Welcome back to our Fermi Paradox series, where we take a look at possible resolutions to Enrico Fermi’s famous question, “Where Is Everybody?” Today, we examine the possibility that the reason for the Great Silence is that most life out there exists in warm water oceans under sheets of ice!
In 1950, Italian-American physicist Enrico Fermi sat down to lunch with some of his colleagues at the Los Alamos National Laboratory, where he had worked five years prior as part of the Manhattan Project. According to various accounts, the conversation turned to aliens and the recent spate of UFOs. Into this, Fermi issued a statement that would go down in the annals of history: “Where is everybody?“
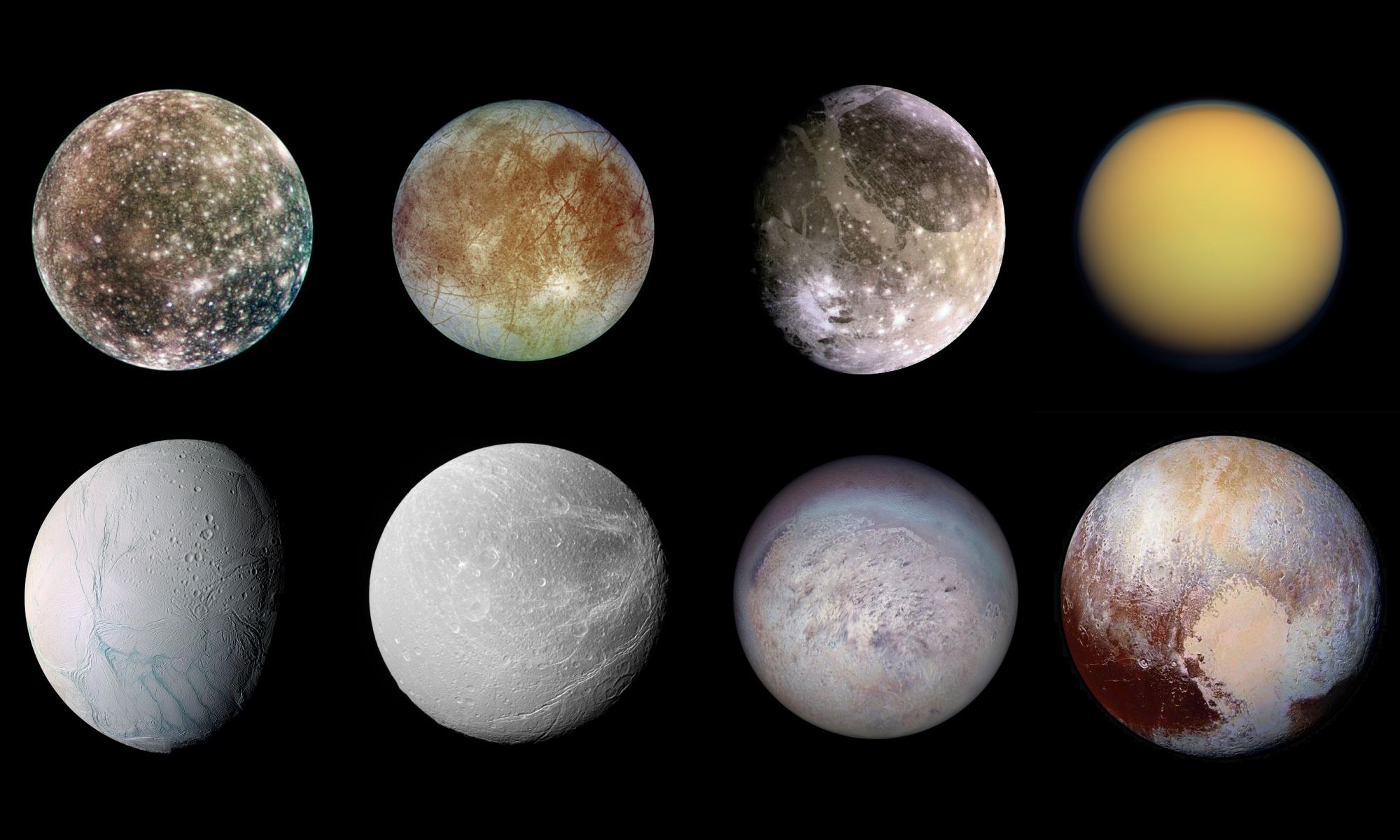
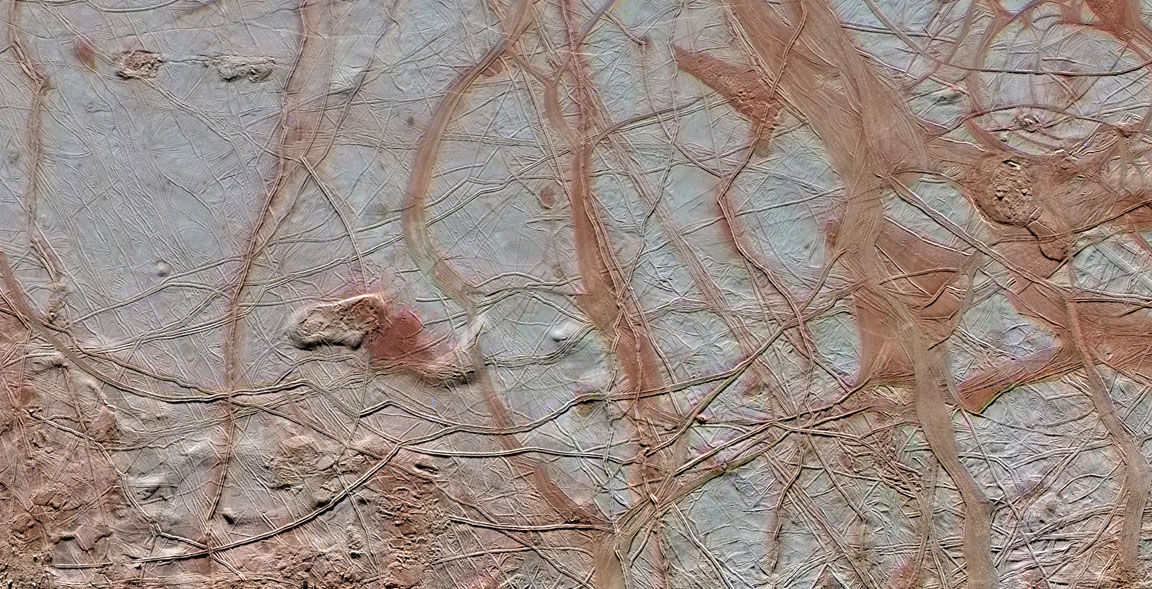
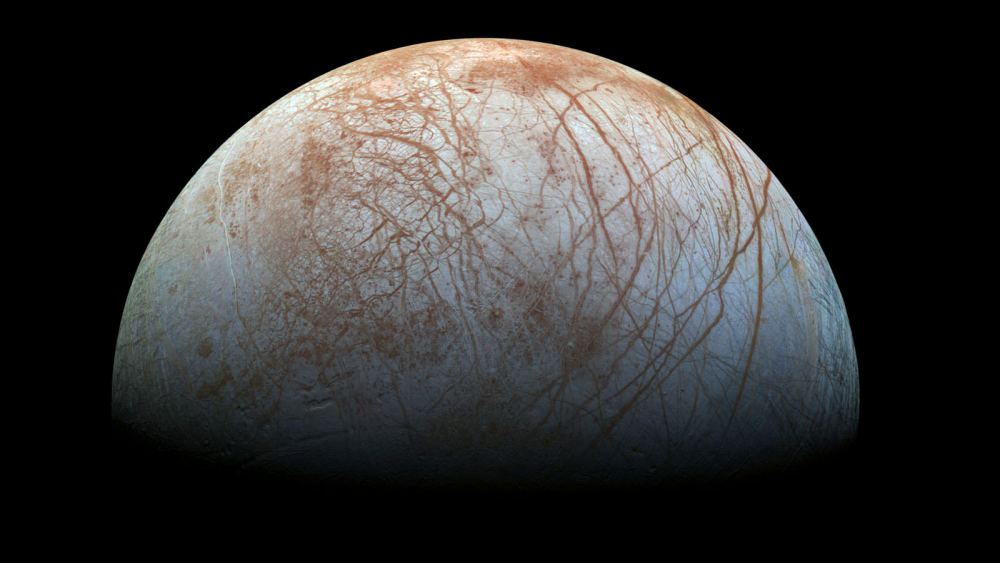
This became the basis of the Fermi Paradox, which refers to the disparity between high probability estimates for the existence of extraterrestrial intelligence (ETI) and the apparent lack of evidence. Since Fermi’s time, there have been several proposed resolutions to his question, which include the possibility that Oceans Worlds (and not rocky planets) might be the best candidates for finding life.
Continue reading “Beyond “Fermi’s Paradox” XIII: What is the “Ocean Worlds” Hypothesis?”