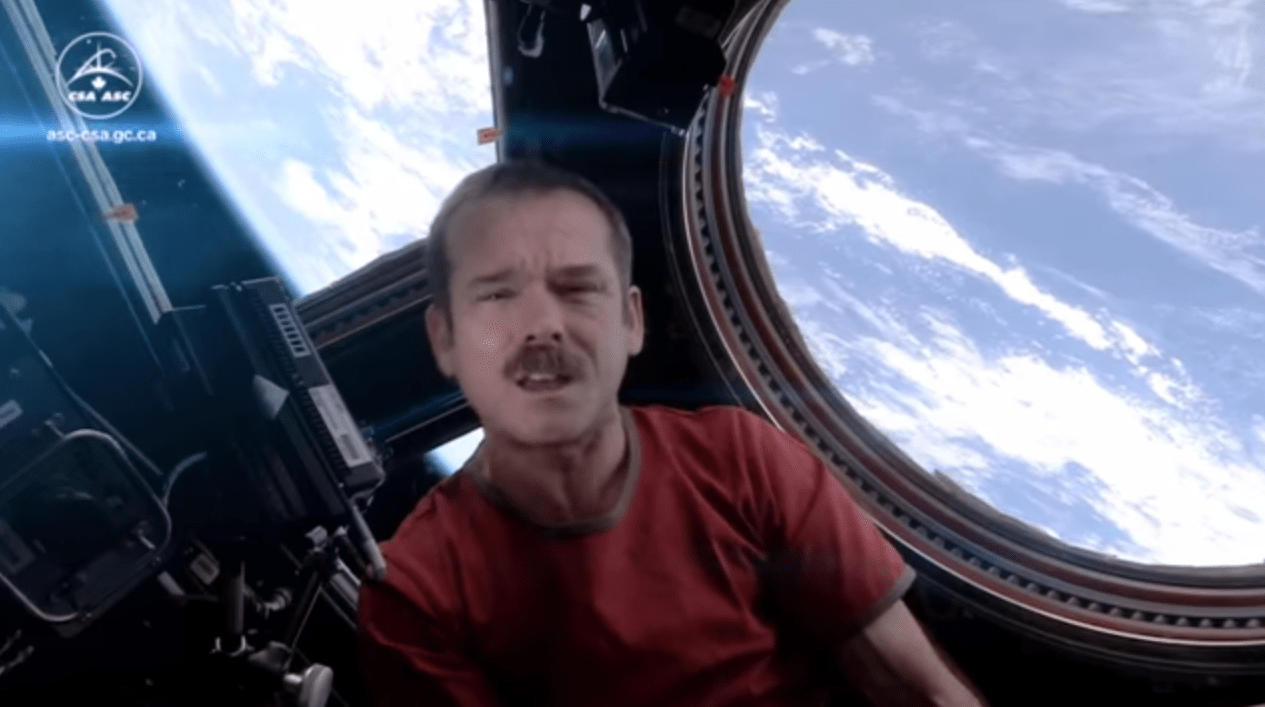
After one turn around the sun, it’s time for Chris Hadfield’s ultimate space music video to go to that great graveyard in the sky.
The astronaut tweeted earlier today (May 13) that singer David Bowie gave permission for Hadfield’s “Space Oddity” to be online for a year, and that the video is coming down today. So be sure to watch on YouTube above while you have the chance.
Update (6/25/14): A clarification on this story. The Ottawa Citizen newspaper clarified that it wasn’t David Bowie that only gave a year’s use of the song: “Space Oddity was the only one of more than 300 songs he has written and recorded for which he did not own or control the copyright. Mr. Bowie offered to have his people call the publisher and convey his strong support, but he had no ability to personally dictate any of the terms of the license or even require the publishers to issue one.”
Hadfield also tweeted today that ” Our Oddity will be back online soon.” We’ll repost it when it becomes available.
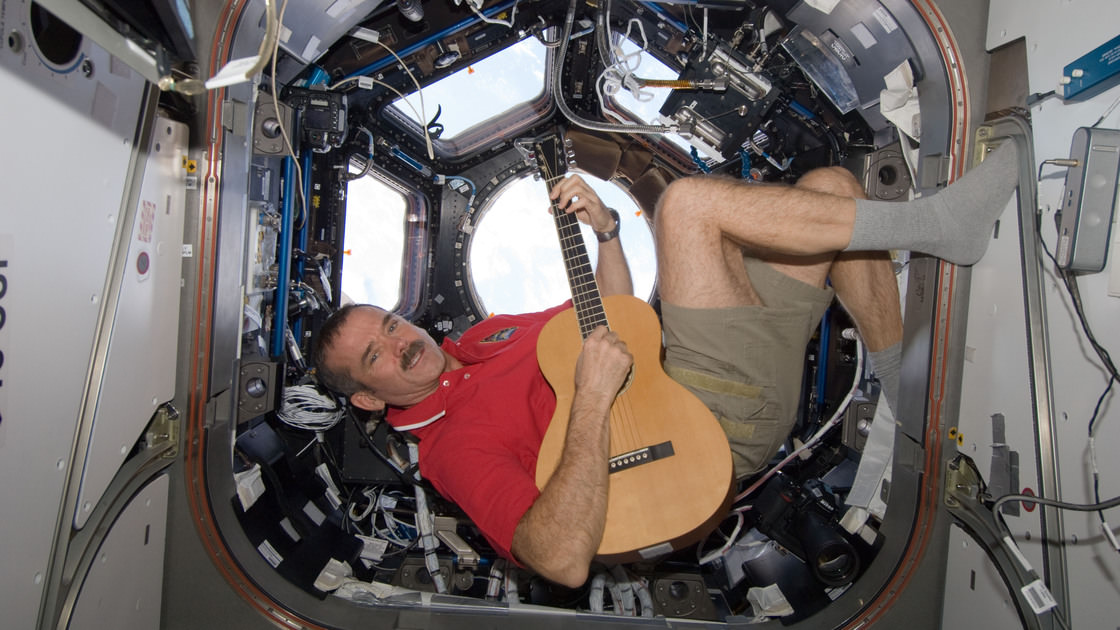
The Canadian’s homage to Bowie — with slightly altered lyrics — garnered more than 22.4 million views as of this morning, Eastern time. It was filmed on board the International Space Station and produced by Hadfield’s son, Evan. Music was recorded on Earth.
The video capped five months of intense public outreach that Hadfield did during Expedition 34/35 in 2012-13. During Expedition 35, he was the first Canadian commander on station, but still found time to record videos and music showcasing his time in space.
Since returning to Earth, Hadfield has already penned one best-selling book — An Astronaut’s Guide To Life On Earth — and is now working on a second that will include photos from his mission.