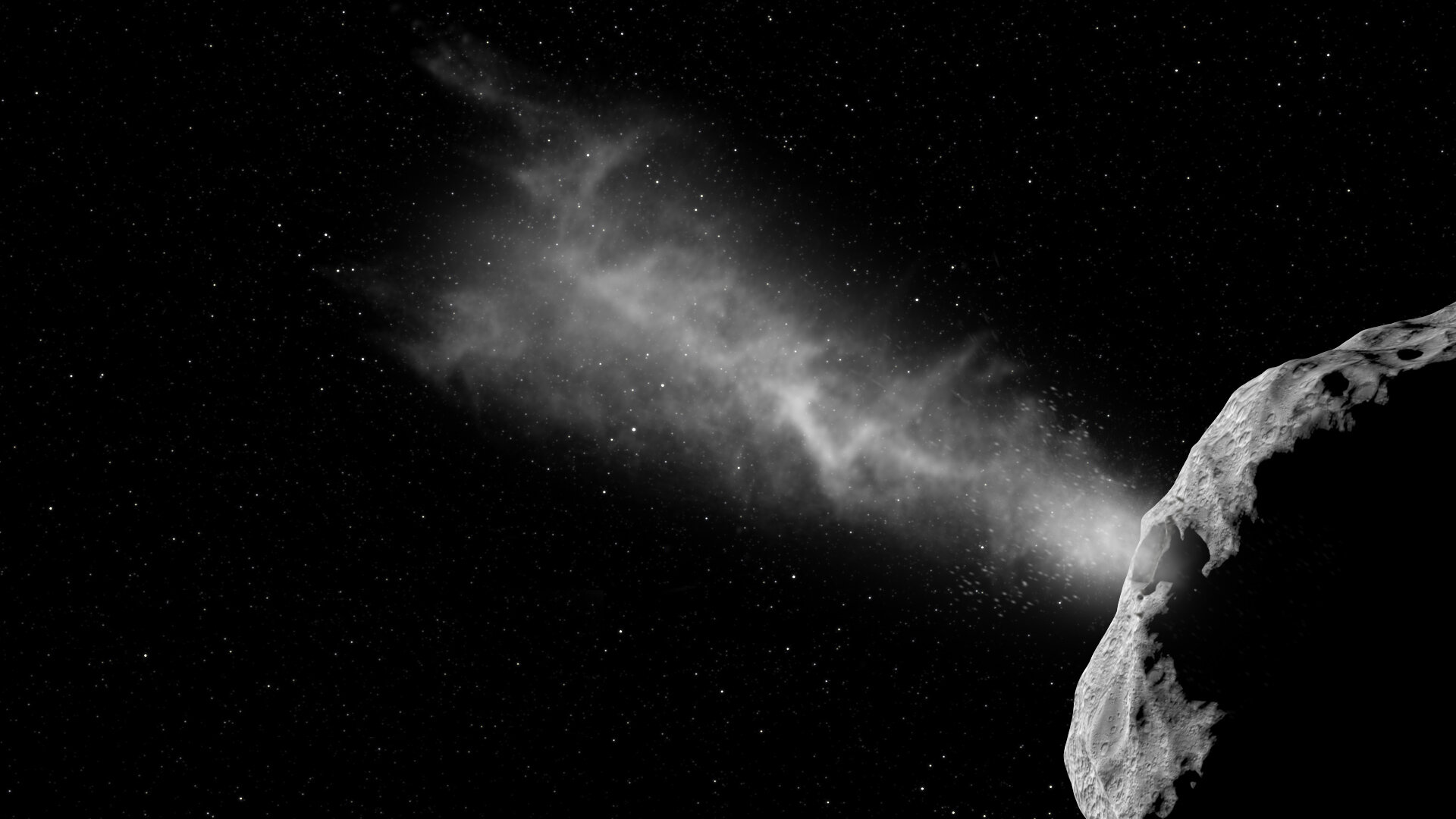
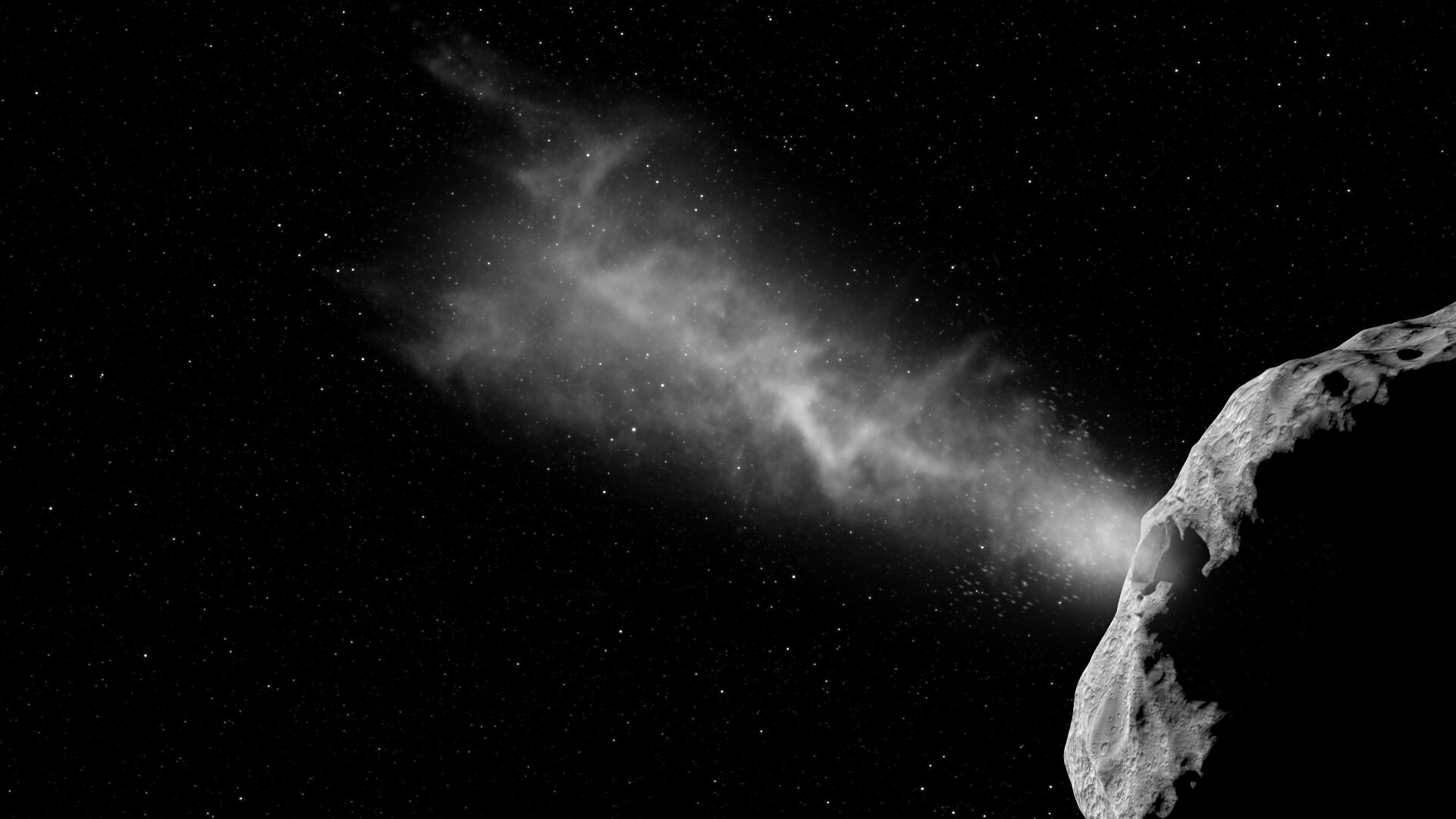
On September 26th, at 23:14 UTC (07:14 PM EST; 04:14 PM PST), NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirect Test (DART) spacecraft successfully struck the 160-meter (525 ft) moonlet Dimorphos that orbits the larger Didymos asteroid. The event was live-streamed all around the world and showed footage from DART’s Didymos Reconnaissance and Asteroid Camera for Optical navigation (DRACO) as it rapidly approached Dimorphos. In the last few seconds, DART was close enough that individual boulders could be seen on the moonlet’s surface.
About 38 seconds after impact, the time it took the signal to reach Earth, the live stream ended, signaling that DART had successfully impacted Dimorphos and was destroyed in the process. Meanwhile, teams of astronomers stretching from the Indian Ocean to the Arabian Peninsula watched the impact with their telescopes. One, in particular – the Les Makes Observatory on the island of Le Reunion in the Indian Ocean – captured multiple images of the impact. These were used to create a real-time video and show the asteroid brightening as it was pushed away, followed by material ejected from the surface.
Continue reading “The First Telescope Images of DART's Impact are Starting to Arrive”