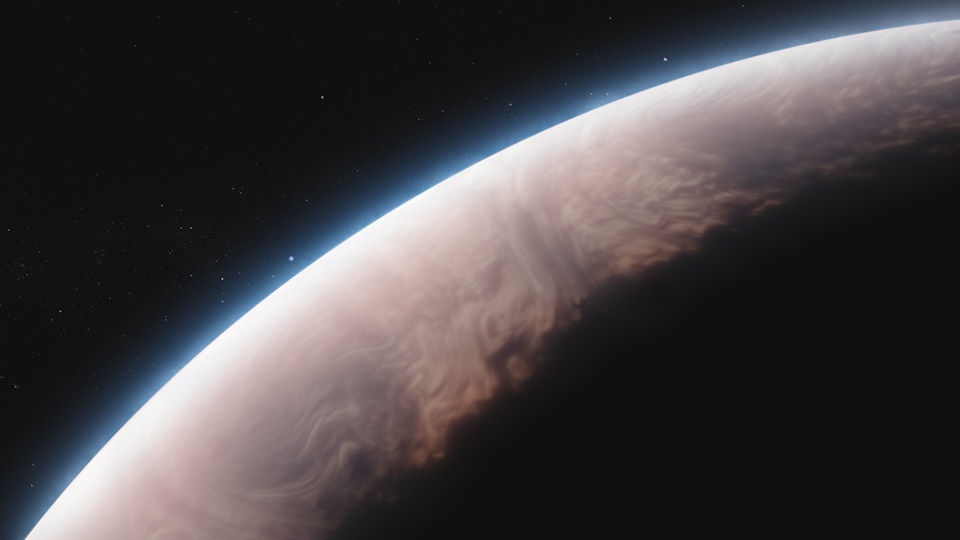
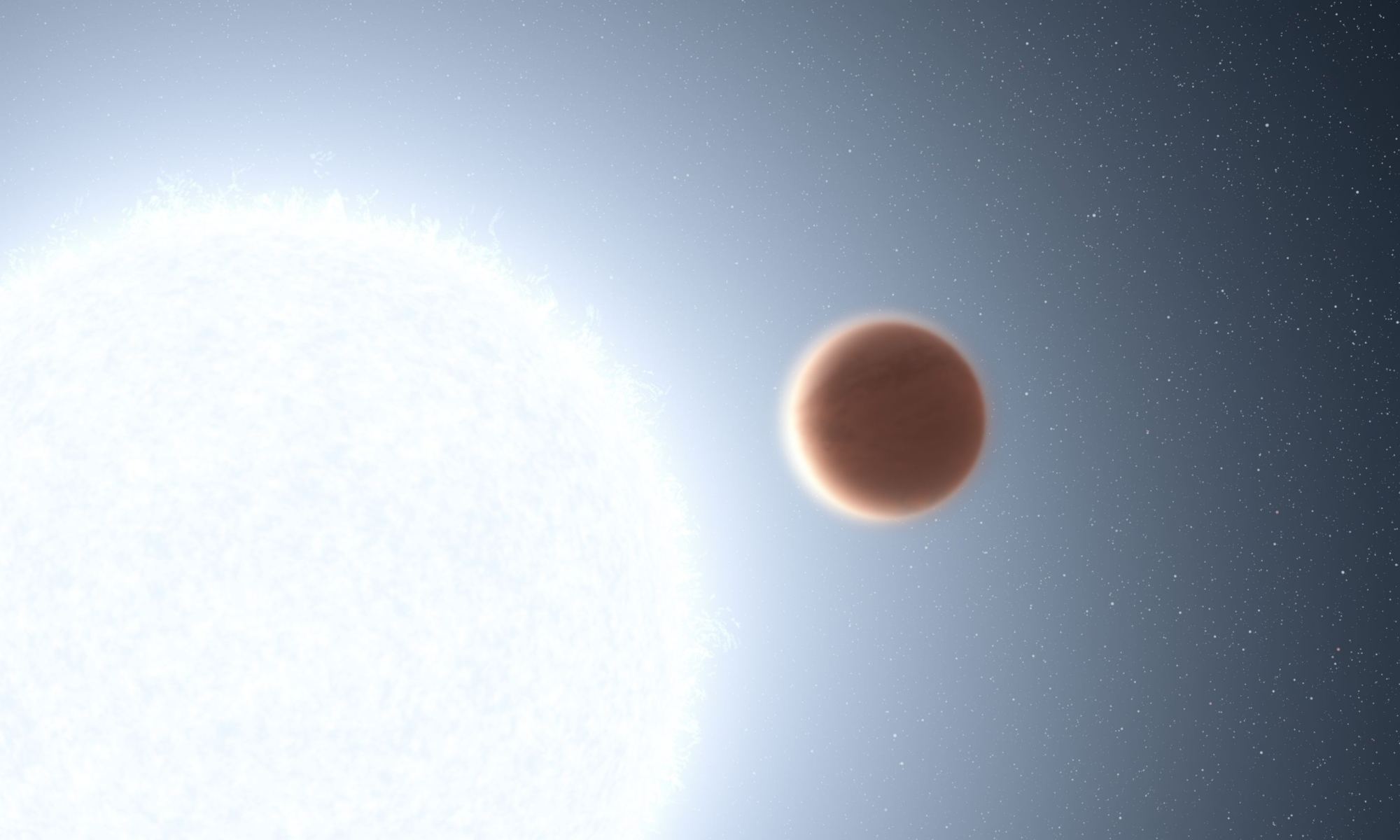
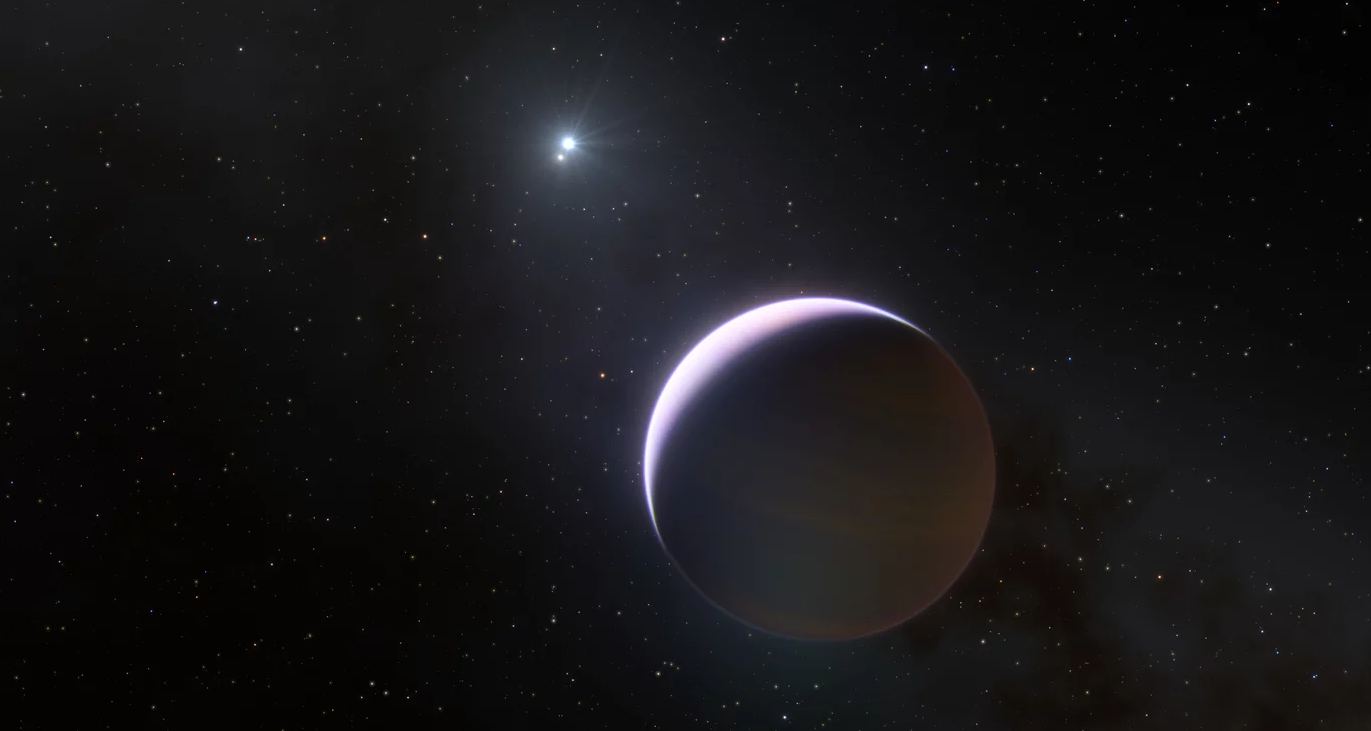
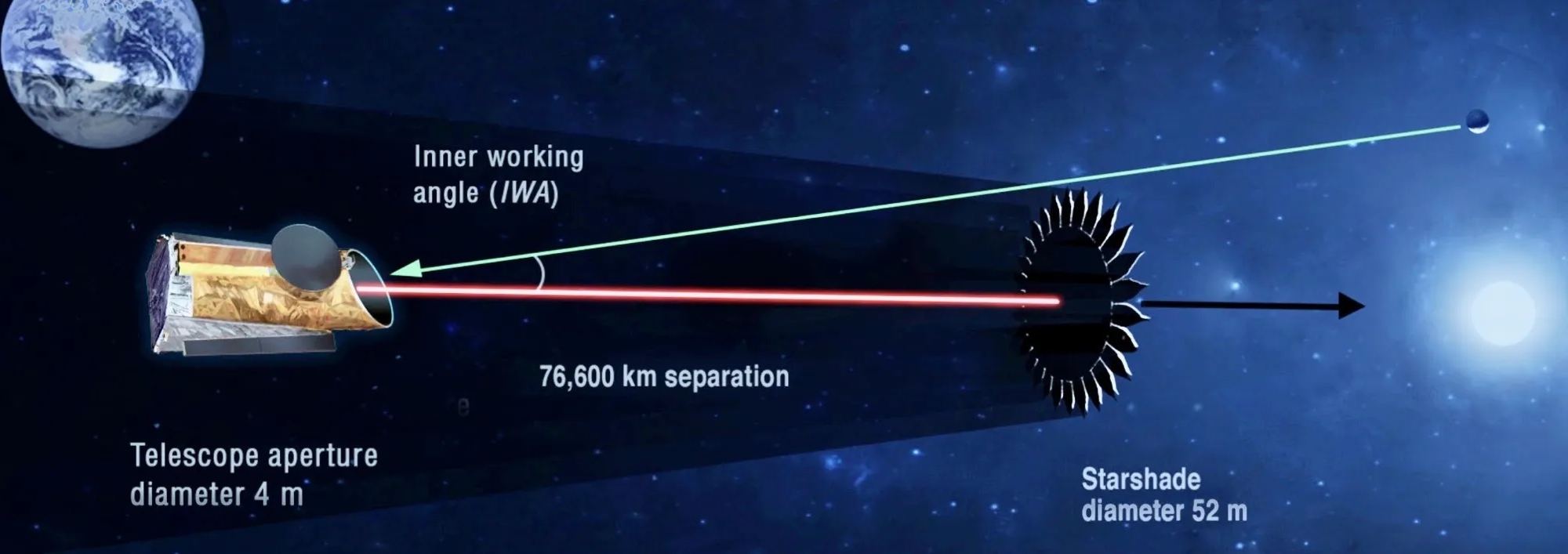
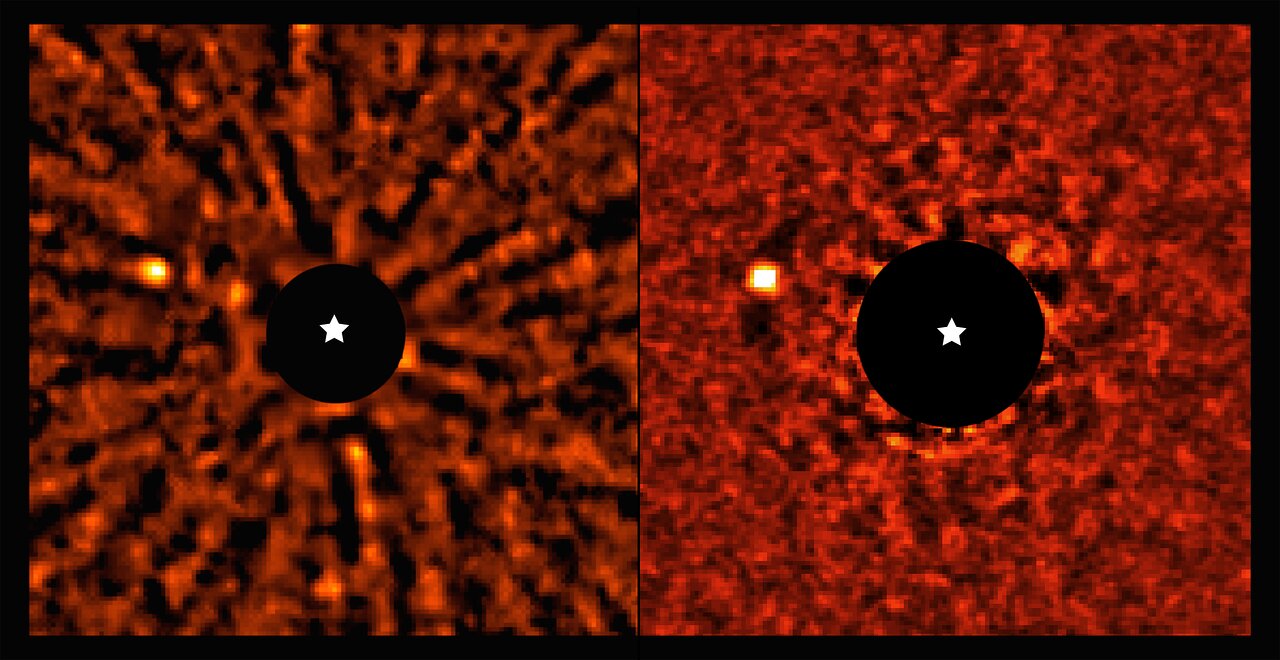
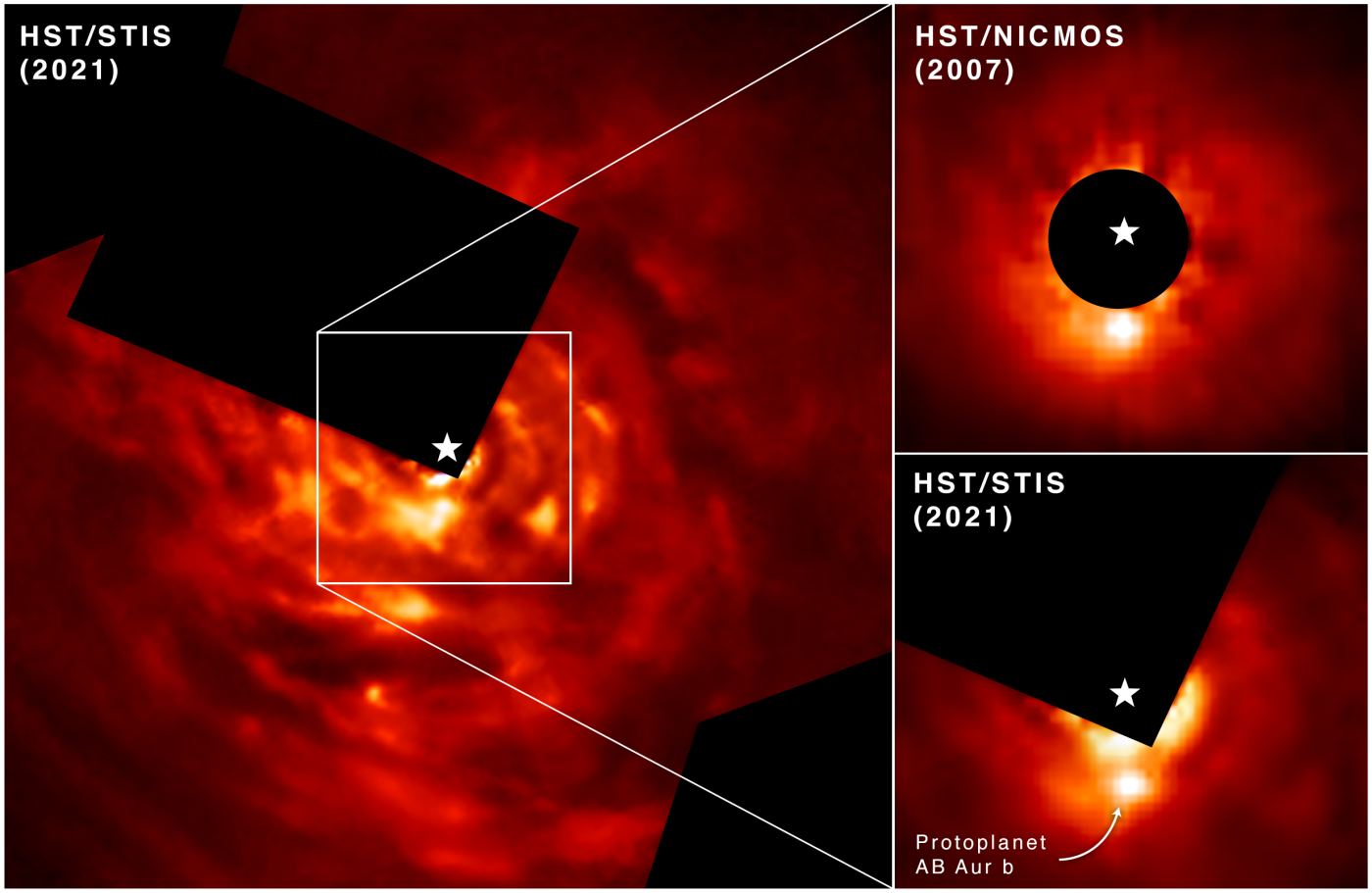
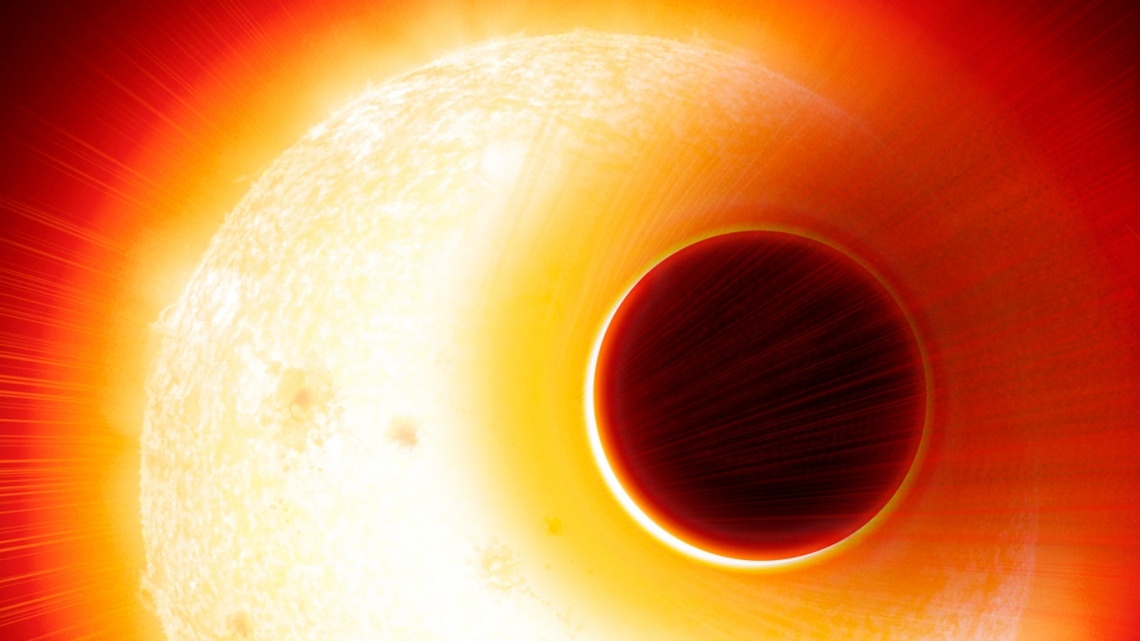
A pair of recent studies conduct in-depth analyses of Jupiter-sized exoplanets, also known as Exo-Jupiters, and were published in Nature Communications and The Astronomical Journal, respectively. The study published in Nature Communications was conducted by an international team of researchers and examines how Exo-Jupiters could be more common than previously thought, while the study published in The Astronomical Journal was conducted by one researcher and examines exoplanetary system, HD 141399, and how it is comprised entirely of Exo-Jupiters with no additional planets.
Continue reading “Exo-Jupiters’ Commonality and Exclusivity Highlighted in Two New Studies”Exo-Jupiters’ Commonality and Exclusivity Highlighted in Two New Studies