Astronomers working with TESS (Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite) data have found a planet where it shouldn’t be: in the space recently filled by its host star when it was a red giant.
Continue reading “It Seems Impossible, But Somehow This Planet Survived its Star’s Red Giant Phase”Astronomers See the Wreckage from a Collision Between Exoplanets
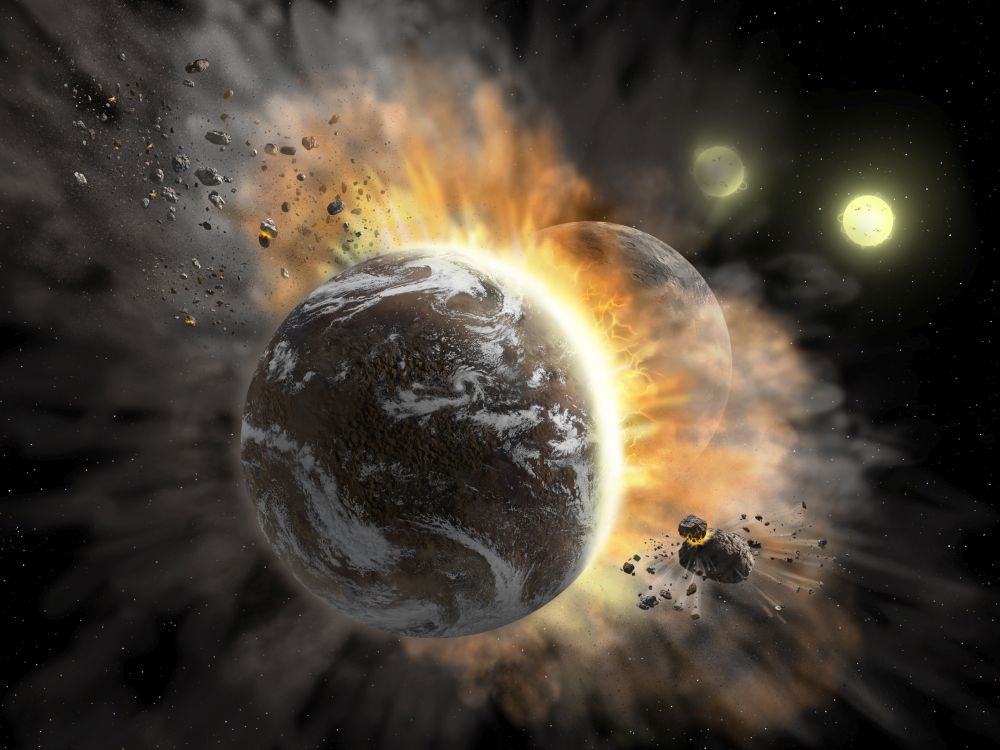

The history of our Solar System is punctuated with collisions. Collisions helped create the terrestrial planets and end the reign of the dinosaurs. And a massive collision between Earth and an ancient body named Theia likely created the Moon.
Now astronomers have found of evidence of a collision between two exoplanets in a distant solar system.
Continue reading “Astronomers See the Wreckage from a Collision Between Exoplanets”Planet Sizes Matter for Habitability Too.
In order to be considered habitable, a planet needs to have liquid water. Cells, the smallest unit of life, need water to carry out their functions. For liquid water to exist, the temperature of the planet needs to be right. But how about the size of the planet?
Without sufficient mass a planet won’t have enough gravity to hold onto its water. A new study tries to understand how size affects the ability of a planet to hold onto its water, and as a result, its habitability.
Continue reading “Planet Sizes Matter for Habitability Too.”A Red Dwarf Star Has a Jupiter-Like Planet. So Massive it Shouldn’t Exist, and Yet, There It Is
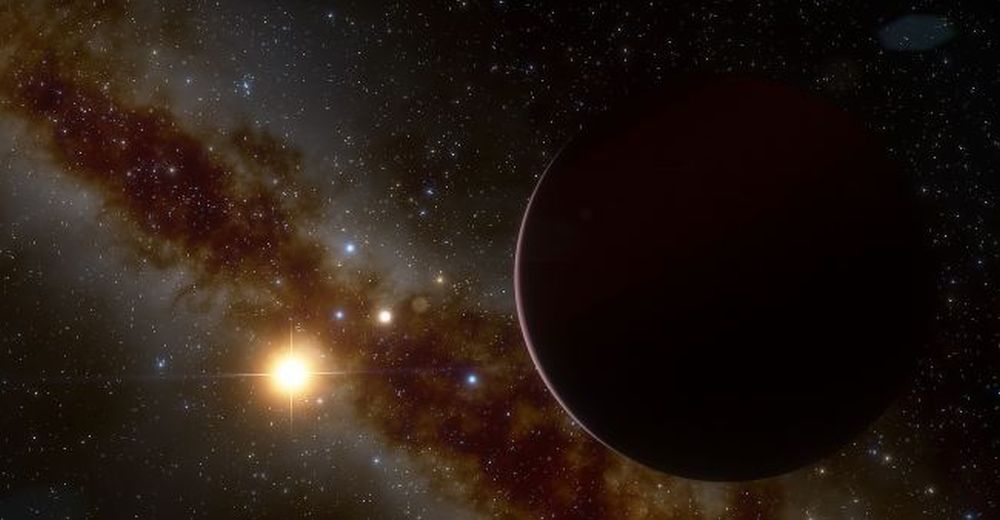

Thanks to the Kepler mission and other efforts to find exoplanets, we’ve learned a lot about the exoplanet population. We know that we’re likely to find super-Earths and Neptune-mass exoplanets orbiting low-mass stars, while larger planets are found around more massive stars. This lines up well with the core accretion theory of planetary formation.
But not all of our observations comply with that theory. The discovery of a Jupiter-like planet orbiting a small red dwarf means our understanding of planetary formation might not be as clear as we thought. A second theory of planetary formation, called the disk instability theory, might explain this surprising discovery.
Continue reading “A Red Dwarf Star Has a Jupiter-Like Planet. So Massive it Shouldn’t Exist, and Yet, There It Is”Better Than Earth? Are There Superhabitable Worlds In The Milky Way?
I’ve said many times in the past that the Earth is the best planet in the Universe. No matter where we go, we’ll never find a planet that’s a better home to Earth life than Earth. Of course, that’s because we, and all other Earth life evolved in this environment. Evolution adapted us to this planet, and it’s unlikely we could ever find another planet this good for us.
However, is it the best planet? Are there places in the Universe which might have the conditions for more diversity of life?
Continue reading “Better Than Earth? Are There Superhabitable Worlds In The Milky Way?”Water Discovered in the Atmosphere of an Exoplanet in the Habitable zone. It Might Be Rain

Astronomers using the Hubble space telescope have discovered water in the atmosphere of an exoplanet in its star’s habitable zone. If confirmed, it will be the first time we’ve detected water—a critical ingredient for life as we know it—on an exoplanet. The water was detected as vapour in the atmosphere, but the temperature of the planet means it could sustain liquid water on its surface, if it’s rocky.
Continue reading “Water Discovered in the Atmosphere of an Exoplanet in the Habitable zone. It Might Be Rain”There Could be Planets Out There Which are Even More Habitable than Earth
When searching for potentially habitable exoplanets, scientists are forced to take the low-hanging fruit approach. Since Earth is the only planet we know of that is capable of supporting life, this search basically comes down to looking for planets that are “Earth-like”. But what if Earth is not the meter stick for habitability that we all tend to think it is?
That was the subject of a keynote lecture that was recently made at the Goldschmidt Geochemistry Congress, which took place from Aug. 18th to 23rd, in Barcelona, Spain. Here, a team of NASA-supported researchers explained how an examination of what goes into defining habitable zones (HZs) shows that some exoplanets may have better conditions for life to thrive than Earth itself has.
Continue reading “There Could be Planets Out There Which are Even More Habitable than Earth”Earth is an Exoplanet to Aliens. This is What They’d See
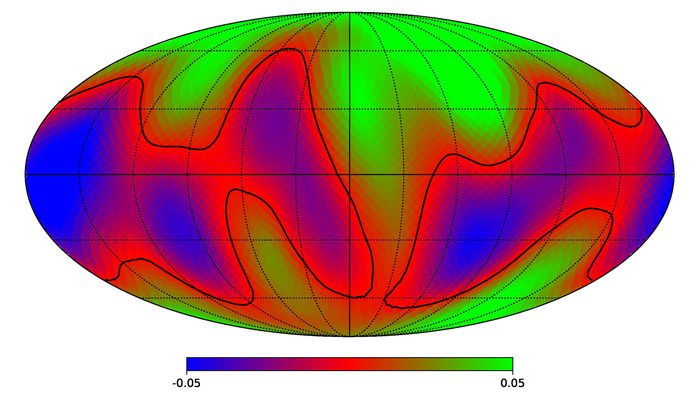
The study of exoplanets has matured considerably in the last ten years. During this time, the majority of the over 4000 exoplanets that are currently known to us were discovered. It was also during this time that the process has started to shift from the process of discovery to characterization. What’s more, next-generation instruments will allow for studies that will reveal a great deal about the surfaces and atmospheres of exoplanets.
This naturally raises the question: what would a sufficiently-advanced species see if they were studying our planet? Using multi-wavelength data of Earth, a team of Caltech scientists was able to construct a map of what Earth would look like to distant alien observers. Aside from addressing the itch of curiosity, this study could also help astronomers reconstruct the surface features of “Earth-like” exoplanets in the future.
Continue reading “Earth is an Exoplanet to Aliens. This is What They’d See”One Year, Almost 1,000 Planetary Candidates. An Update On TESS
NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet Survey Telescope launched back in April, 2018. After a few months of testing, it was ready to begin mapping the southern sky, searching for planets orbiting stars relatively nearby.
We’re just over a year into the mission now, and on July 18th, TESS has shifted its attention to the Northern Hemisphere, continuing the hunt for planets in the northern skies.
Continue reading “One Year, Almost 1,000 Planetary Candidates. An Update On TESS”Snowball Exoplanets Might Be Better for Life Than We Thought
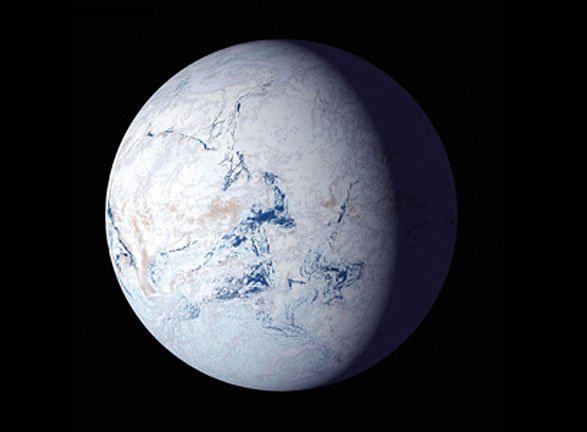

When astronomers discover a new exoplanet, one of the first considerations is if the planet is in the habitable zone, or outside of it. That label largely depends on whether or not the temperature of the planet allows liquid water. But of course it’s not that simple. A new study suggests that frozen, icy worlds with completely frozen oceans could actually have livable land areas that remain habitable.
The new study was published in the AGU’s Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets. It focuses on how CO2 cycles through a planet and how it affects the planet’s temperature. The title is “Habitable Snowballs: Temperate Land Conditions, Liquid Water, and Implications for CO2 Weathering.”
Continue reading “Snowball Exoplanets Might Be Better for Life Than We Thought”