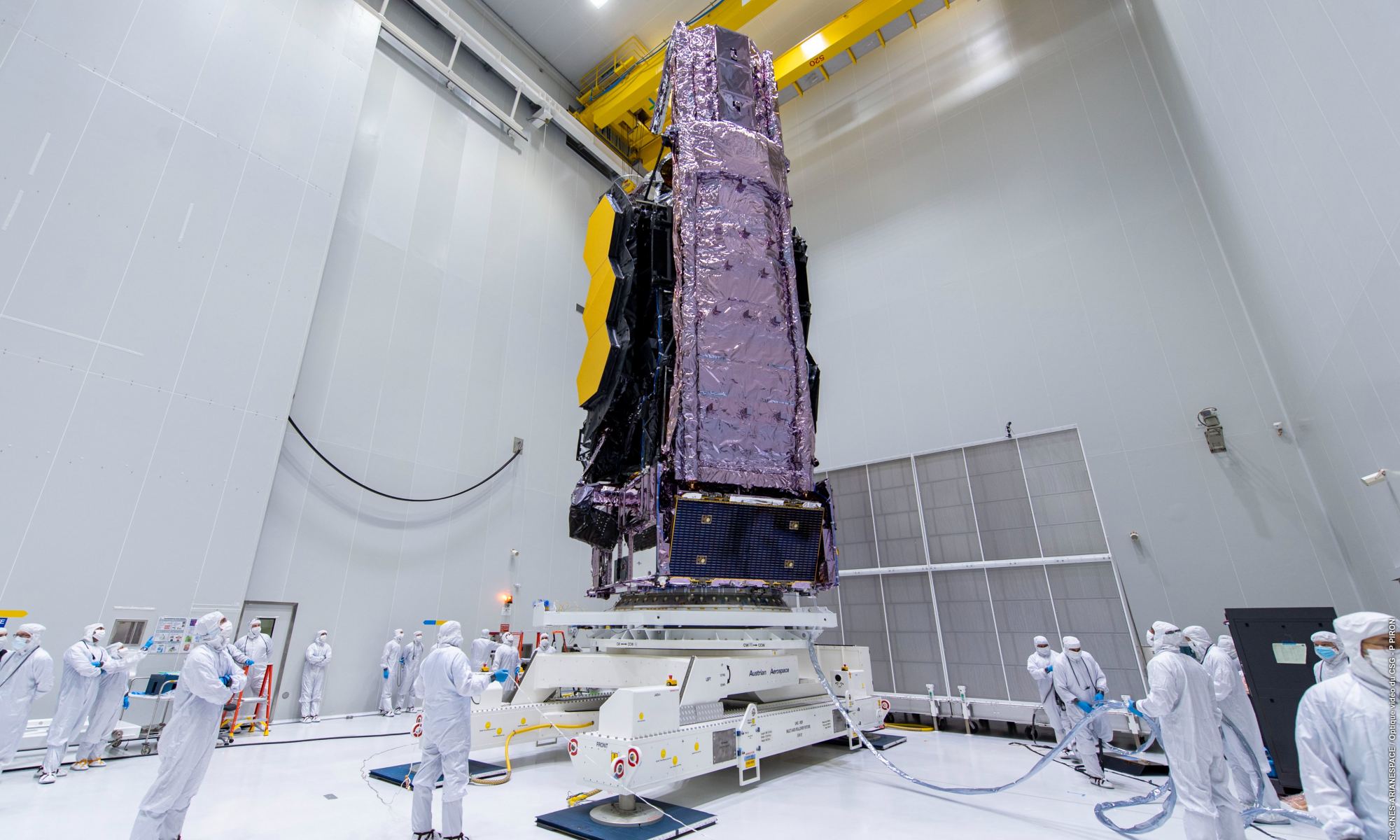
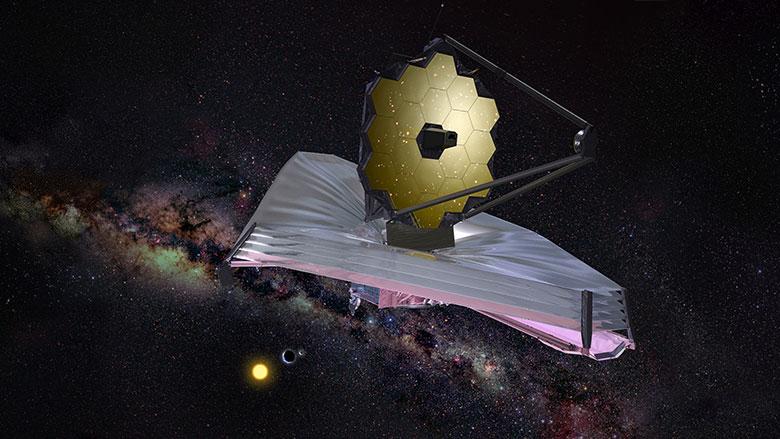
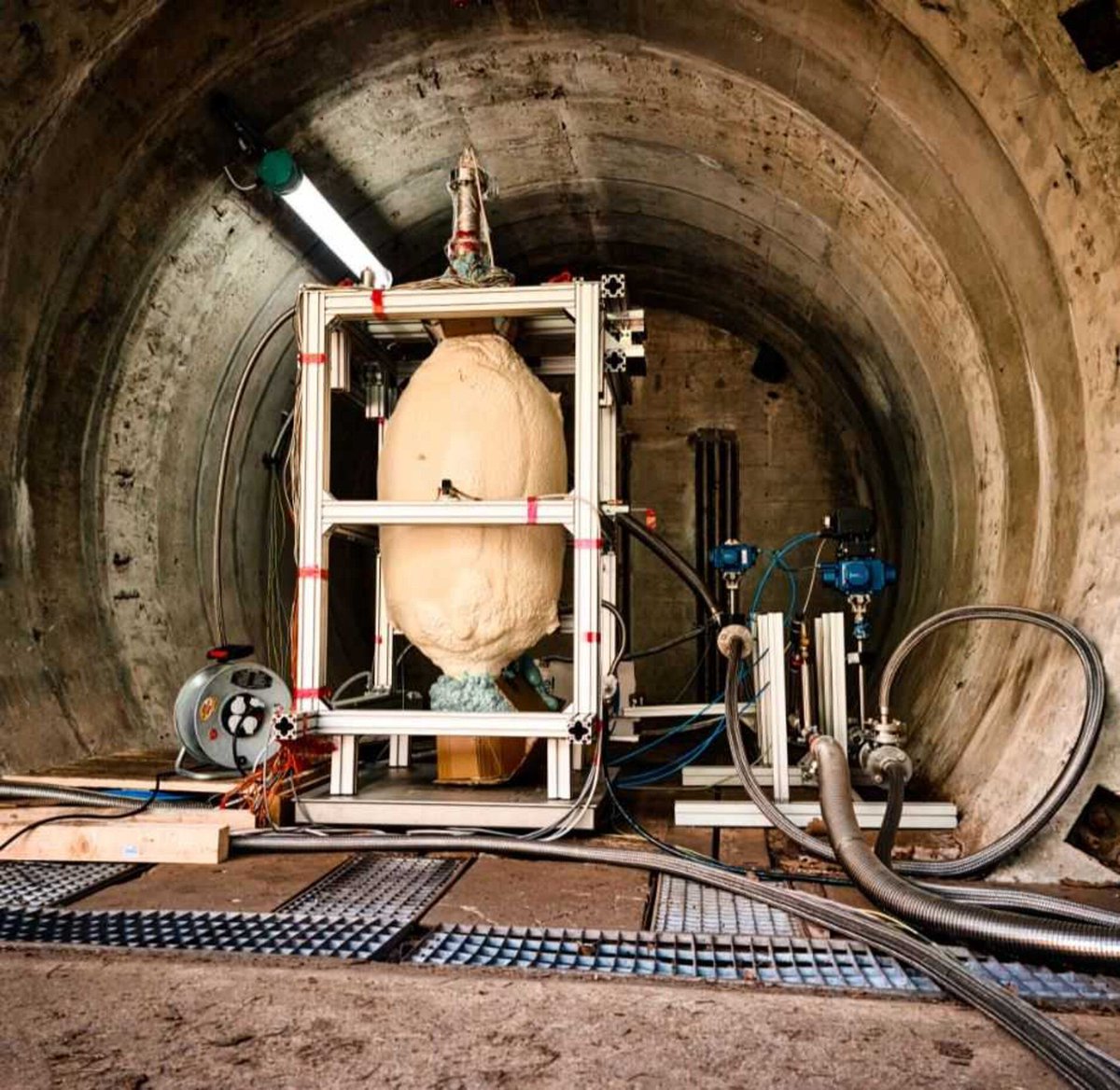
On Oct. 12th, the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) arrived safely at Port de Pariacabo in French Guiana after spending 16 days traveling between California and South America. Since then, the observatory was transported to a cleanroom in the Guyanese Space Center (GSC). Here, crews “unboxed” the observatory from its protective cargo container in preparation for launch – now targetted for Dec. 18th.
These events were captured in a series of beautiful images recently shared by the Guyanese Space Center, the European Space Agency (ESA), and NASA via their JWST Twitter accounts (more are posted on the NASA JWST Flickr page). This process involved carefully lifting the telescope from its packing container and raising it vertically, the same configuration Webb its launches to space aboard an Ariane 5 rocket.
Continue reading “I Could Look at James Webb Unboxing Pictures all Day”