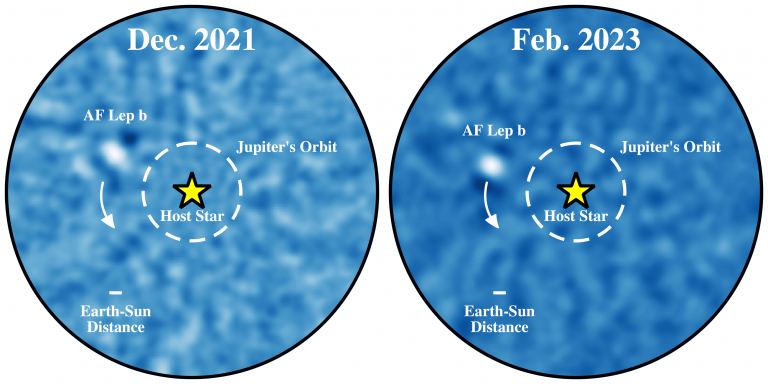
Thanks to the laws of physics, there are two basic rules about telescopes. The first is that the bigger your primary lens or mirror, the higher the resolution of your telescope. The second is that lenses and mirrors have to be curved to focus light into an image. So, if you want a space telescope sensitive enough to see the atmospheres of distant exoplanets, Your telescope is going to need a large curved mirror or lens. But neither of these things is technically true, as a newly proposed telescope design demonstrates.
Continue reading “Thin Flat Lenses Could Unleash a Revolution in Space Telescopes”Thin Flat Lenses Could Unleash a Revolution in Space Telescopes