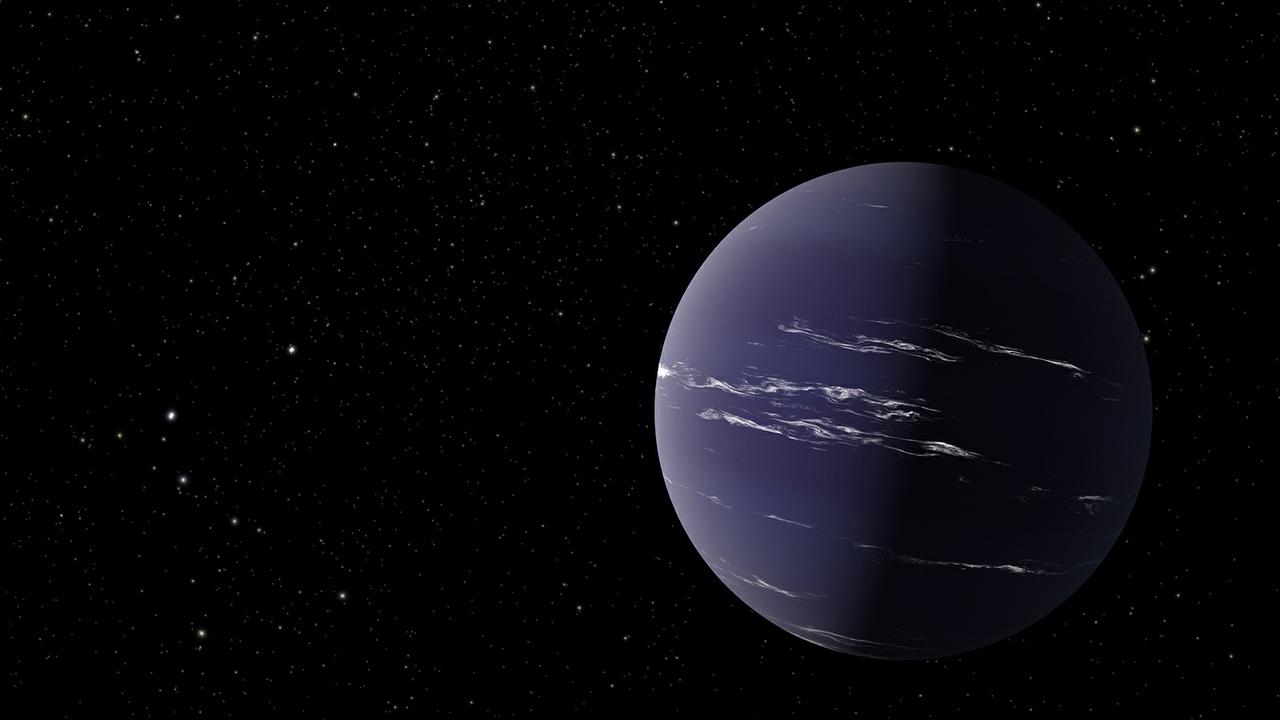
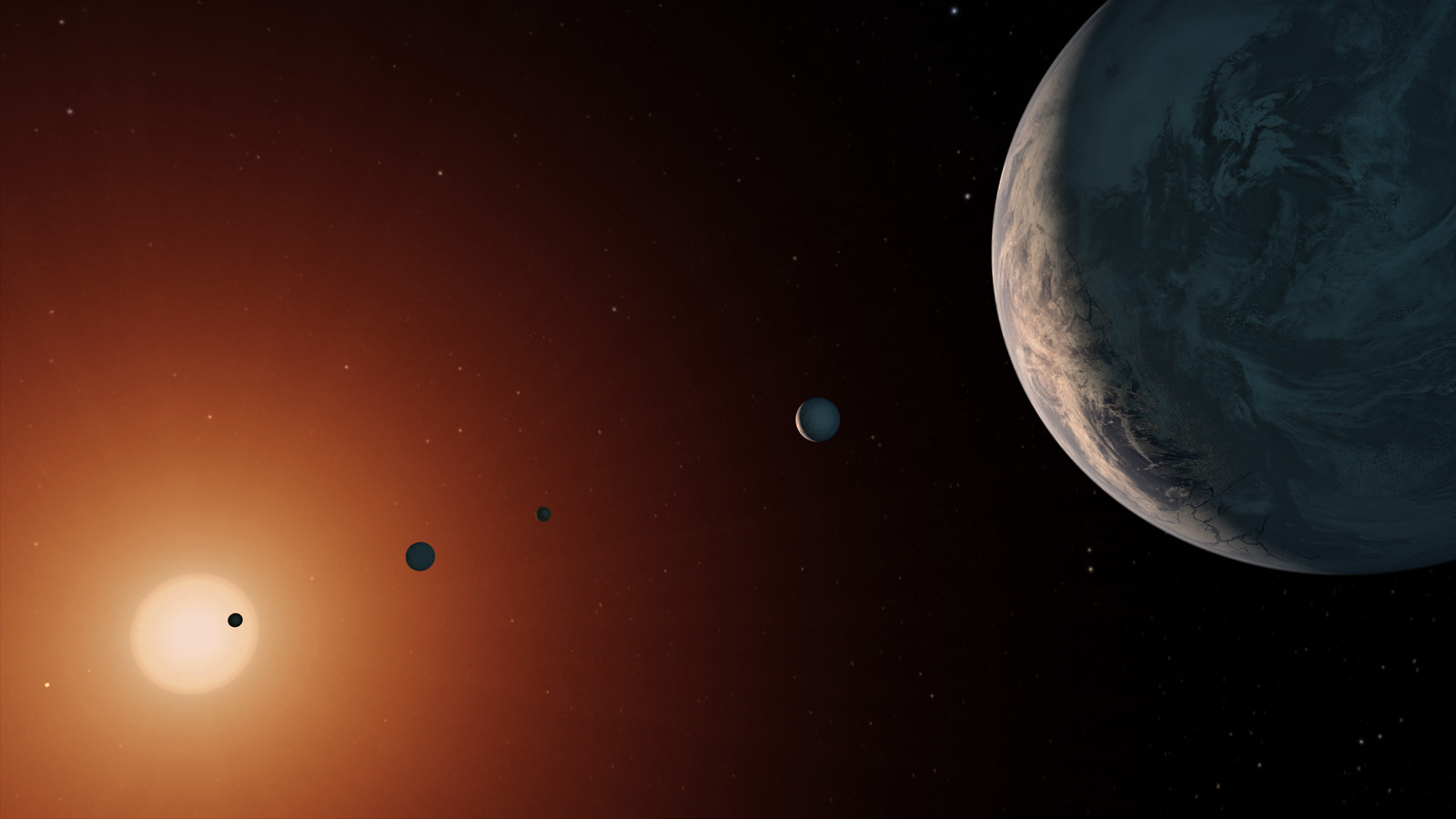
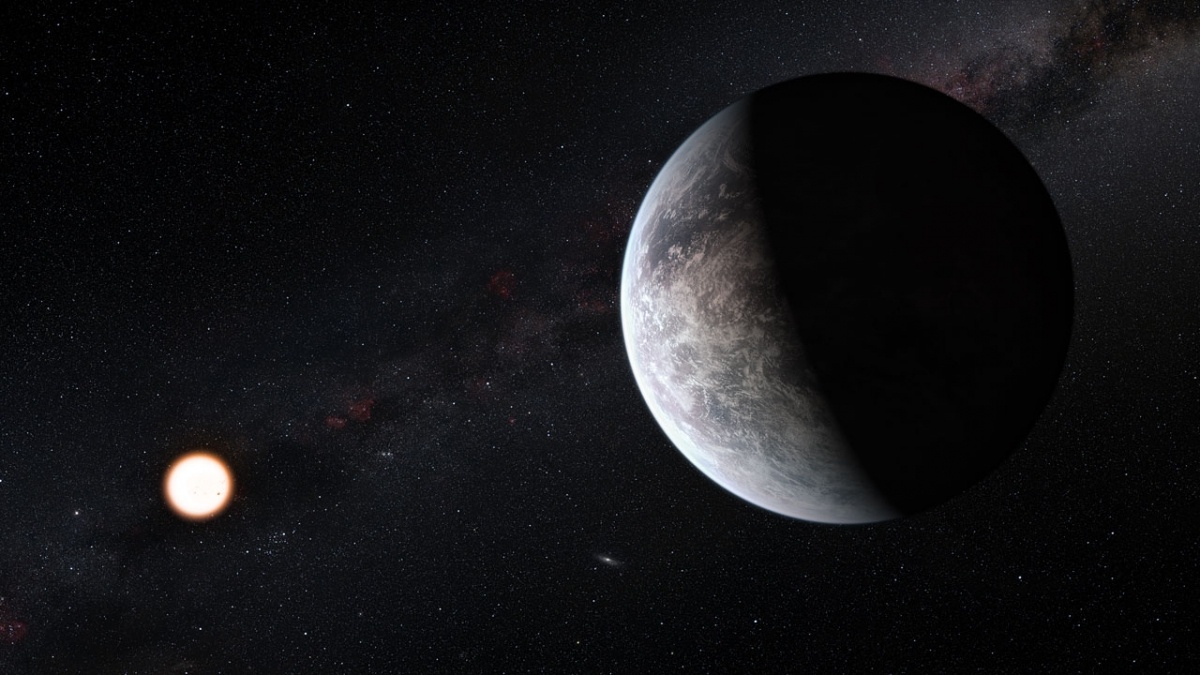
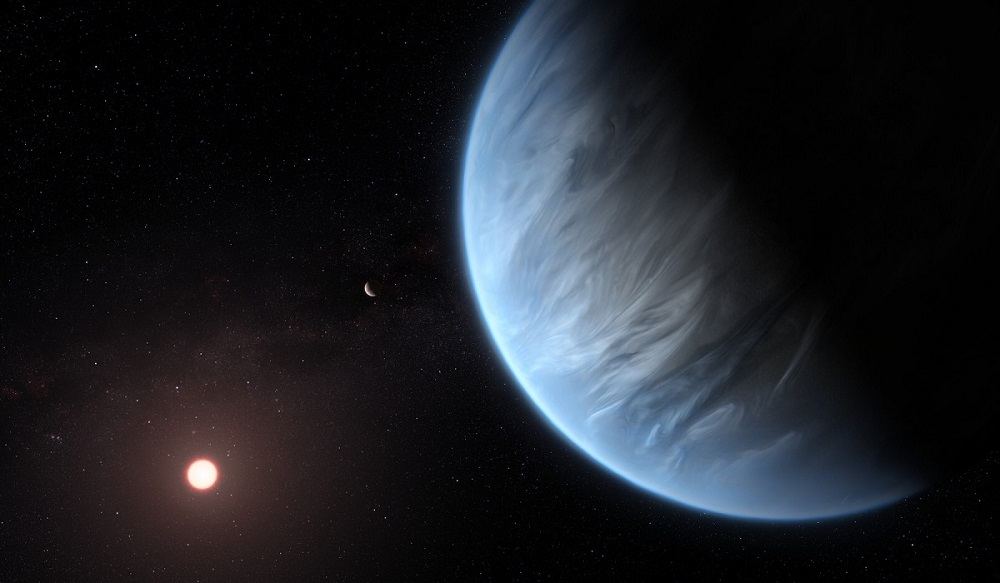
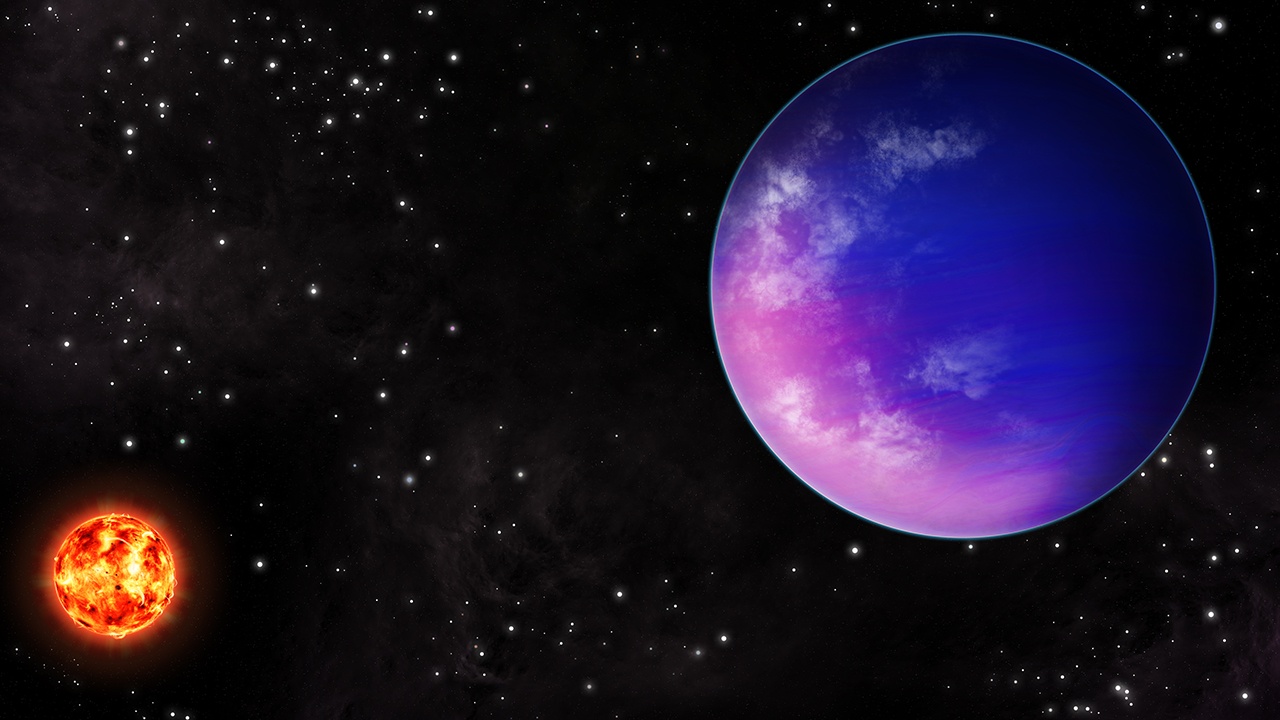
TESS (Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite) has found a new planet, and the discovery of this sub-Neptune exoplanet has scientists excited about atmospheres. The combination of the planet’s size, its thick atmosphere, and its orbit around a small M-class star close to Earth provides researchers with an opportunity to learn more about exoplanet atmospheres. We’re getting better and better at finding exoplanets, and studying their atmospheres is the next step in understanding them as a whole.
Continue reading “Astronomers Have Found the Perfect Exoplanet to Study Another World’s Atmosphere”Astronomers Have Found the Perfect Exoplanet to Study Another World’s Atmosphere