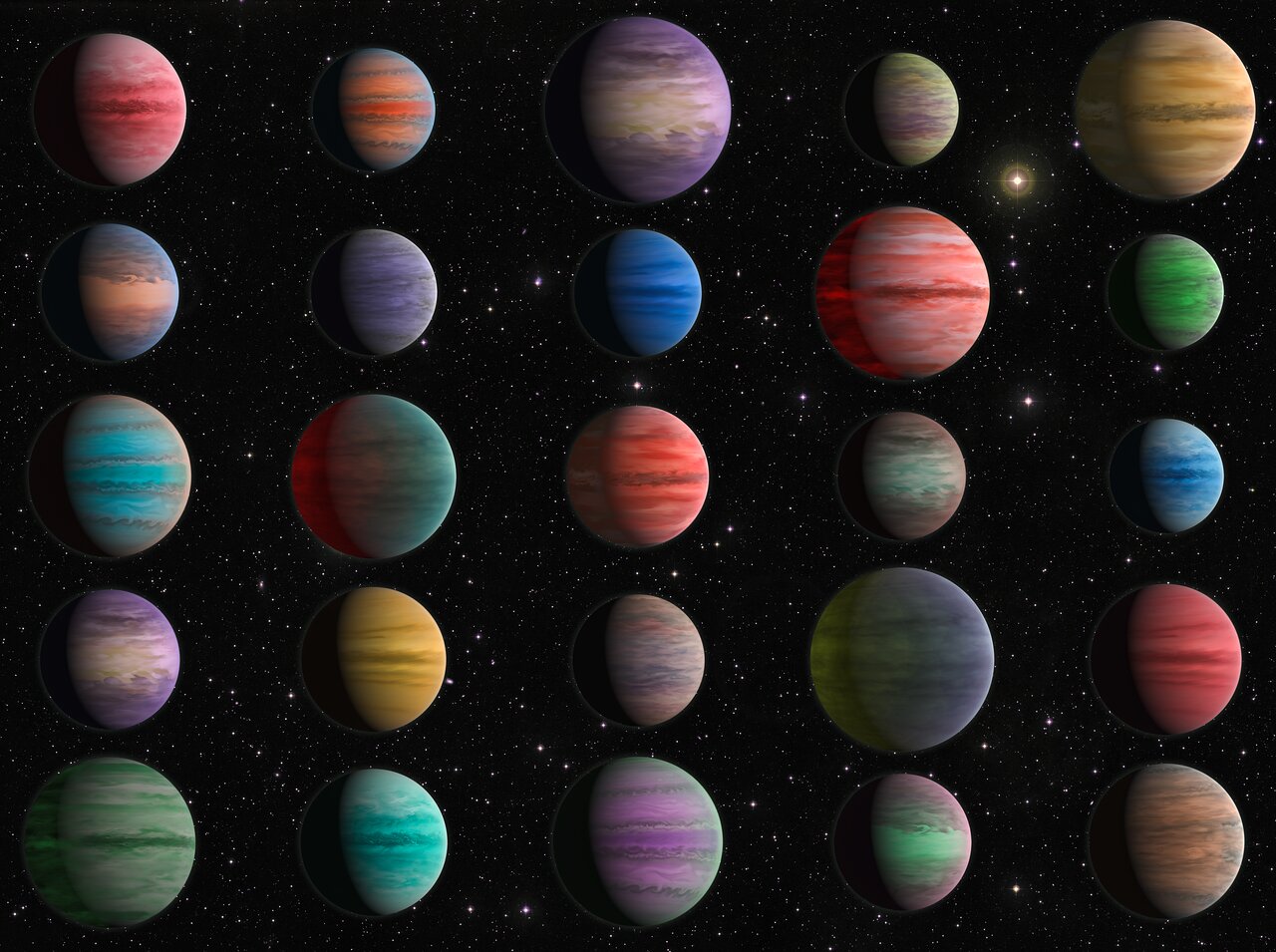
Hot Jupiters are giant exoplanets – even more massive than Jupiter – but they orbit closer to their star than Mercury. When they were first discovered, hot Jupiters were considered oddballs, since we don’t have anything like them in our own Solar System. But they appear to be common in our galaxy. As exoplanets go, they are fairly easy to detect, but because we don’t have up-close experience with them, there are still many unknowns.
A new study used archival data from the Hubble and Spitzer space telescopes to study this class of giant gas exoplanets, and undertook one of the largest surveys ever of exoplanet atmospheres. The researchers said they employed high performance computers to analyses the atmospheres of 25 hot Jupiters using data from about 1,000 hours of telescope observations. Their findings, published in the Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, help to answer several long-standing questions about hot Jupiters.
Continue reading “Hubble has Characterized 25 Hot Jupiters. Here’s What we Know so far”