When you have a Mars mission that is designed to search for life or life-friendly environments, it would be several shades of awkward if something biological was discovered — and it ended up being an Earth microbe that clung on for the ride. Beyond that, there’s the worry that an Earth microbe could contaminate the planet’s environment, altering or perhaps wiping out anything that was living there.
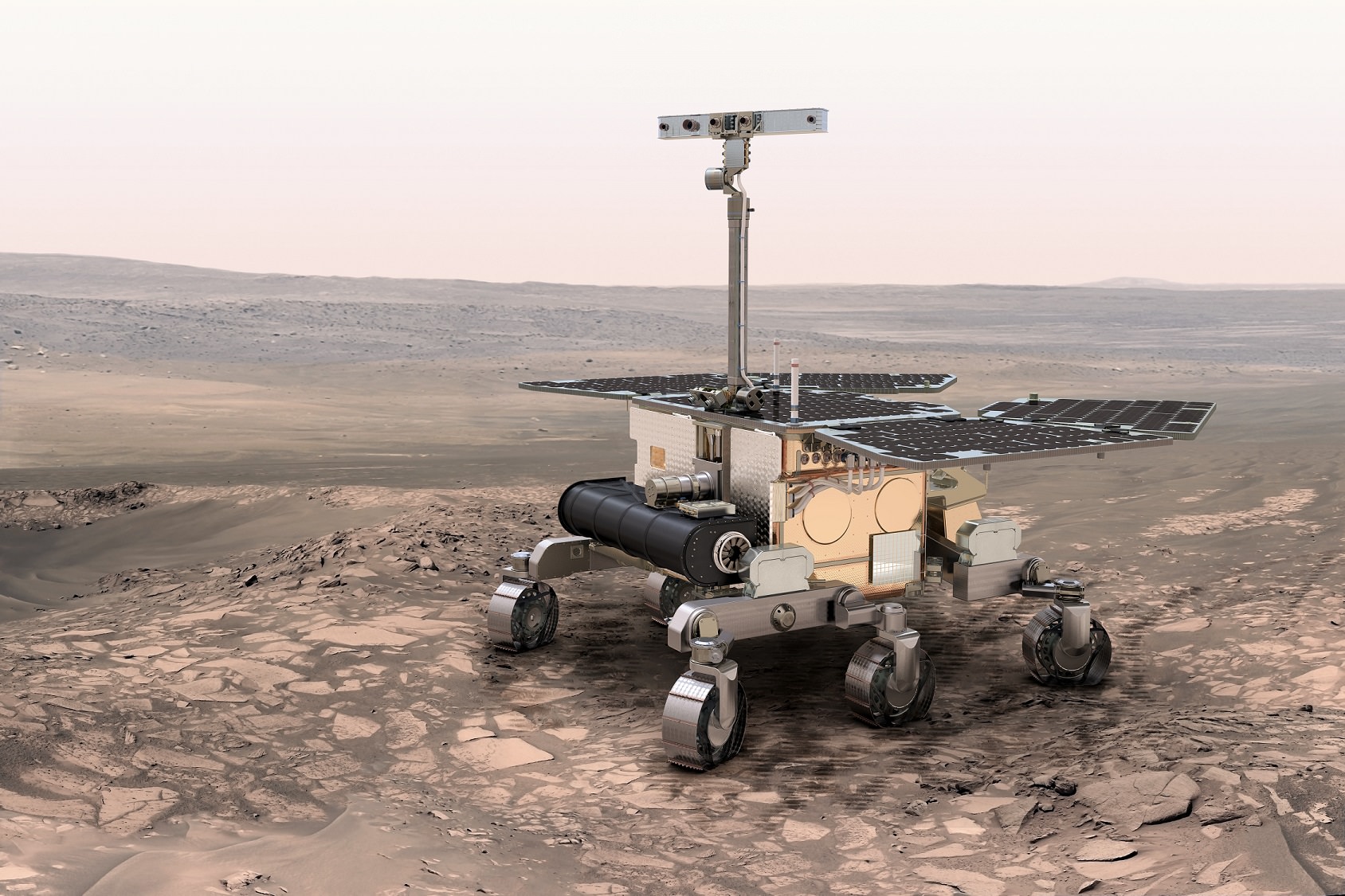
A recent European Space Agency post highlighted that agency’s efforts to keep Mars safe from its forthcoming ExoMars missions in 2016 or 2018. (And it also should be noted that NASA has its own planetary protection protocols, as well as other agencies.)
“We have a long-term programme at ESA – and also NASA – to regularly monitor and evaluate biological contamination in cleanrooms and on certain type of spacecraft,” stated Gerhard Kminek, ESA’s planetary protection officer. “The aim,” he added, “is to quantify the amount of biological contamination, to determine its diversity – finding out what is there using gene sequence analysis, and to provide long-term cold storage of selected samples.”
The process isn’t perfect, ESA admits, but the biological contamination that these scrutinized missions have is extraordinarily low compared to other Earthly manufacturing processes. There is, in fact, an obligation on the part of space-faring nations to keep planets safe if they signed on to the United Nations Outer Space Treaty. (That said, enforcement is a tricky legal issue as there is no international court for this sort of thing and that would make it hard to levy penalties.)

Spacefaring nations have international standards for biological contamination limits, and they also must monitor the “impact probability” of an orbital spacecraft smacking into the planet or moon below when they do maneuvers. Sometimes this means that spacecraft are deliberately crashed in one spot to prevent contamination elsewhere. A famous example is the Galileo mission to Jupiter, which was thrown into the giant planet in 2003 so it wouldn’t accidentally hit the ice-covered Europa moon.
Moving forward to ExoMars — the Mars orbiting and landing missions of 2016 and 2018 — ESA plans to perform about 4,500 samplings of each spacecraft to monitor biological contamination. This estimate came from the number performed at NASA on the Curiosity rover, which is trundling around Mars right now. Changes in processing, though, mean the ESA checks will take less time (presumably making it less expensive.)
For the curious, yes, planetary protection protocols would also apply during a “sample return” mission where soil or other samples are sent back to Earth. While that’s a little ways off, ESA also elaborated on the procedures it takes to keep spacecraft it creates safe from contamination.
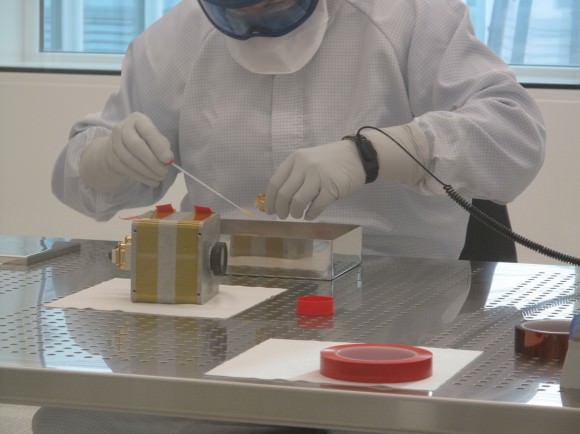

“Samples are acquired in various ways: air samplers collect a certain amount of air on a filter, while wipes dampened with ultra-pure water are run across space hardware or cleanroom surfaces. Swabs are used to sample smaller items such as payloads or electronics,” ESA stated.
“To quantify the biological contamination, the samples are then filtered onto culture plates and incubated for between seven hours and three days depending on the specific method used, to see how much turns up. Statistical analysis is used to assess the overall cleanroom or flight hardware ‘bioburden’, and check whether it falls within the required standard or if further measures are needed to reduce it.”
Sometimes a hardy survivor is found, which is scientifically interesting because investigators want to know how it made it. ESA has a database of these microbes, and NASA has records as well. In November, the agencies announced a new bacterium, Tersicoccus phoenicis, that so far has only been found in “cleanrooms” for NASA’s Mars Phoenix lander (near Orlando, Florida) and ESA’s Herschel and Planck observatories (in Kourou, French Guiana).
Source: ESA