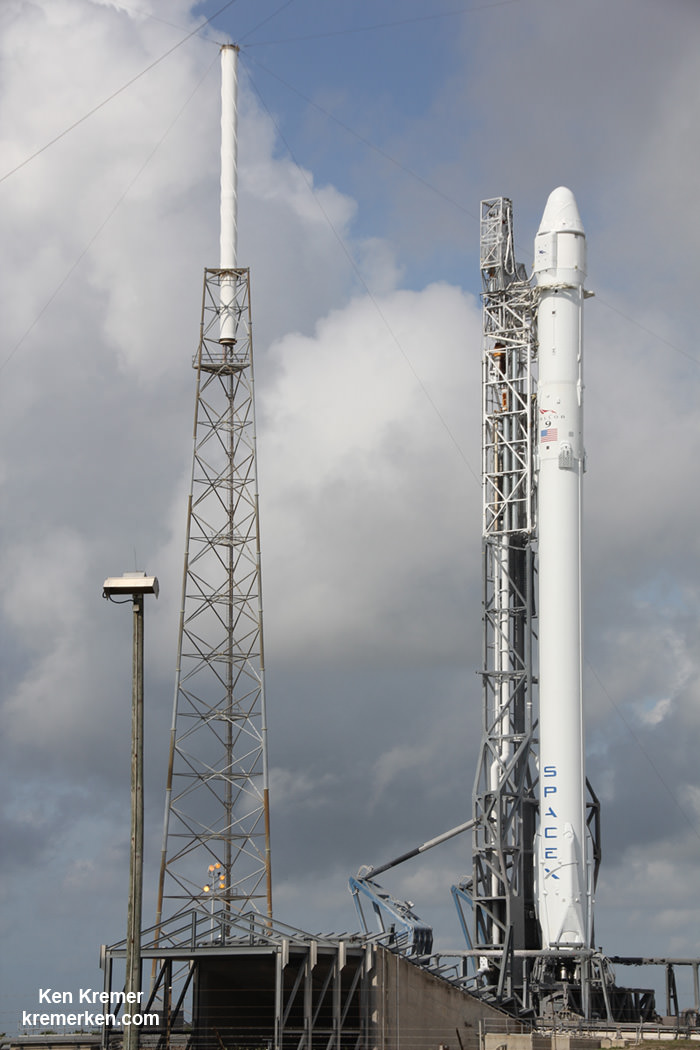
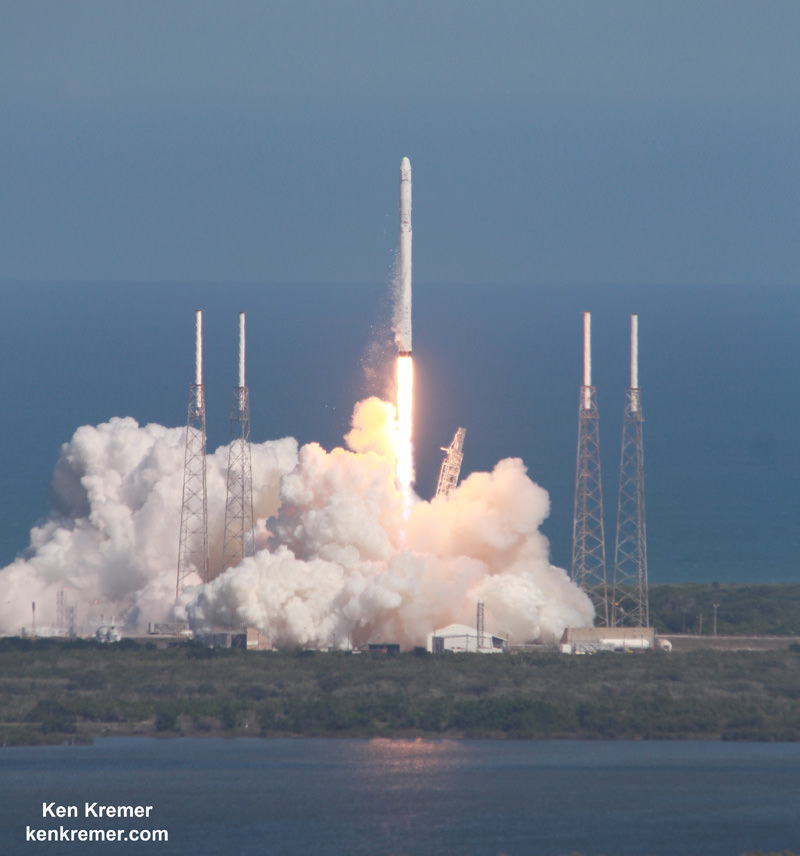
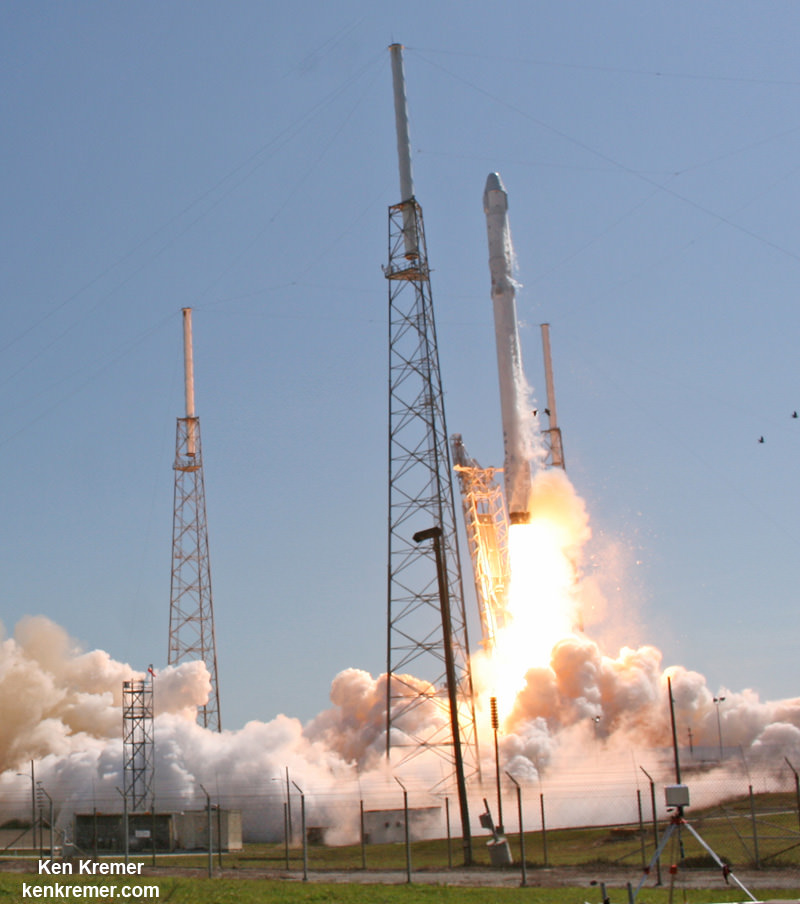
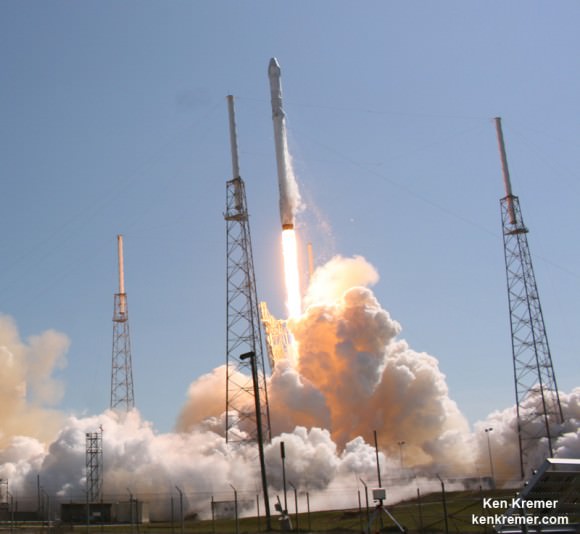
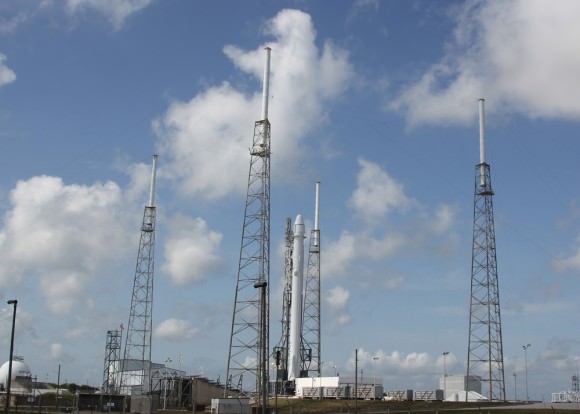
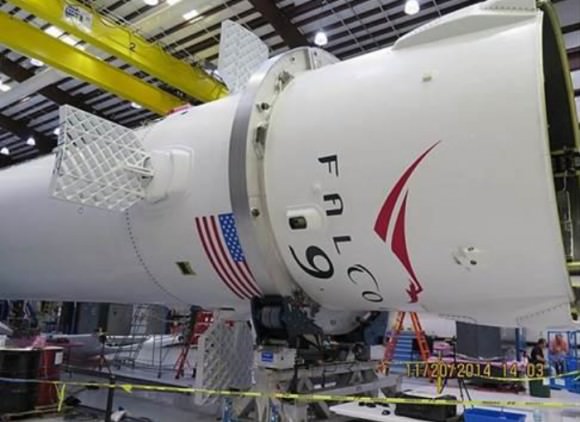
SpaceX Falcon 9 and Dragon are due to blastoff on June 28, 2015 from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida at 10:21 a.m. EDT on the CRS-7 mission to the International Space Station. Photo of last SpaceX launch to ISS in April 2015. Credit: Ken Kremer/kenkremer.com
Story updated[/caption]
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FL – With launch less than a day away for SpaceX’s seventh commercial resupply mission carrying a two ton payload of critical science and cargo for the future buildup of human spaceflight to the International Space Station (ISS) on Sunday, June 28, “everything is looking great” and all systems are GO, Hans Koenigsmann, SpaceX VP of mission assurance announced at a media briefing for reporters at the Kennedy Space Center.
The weather outlook along the Florida Space Coast is fantastic as U.S. Air Force 45th Weather Squadron forecasters are predicting a 90 percent chance of favorable conditions for lift off of the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon spacecraft, slated for 10:21 a.m. EDT, Sunday, June 28, from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
The Falcon 9 first stage is outfitted with four landing legs and grid fins to enable the landing attempt, which is a secondary objective of SpaceX. Cargo delivery to the station is the overriding primary objective and the entire reason for the CRS-7 mission.
If you are free this weekend and all continues to go well, this could well be your chance to be an eyewitness to a magnificent space launch in sunny Florida – and see a flight that signifies significant progress towards restoring America’s ability to once again launch our astronauts on American rockets from American soil.
NASA Television plans live launch coverage starting at 9 a.m EDT on June 28:
You can watch the launch live on NASA TV here: http://www.nasa.gov/nasatv
SpaceX also plans live launch coverage: www.spacex.com/webcast

The launch window is instantaneous, meaning that the rocket must liftoff at the precisely appointed time. Any delays like on Monday due to weather or technical factors will force a scrub.
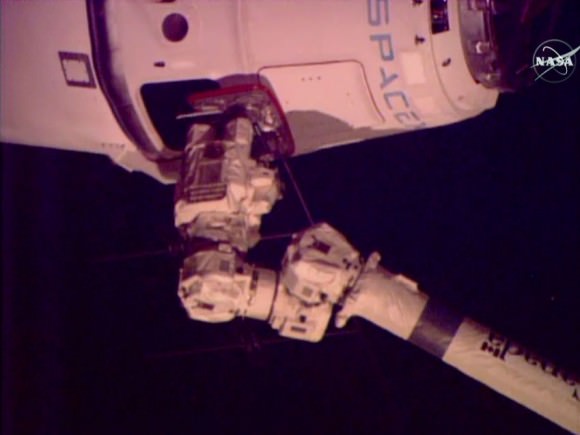
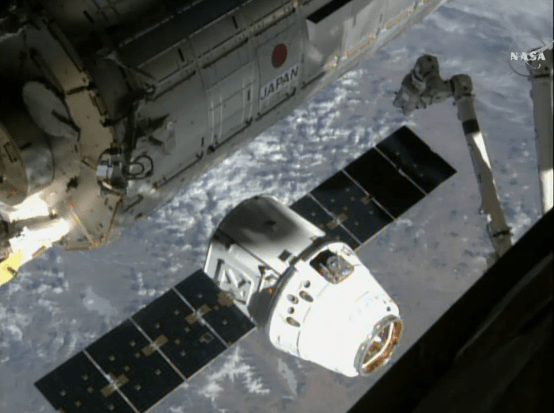
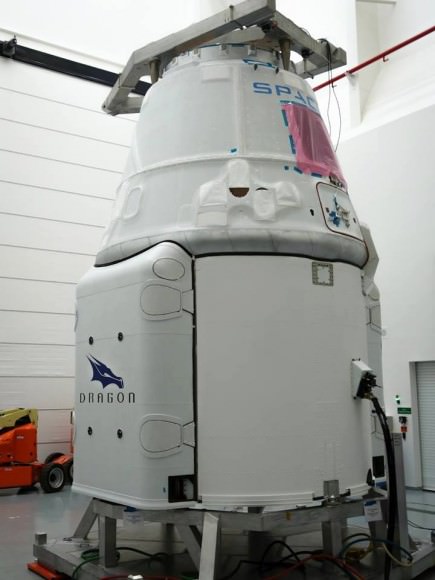
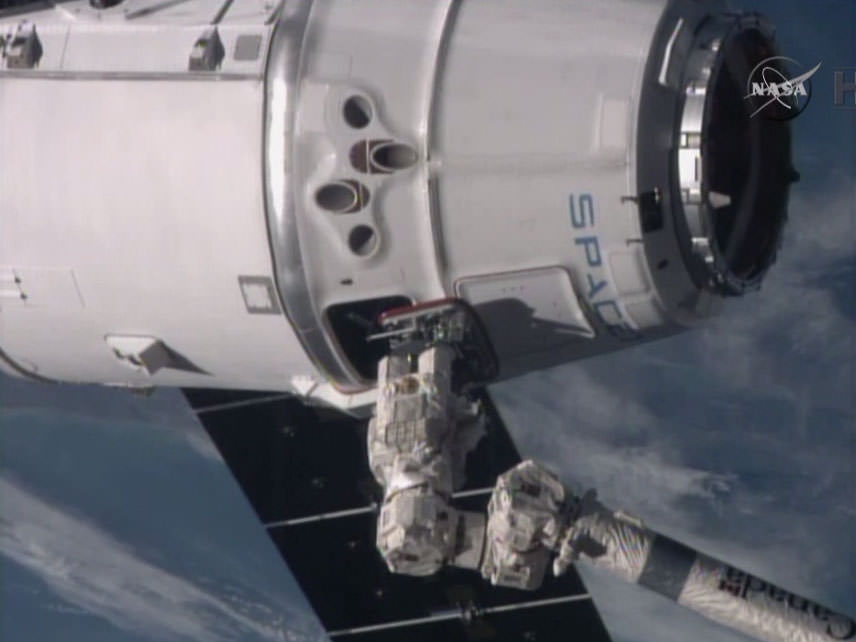
The mission is critical for NASA in more ways than one, in addition to the science cargo, the SpaceX Dragon spaceship is loaded with the first of two International Docking Adapters (IDA’s), pictured below, that will be connected to the space station to provide a place for Commercial Crew spacecraft carrying astronauts to dock to the orbiting laboratory as soon as 2017.
The approximately 30 inch thick and ring shaped IDA is loaded in the unpressurized truck section at the rear of the Dragon.
The pressurized section of the Dragon is packed with over 4,000 pounds of research experiments, spare parts, gear, high pressure supply gases, food, water and clothing for the astronaut and cosmonaut crews comprising Expeditions 44 and 45.
These include critical materials for the science and research investigations for the first ever one-year crew to serve aboard the ISS – comprising NASA astronaut Scott Kelly and Russian cosmonaut Mikhail Kornienko.
The science payloads will offer new insight to combustion in microgravity, perform the first space-based observations of meteors entering Earth’s atmosphere, continue solving potential crew health risks and make new strides toward being able to grow food in space, says NASA.
Some three dozen student science experiments are also flying aboard. The cargo also includes the METEOR camera.
Both IDA’s were built by Boeing. They will enable docking by the new space taxis being built by Boeing and Space X – the CST-100 and crew Dragon respectively, to carry our crews to the ISS and end our sole source reliance on the Russian Soyuz capsule.
IDA 1 will be attached to the forward port on the Harmony node, where the space shuttles used to dock.

If Dragon launches on Sunday as planned, it will reach the space station after a two day pursuit on Tuesday, June 30.
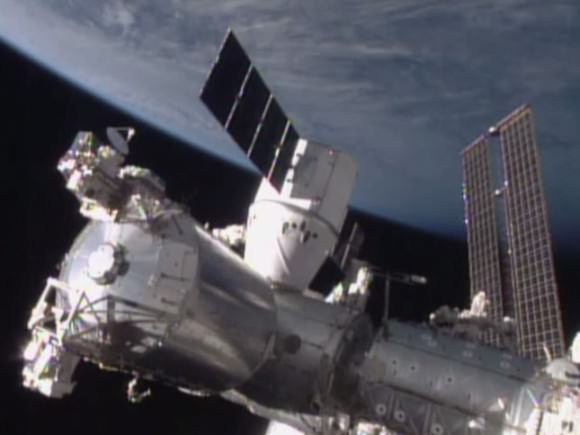
NASA’s Scott Kelly of NASA will use the station’s Canadarm2 robotic arm to reach out and capture Dragon at about 7 a.m. He will be assisted by Station commander Gennady Padalka of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) as they operate the 57 foot long arm from the station’s cupola.
NASA TV coverage of rendezvous and grapple of Dragon will begin at 5:30 a.m. on Tuesday. Coverage of Dragon’s installation to the Earth-facing port of the Harmony module will begin at 8:30 a.m.
The ship will remain berthed at the ISS for about five weeks.
Watch for Ken’s continuing onsite coverage of the CRS-7 launch from the Kennedy Space Center and Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.
………….
Learn more about SpaceX, Boeing, Space Taxis, Europa, Rosetta, Mars rovers, Orion, SLS, Antares, NASA missions and more at Ken’s upcoming outreach events:
Jun 27-28: “SpaceX launch, Orion, Commercial crew, Curiosity explores Mars, Antares and more,” Kennedy Space Center Quality Inn, Titusville, FL, evenings