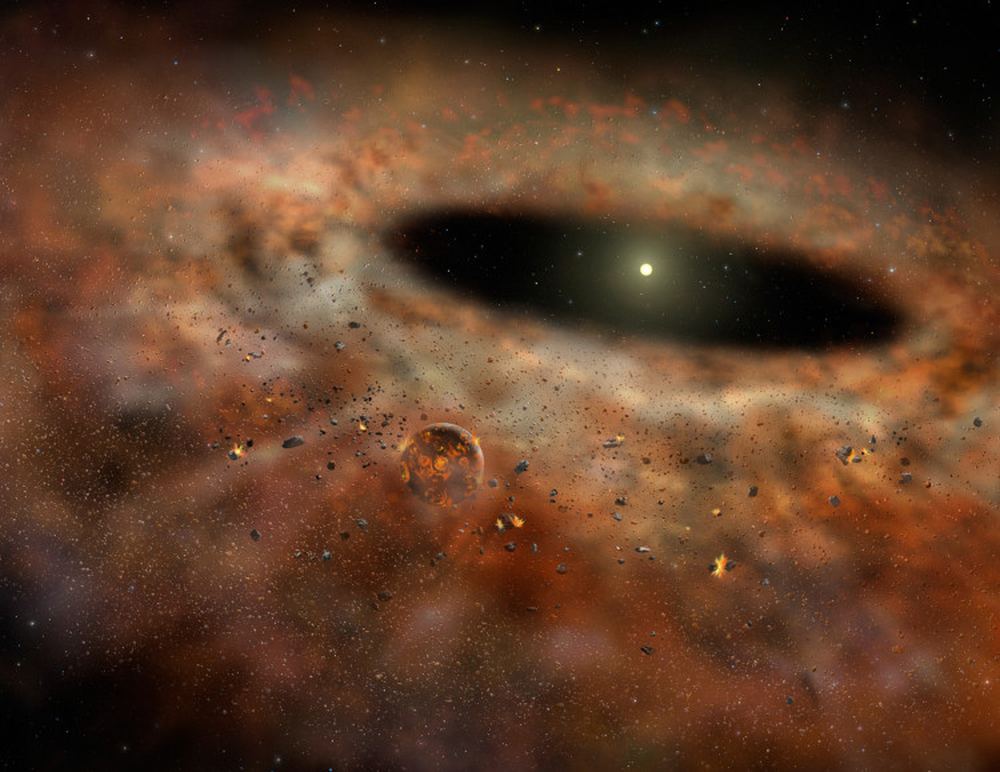
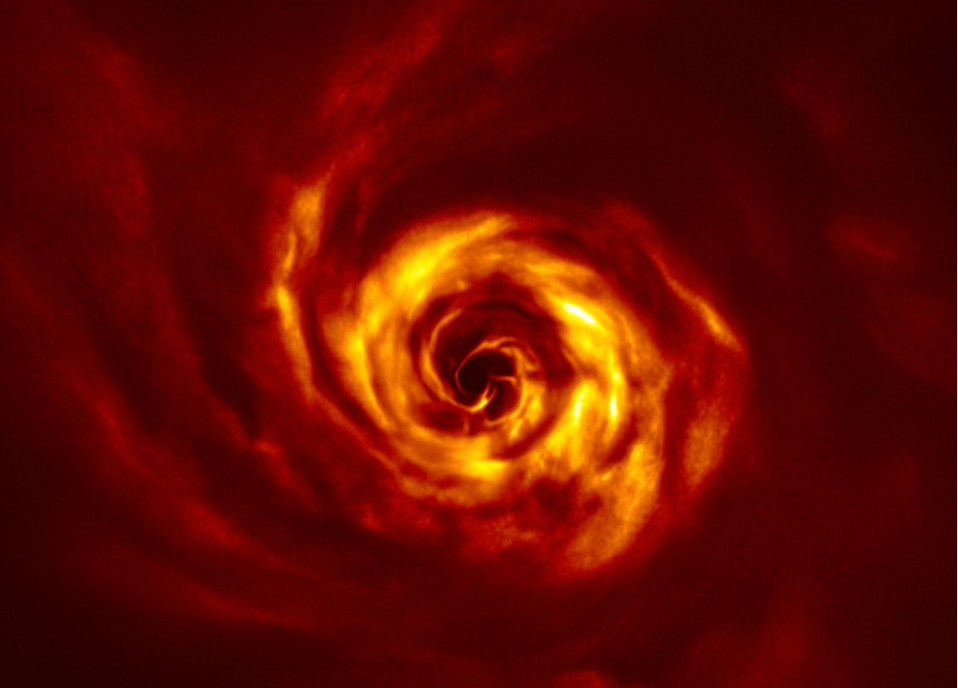
Astronomers like to observe young planets forming in circumstellar debris disks, the rotating rings of material around young stars. But when they measure the amount of material in those disks, they don’t contain enough material to form large planets. That discrepancy has puzzled astronomers.
The answer might come down to timing.
A new study suggests that planets form much quicker than astronomers think.
Continue reading “Planets Form in Just a Few Hundred Thousand Years”