Extremophiles teach us that life is found in unlikely places, which is why after looking at microbes happily living in hot springs or surviving after 18 months in space, scientists are trying to expand our definition of what a habitable environment is. So perhaps this ancient Martian volcano would be an example.
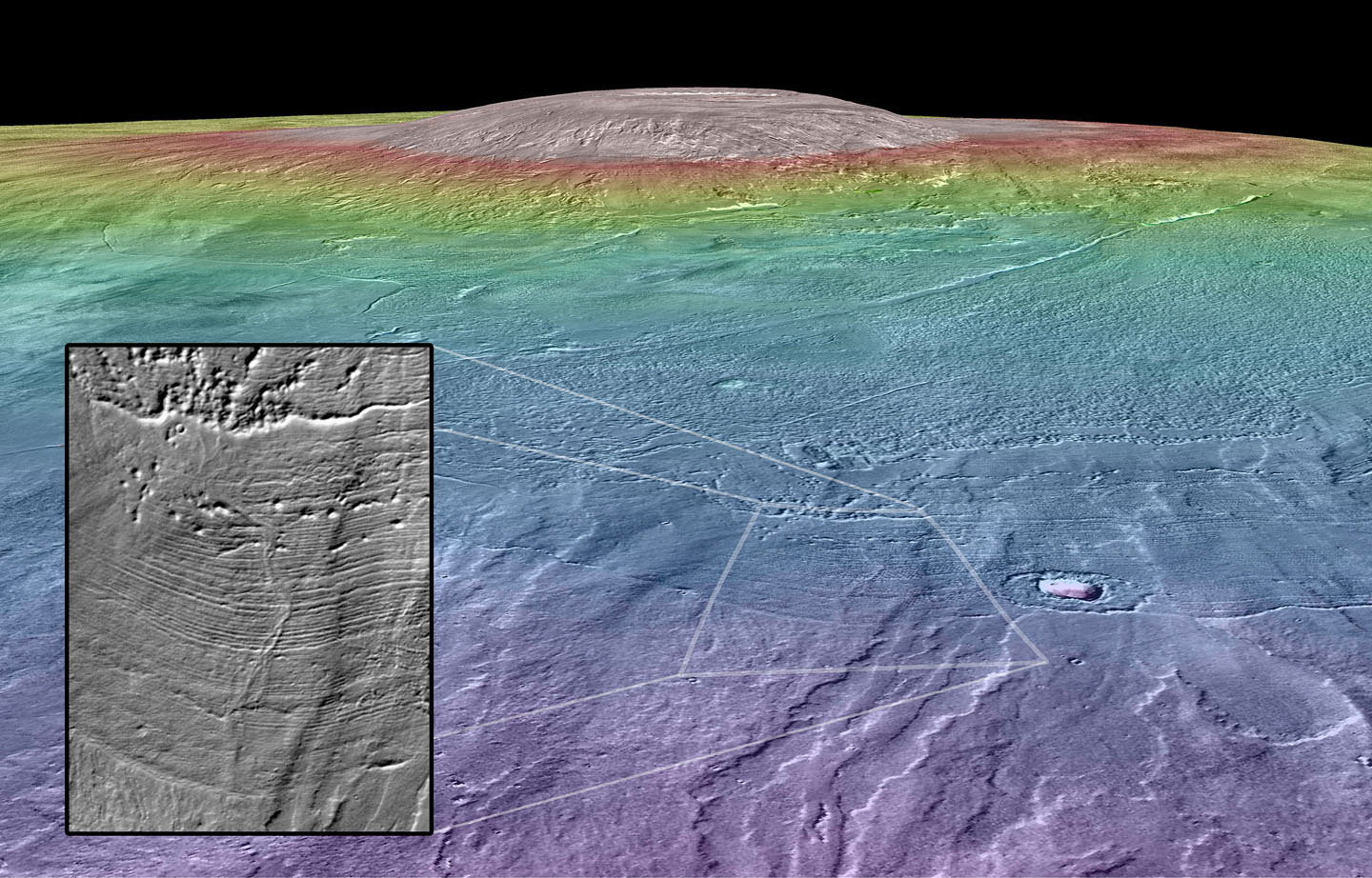
Meet Arsia Mons. It’s the third-tallest volcano on the Red Planet and one of the largest volcanoes we know of in the solar system.
New research shows that a combination of eruptions and a glacier on its northwest side could have formed something called “englacial lakes”, which is water that is created inside glaciers. (The researchers compare this to “liquid bubbles in a half-frozen ice cube.”) These in sum would have been massive, on the order of hundreds of cubic miles.
“This is interesting because it’s a way to get a lot of liquid water very recently on Mars,” stated Kat Scanlon, a graduate student at Brown who led the research, adding that she is also interested to see if signs of a habitable environment turn up in even older regions, of 2.5 billion years old or more.
“There’s been a lot of work on Earth — though not as much as we would like — on the types of microbes that live in these englacial lakes,” Scanlon added. “They’ve been studied mainly as an analog to [Saturn’s moon] Europa, where you’ve got an entire planet that’s an ice covered lake.”
While the glacial ice idea is not new — it’s been talked about since the 1970s — Scanlon’s team pushed the research forward by bringing in new information from NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.

“Scanlon found pillow lava formations, similar to those that form on Earth when lava erupts at the bottom of an ocean,” Brown University stated.
“She also found the kinds of ridges and mounds that form on Earth when a lava flow is constrained by glacial ice. The pressure of the ice sheet constrains the lava flow, and glacial meltwater chills the erupting lava into fragments of volcanic glass, forming mounds and ridges with steep sides and flat tops. The analysis also turned up evidence of a river formed in a jökulhlaup, a massive flood that occurs when water trapped in a glacier breaks free.”
Scanlon estimated that two of the “deposits” would have had lakes of 9.6 cubic miles (40 cubic kilometers) each, while a third would have had 4.8 cubic miles (20 cubic kilometers). They could have stayed liquid for hundreds or perhaps thousands of years.
That’s a short period in the history of life, but Scanlon’s team says it could have been enough for microbes to colonize the locations, if microbes were on Mars in the first place.
You can read more about the research in the journal Icarus.
Source: Brown University