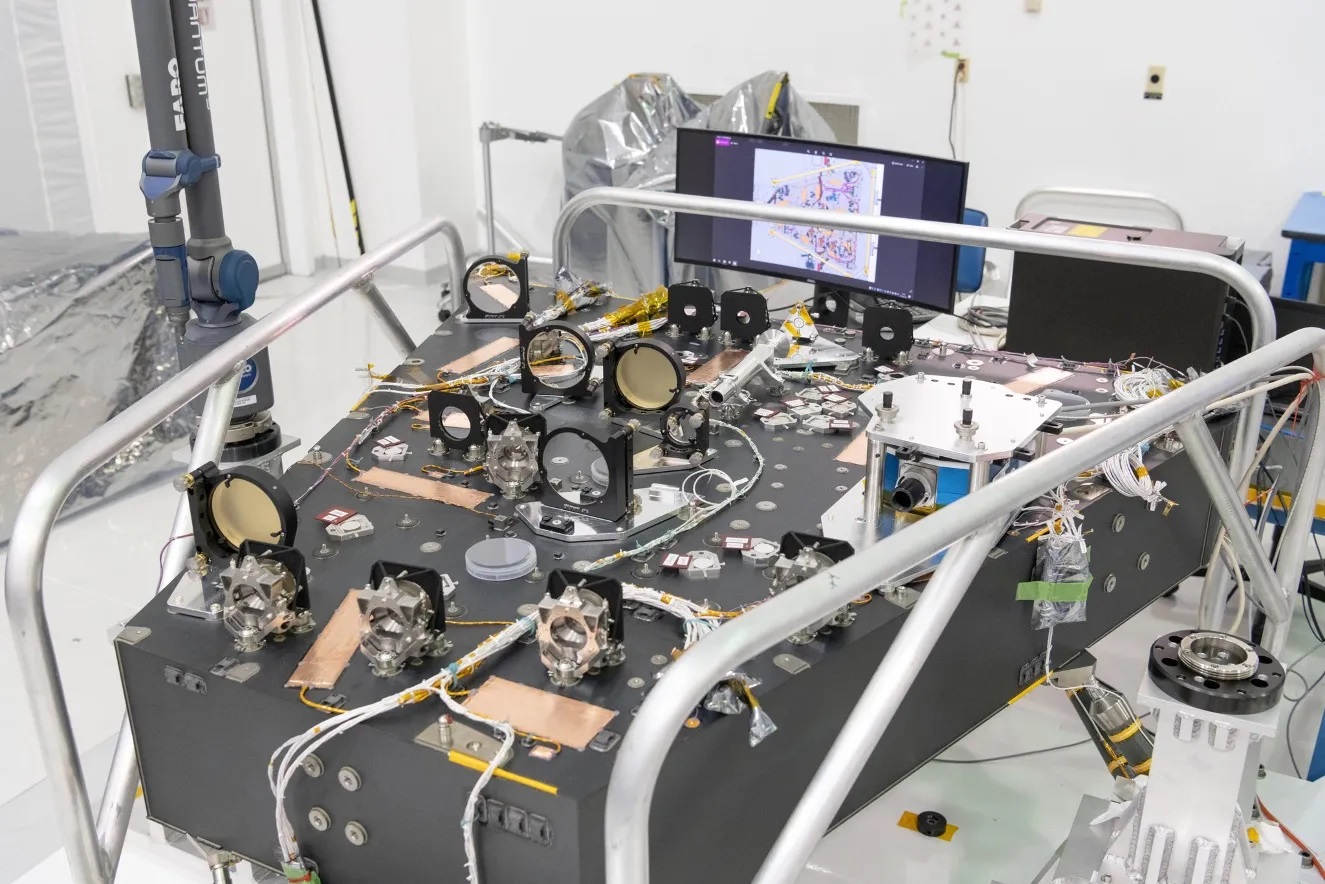
Observing distant objects is no easy task, thanks to our planet’s thick and fluffy atmosphere. As light passes through the upper reaches of our atmosphere, it is refracted and distorted, making it much harder to discern objects at cosmological distances (billions of light years away) and small objects in adjacent star systems like exoplanets. For astronomers, there are only two ways to overcome this problem: send telescopes to space or equip telescopes with mirrors that can adjust to compensate for atmospheric distortion.
Since 1970, NASA and the ESA have launched more than 90 space telescopes into orbit, and 29 of these are still active, so it’s safe to say we’ve got that covered! But in the coming years, a growing number of ground-based telescopes will incorporate adaptive optics (AOs) that will allow them to perform cutting-edge astronomy. This includes the study of exoplanets, which next-generation telescopes will be able to observe directly using coronographs and self-adjusting mirrors. This will allow astronomers to obtain spectra directly from their atmospheres and characterize them to see if they are habitable.
Continue reading “Next Generation Space Telescopes Could Use Deformable Mirrors to Image Earth-Sized Worlds”