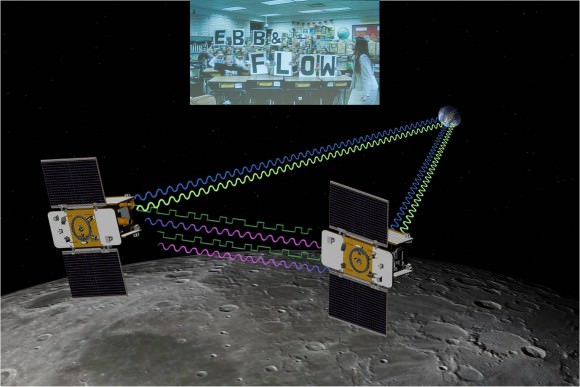
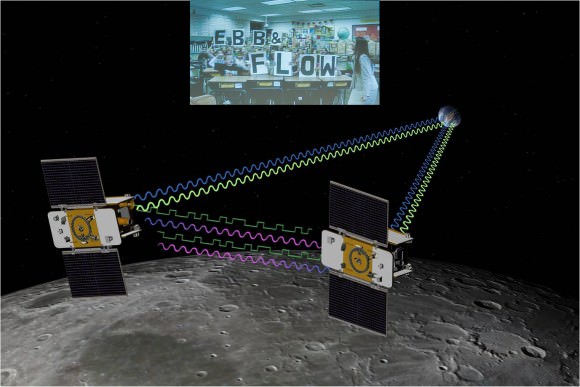
4th Grade Students from Bozeman, Montana (inset) won NASA’s contest to rename the GRAIL A and GRAIL B spacecraft and also chose the first lunar targets to be photographed by the onboard MoonKAM camera system. Artist concept of twin GRAIL spacecraft flying in tandem orbits around the Moon to measure its gravity field Credit: NASA/JPL -M ontage: Ken Kremer
5th to 8th grade students can send suggestions for lunar surface targets to the GRAIL MoonKAM Mission Operations Center at UC San Diego, Calif. Students will use the images to study lunar features such as craters, highlands, and maria while also learning about future landing sites.
NASA calls MoonKAM – “The Universe’s First Student-Run Planetary Camera”. MoonKAM means Moon Knowledge Acquired by Middle school students.
The MoonKAM project is managed by Dr Sally Ride, America’s first female astronaut.
“What might seem like just a cool activity for these kids may very well have a profound impact on their futures,” Ride said in a NASA statement. “The students really are excited about MoonKAM, and that translates into an excitement about science and engineering.”
“MoonKAM is based on the premise that if your average picture is worth a thousand words, then a picture from lunar orbit may be worth a classroom full of engineering and science degrees,” says Zuber. “Through MoonKAM, we have an opportunity to reach out to the next generation of scientists and engineers. It is great to see things off to such a positive start.”

Altogether there are eight MoonKAM cameras aboard Ebb and Flow – one 50 mm lens and three 6 mm lenses. Each probe is the size of a washing machine and measures just over 3 feet in diameter and height.
Snapping the first images was delayed a few days by the recent series of powerful solar storms.
“Due to the extraordinary intensity of the storms we took the precaution of turning off the MoonKAMs until the solar flux dissipates a bit,” Zuber told me.
“GRAIL weathered the storm well. The spacecraft and instrument are healthy and we are continuing to collect science data.”
The washing-machine sized probes have been flying in tandem around the Moon since entering lunar orbit in back to back maneuvers over the New Year’s weekend. Engineers spent the past two months navigating the spaceship duo into lower, near-polar and near-circular orbits with an average altitude of 34 miles (55 kilometers) that are optimized for science data collection and simultaneously checking out the spacecraft systems.
Ebb and Flow were launched to the Moon on September 10, 2011 aboard a Delta II rocket from Cape Canaveral, Florida and took a circuitous 3.5 month low energy path to the moon to minimize the overall costs.
The Apollo astronauts reached the Moon in just 3 days. NASA’s next generation Orion space capsule currently under development will send American astronauts back to lunar orbit by 2021 or sooner.
NASA has just granted an extension to the GRAIL mission. Watch for my follow-up report detailing the expanded science goals of GRAIL’s extended lunar journey.

…….
March 24 (Sat): Free Lecture by Ken Kremer at the New Jersey Astronomical Association, Voorhees State Park, NJ at 830 PM. Topic: Atlantis, the End of Americas Shuttle Program, Orion, SpaceX, CST-100, Moon and the Future of NASA Human & Robotic Spaceflight