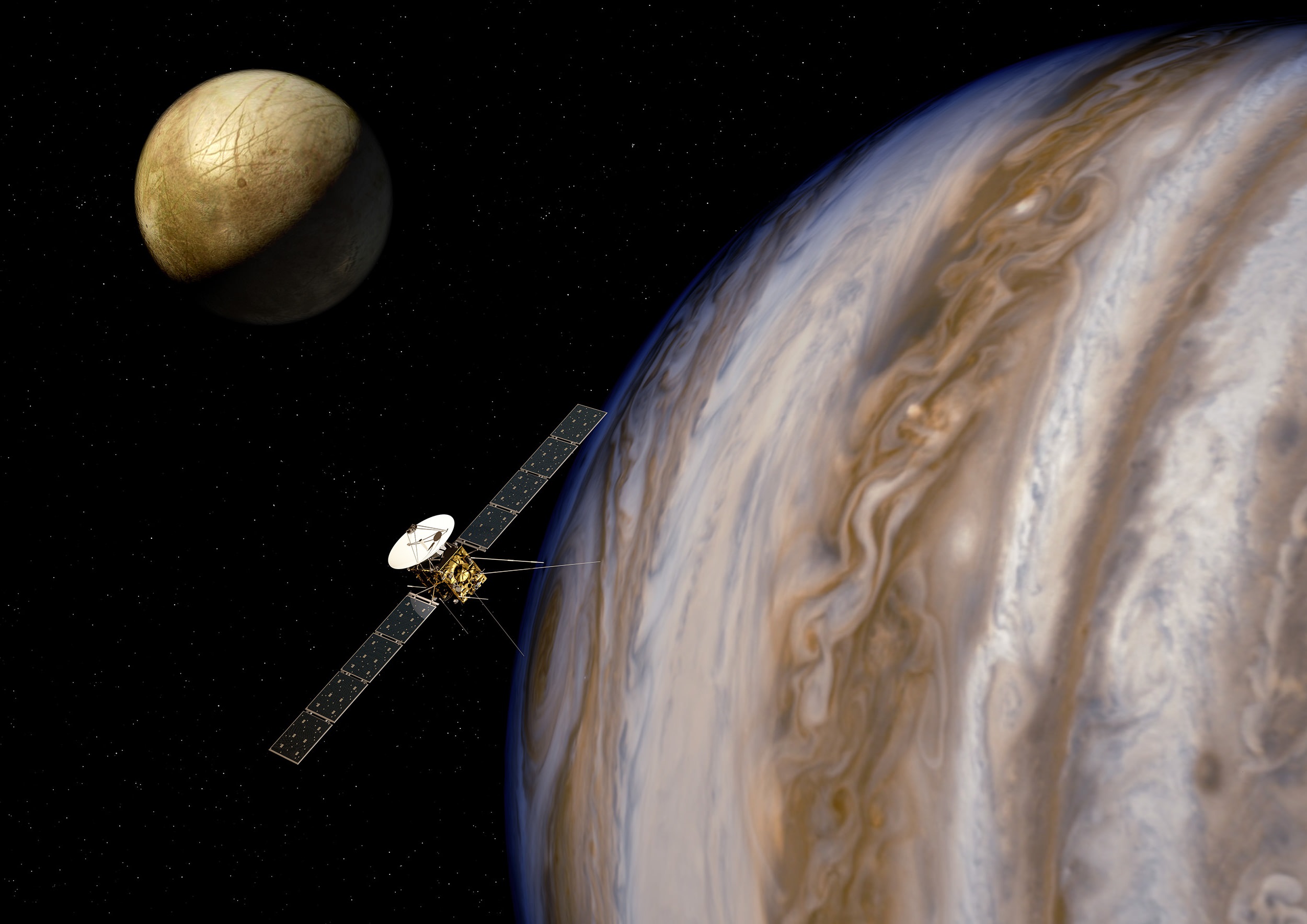
Jupiter is the most-visited planet in the Solar System, thanks largely to NASA. It all started with Pioneer 10 and 11, followed by Voyager 1 and 2. Those were all flyby missions, and it wasn’t until 1996 that the Galileo spacecraft became the first to orbit the gas giant and even send a probe into its atmosphere. Then in 2016, the Juno spacecraft entered orbit around Jupiter and is still there today.
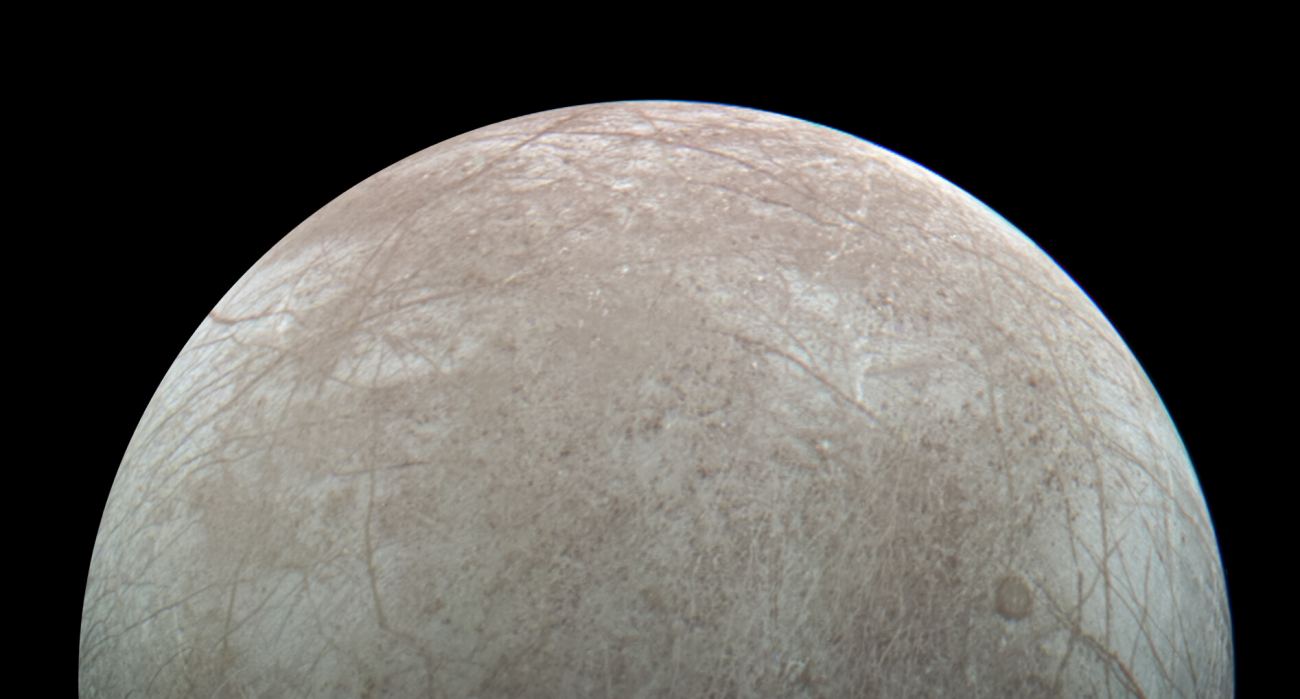
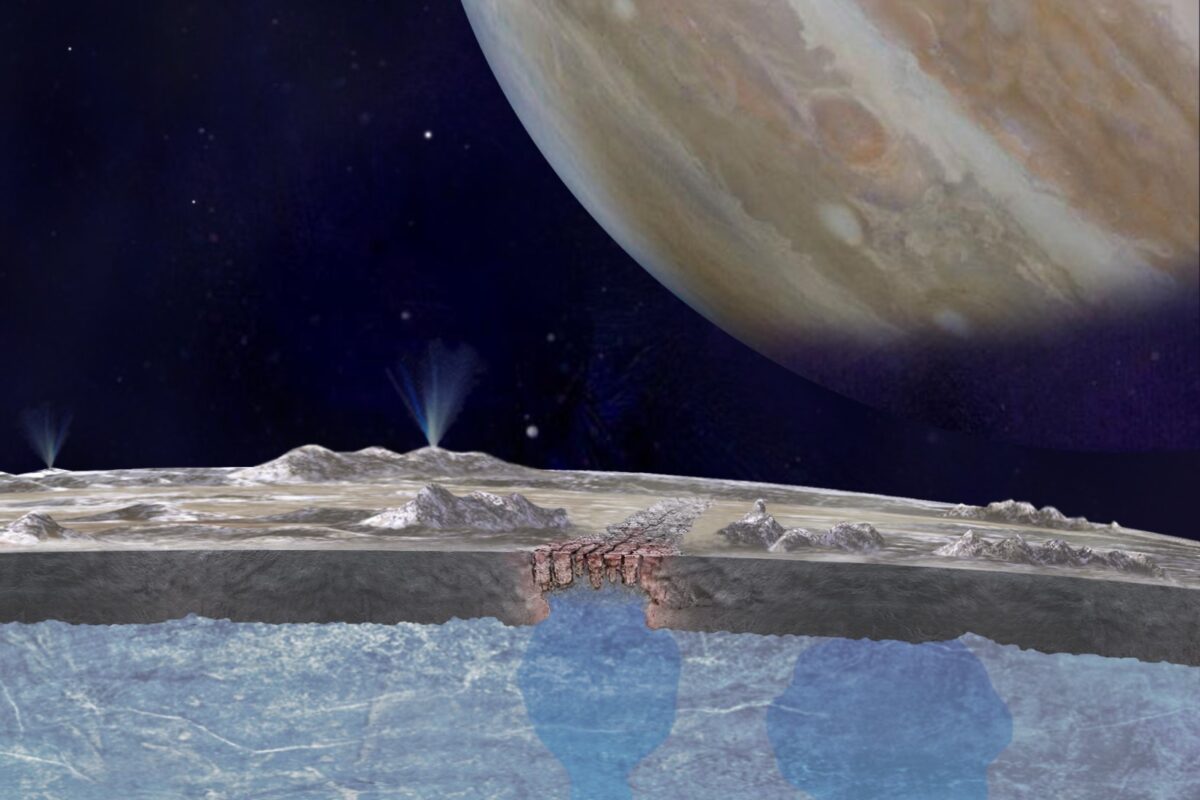
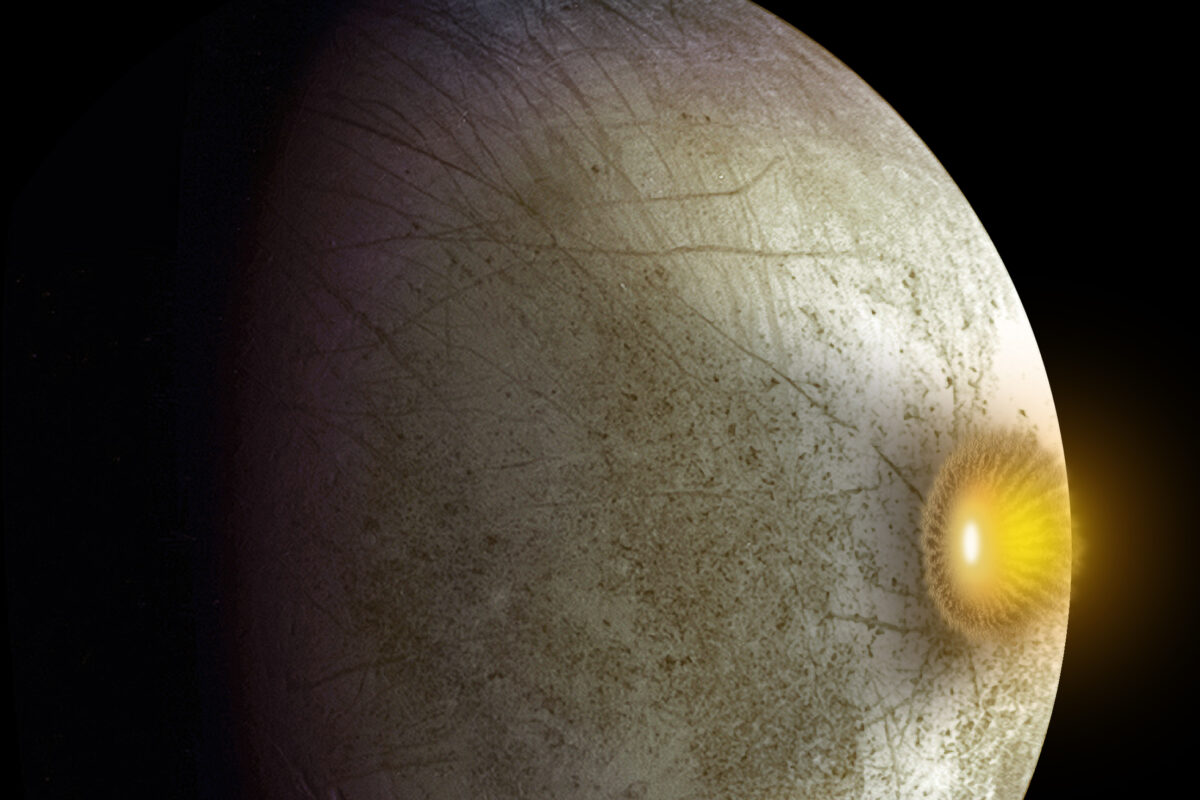
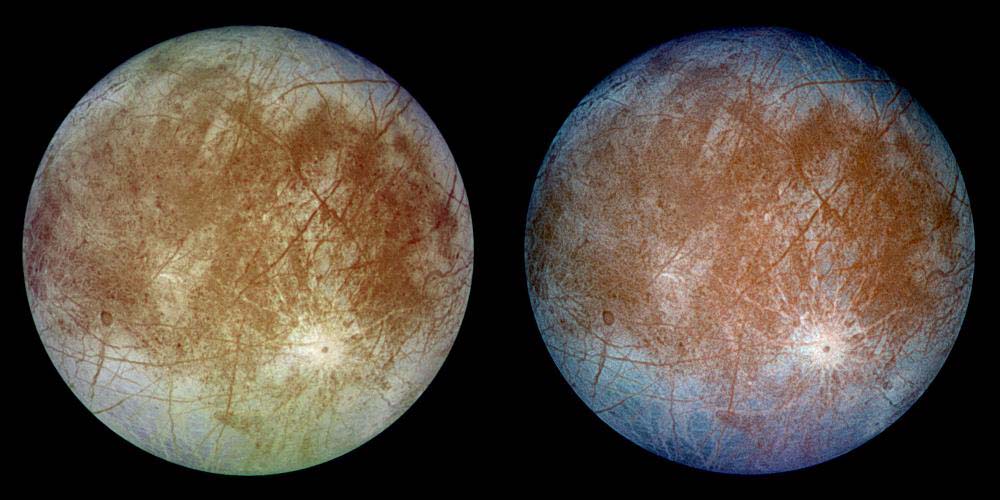
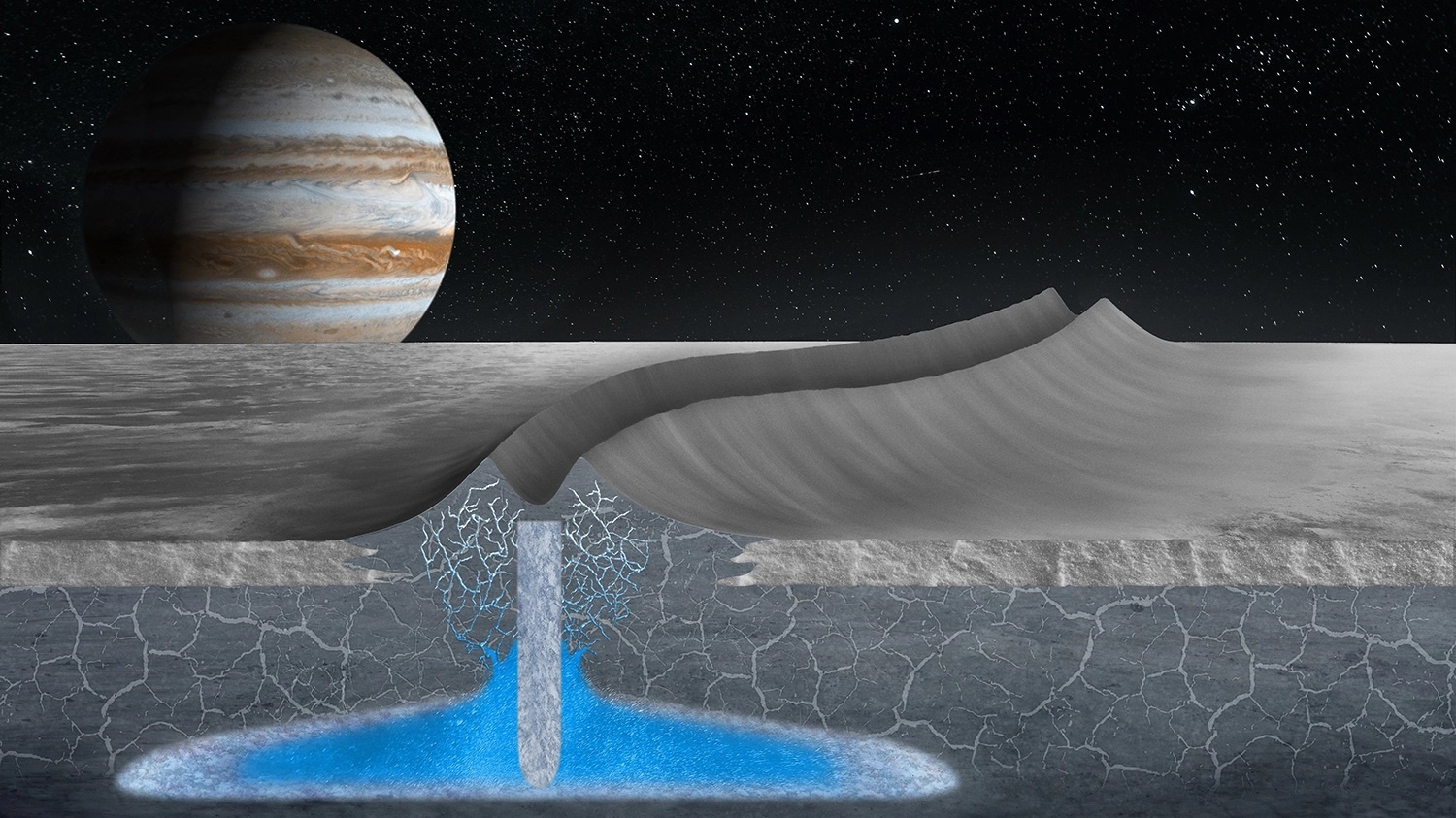
All of these missions were focused on Jupiter, but along the way, they gave us tantalizing hints of the icy moon Europa. The most impactful thing we’ve learned is that Europa, though frozen on the surface, holds an ocean under all that ice. And that warm, salty ocean might contain more water than all of Earth’s oceans combined.
Might it hold life?
Continue reading “Comet Impacts Could Have Brought the Raw Ingredients for Life to Europa’s Ocean”