What is a dwarf planet? Some astronomers have been asking that question after Pluto was demoted from planethood almost a decade ago, partly due to discoveries of other worlds of similar proportions.
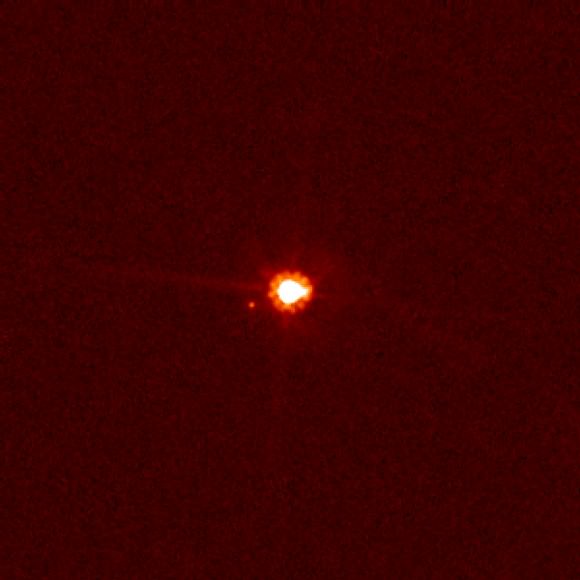
Today, astronomers announced the discovery of 2012 VP113, a world that, assuming its reflectivity is moderate, is 280 miles (450 kilometers) in size and orbiting even further away from the sun than Pluto or even the more distant Sedna (announced in 2004). If 2012 VP113 is made up mostly of ice, this would make it large (and round) enough to be a dwarf planet, the astronomers said.
Peering further into 2012 VP113’s discovery, however, brings up several questions. What are the boundaries of the Oort Cloud, the region of icy bodies where the co-discoverers say it resides? Was it placed there due to a sort of Planet X? And what is the definition of a dwarf planet anyway?
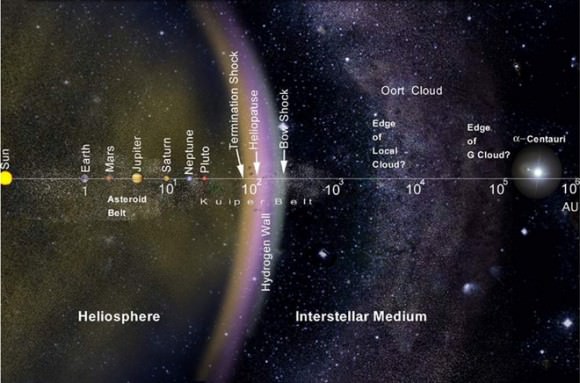
First, a bit about 2012 VP113. Its closest approach to the Sun is about 80 astronomical units, making it 80 times further from the Sun than Earth is. This puts the object in a region of space previously known only to contain Sedna (76 AU away). It’s also far away from the Kuiper Belt, a region of rocky and icy bodies between 30 and 50 AU that includes Pluto.

“The detection of 2012 VP113 confirms that Sedna is not an isolated object; instead, both bodies may be members of the inner Oort Cloud, whose objects could outnumber all other dynamically stable populations in the Solar System,” the authors wrote in their discovery paper, published today in Nature.
The Oort cloud (named after the Dutch astronomer Jan Oort, who first proposed it) is thought to contain a vast number of smallish, icy bodies. This NASA web page defines its boundaries as between 5,000 and 100,000 AUs, so 2012 VP113 obviously falls short of this measure.
The astronomers hypothesize that 2012 VP113 is part of a collection of “inner Oort cloud objects” that make their closest approach at a distance of more than 50 AU, a boundary that is thought to avoid any “significant” interference from Neptune. Orbits of these objects would range no further than 1,500 AU, a location hypothesized as part of the “outer Oort cloud” — the spot where “galactic tides start to become important in the formation process,” the team wrote.
“Some of these inner Oort cloud objects could rival the size of Mars or even Earth. This is because many of the inner Oort cloud objects are so distant that even very large ones would be too faint to detect with current technology,” stated Scott Sheppard, co-author of the paper and a solar system researcher at the Carnegie Institution for Science. (The lead author is the Gemini Observatory’s Chadwick Trujillo, who co-discovered several dwarf planets with the California Institute of Technology’s Mike Brown.)
One large question is how 2012 VP113 and Sedna came to be. And of course, with only two objects, it’s hard to draw any definitive conclusions. Theory 1 supposes that the gas giant planets beyond Earth ejected a “rogue” planet (or planets) that in turn threw objects from the Kuiper Belt to the more distant inner Oort Cloud. “These planet-sized objects could either remain (unseen) in the Solar System or have been ejected from the Solar System during the creation of the inner Oort Cloud,” the researchers wrote.
(Planet X hopers: Note that NASA just released results from its Wide-Field Infrared Survey Explorer that found nothing Saturn’s size (or bigger) as far as 10,000 AU, and nothing bigger than Jupiter at 26,000 AU.)
Theory 2 postulates that a passing star moved objects closer to the Sun into the inner Oort cloud. The last, “less-explored” theory is that these objects are “extrasolar planetesimals” — small worlds from other stars — that happened to be close to the Sun when it was born in a field of stars.
However these objects came to be, the astronomers estimate there are 900 objects with orbits similar to Sedna and 2012 VP113 that have diameters larger than 620 miles (1,000 kilometers). How do we know which are dwarf planets, however, given their distance and small size?

The International Astronomical Union’s definition of a dwarf planet doesn’t mention how big an object has to be to qualify as a dwarf planet. It reads: “A dwarf planet is an object in orbit around the Sun that is large enough (massive enough) to have its own gravity pull itself into a round (or nearly round) shape. Generally, a dwarf planet is smaller than Mercury. A dwarf planet may also orbit in a zone that has many other objects in it. For example, an orbit within the asteroid belt is in a zone with lots of other objects.”
That same page mentions there are only five recognized dwarf planets: Ceres, Pluto, Eris, Makemake and Haumea. Brown led the discovery of the last three dwarf planets in this list, and calls himself “the man who killed Pluto” because his finds helped demote Pluto from planethood to dwarf planet status.
It’s hard for official bodies to keep up with the pace of discovery, however. Brown’s webpage lists 46 “likely” dwarf planets, which under this definition would give him 15 discoveries.
“Reality … does not pay much attention to official lists kept by the IAU or by anyone else,” he wrote on that page. “A more interesting question to ask is: how many round objects are there in the solar system that are not planets? These are, by the definition, dwarf planets, whether or not they ever make it to any offiicially sanctioned list. If the category of dwarf planet is important, then it is the reality that is important, not the official list.”
His analysis (which focuses on Kuiper Belt objects) notes that most objects are too faint for us to notice if they are round or not, but you can get a sense of how round an object is by its size and composition. The asteroid belt’s Ceres (at 560 miles or 900 km) is the only known round, rocky object.
For icier objects, he suggested looking to icy moons to understand how small an object can be and still be round. Saturn’s moon Mimas is round at 250 miles (400 km), which he classifies as a “reasonable lower limit” (since observed satellites of 125 miles/200 km are not round).
Discovery of 2012 VP113 came courtesy of the new Dark Energy Camera (DECam) at the National Optical Astronomy Observatory’s 4-meter telescope in Chile. The orbit was determined with the Magellan 6.5-meter telescope at Carnegie’s Las Campanas Observatory, also in Chile.
The paper, called “A Sedna-like body with a perihelion of 80 astronomical units”, will soon be available on Nature’s website.








