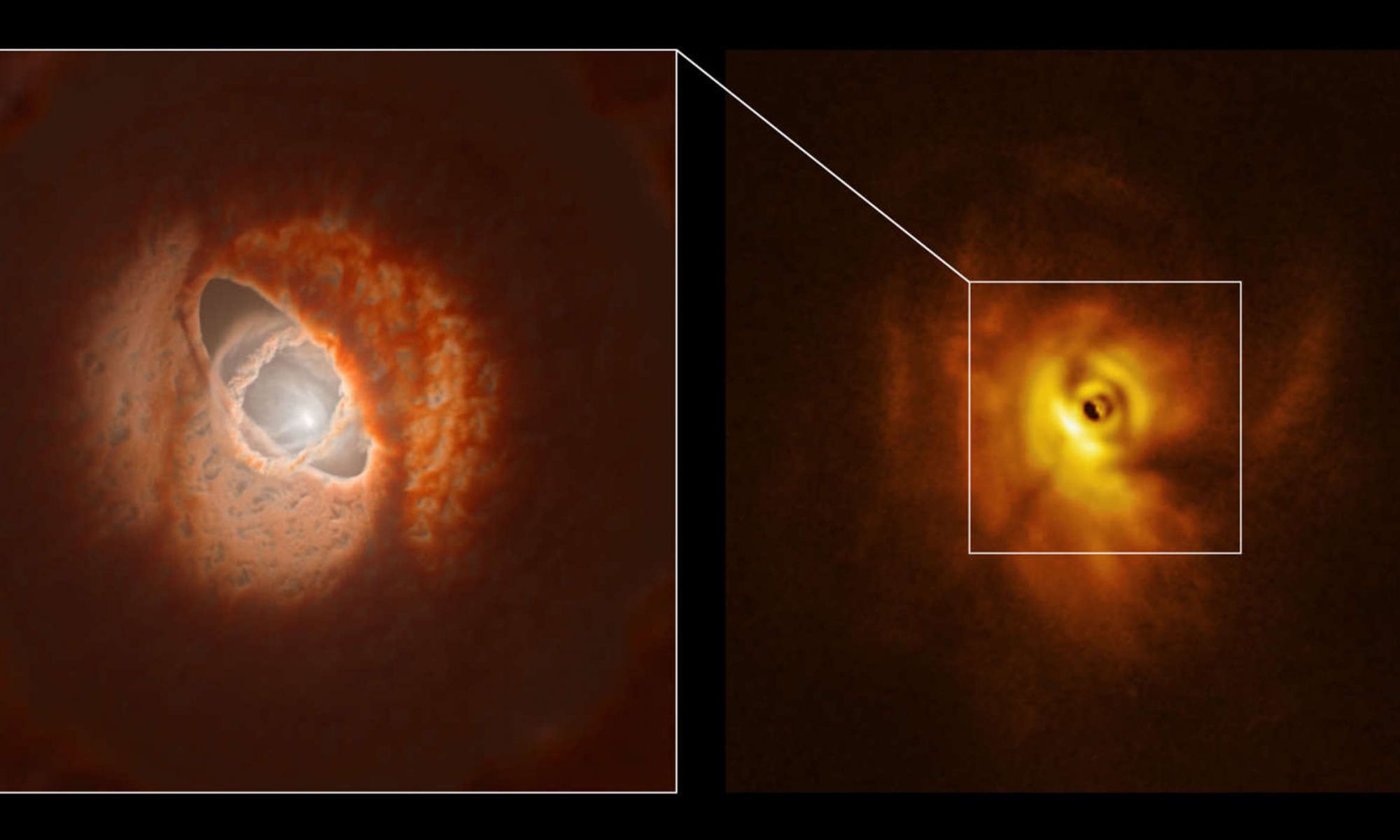
A lot has to go right for a planet to support life. Some of the circumstances that allow life to bloom on any given planet stem from the planet’s initial formation. Here on Earth, circumstances meant Earth’s crust contains about 5% iron by weight.
A new paper looks at how Earth’s iron diminished over time and how that shaped the development of complex life here on Earth. Is iron necessary for complex life to develop on other worlds?
Continue reading “Life on Earth Needed Iron. Will it be the Same on Other Worlds?”