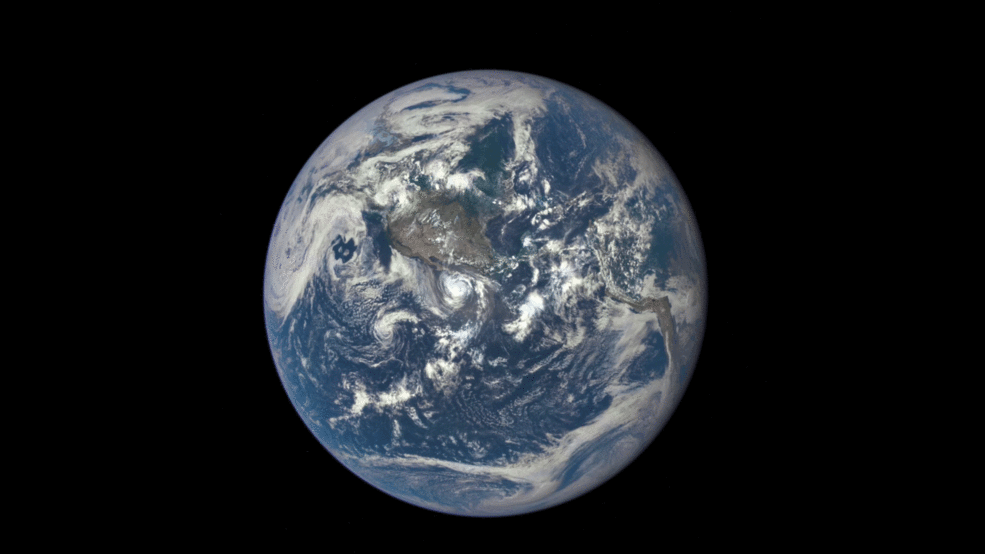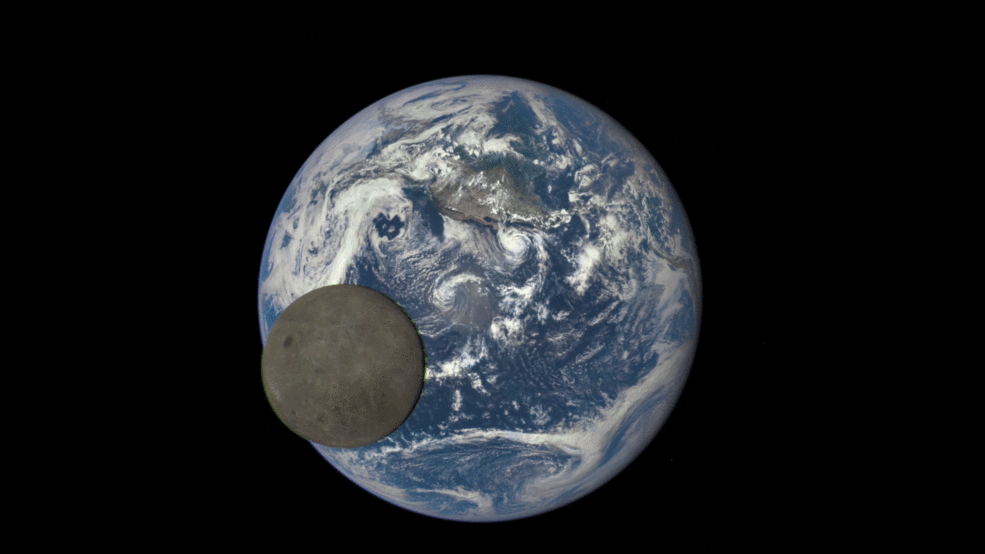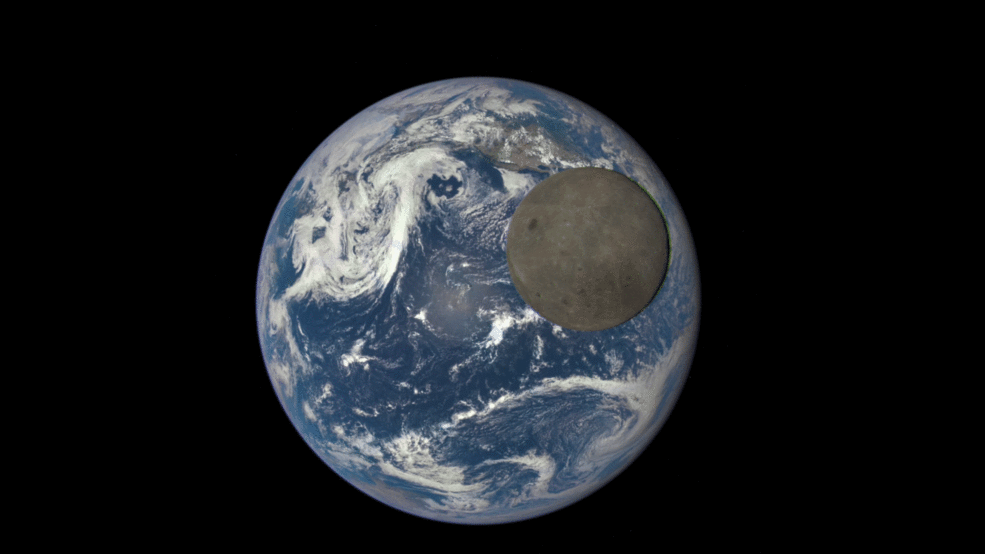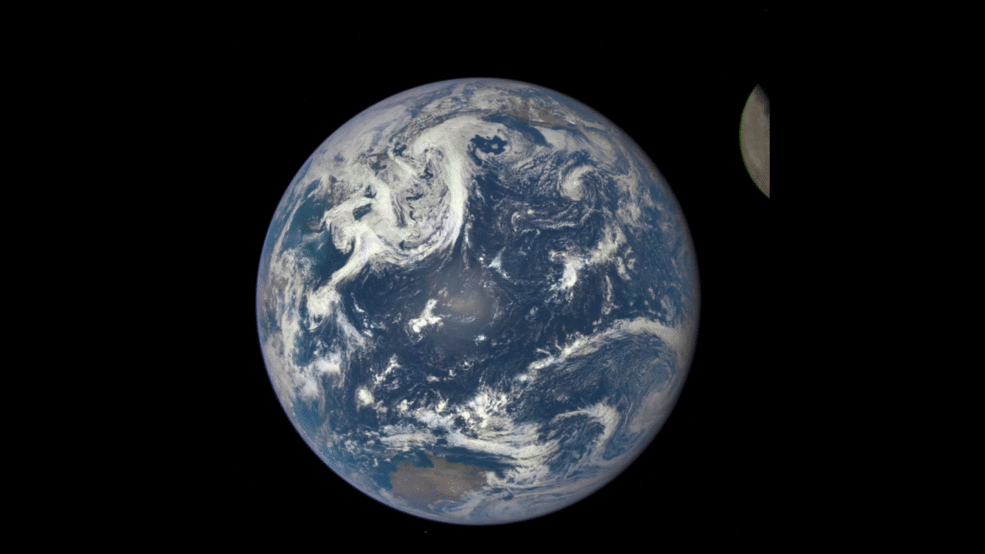
This animation shows images of the far side of the moon, illuminated by the sun, as it crosses between the DISCOVR spacecraft’s Earth Polychromatic Imaging Camera (EPIC) camera and telescope, and the Earth – one million miles away. Credit: NASA/NOAA
See YouTube version and EPIC camera below[/caption]
An eye-poppingly ‘EPIC’ view of the sunlit far side of the Moon transiting the sunlit side of Earth was recently captured by NASA’s Earth Polychromatic Imaging Camera (EPIC) camera from one million miles away. “Wow!” – is an understatement!
The stunning animation of the Moon crossing in front of the Earth, shown above, and seemingly unlike anything else, was created from a series of images taken in July by NASA’s EPIC camera flying aboard the orbiting Deep Space Climate Observatory (DSCOVR), a space weather monitoring satellite, according to a NASA statement.
Have just witnessed NASA’s New Horizons flyby of the Pluto-Charon double planet system, the similarity to what some call the Earth-Moon double planet system is eerie. You could imagine ones heart going out to Earth’s Australian continent as an upside down version of Pluto’s bright heart shaped ‘Tombaugh Regio’ region in the southern hemisphere.
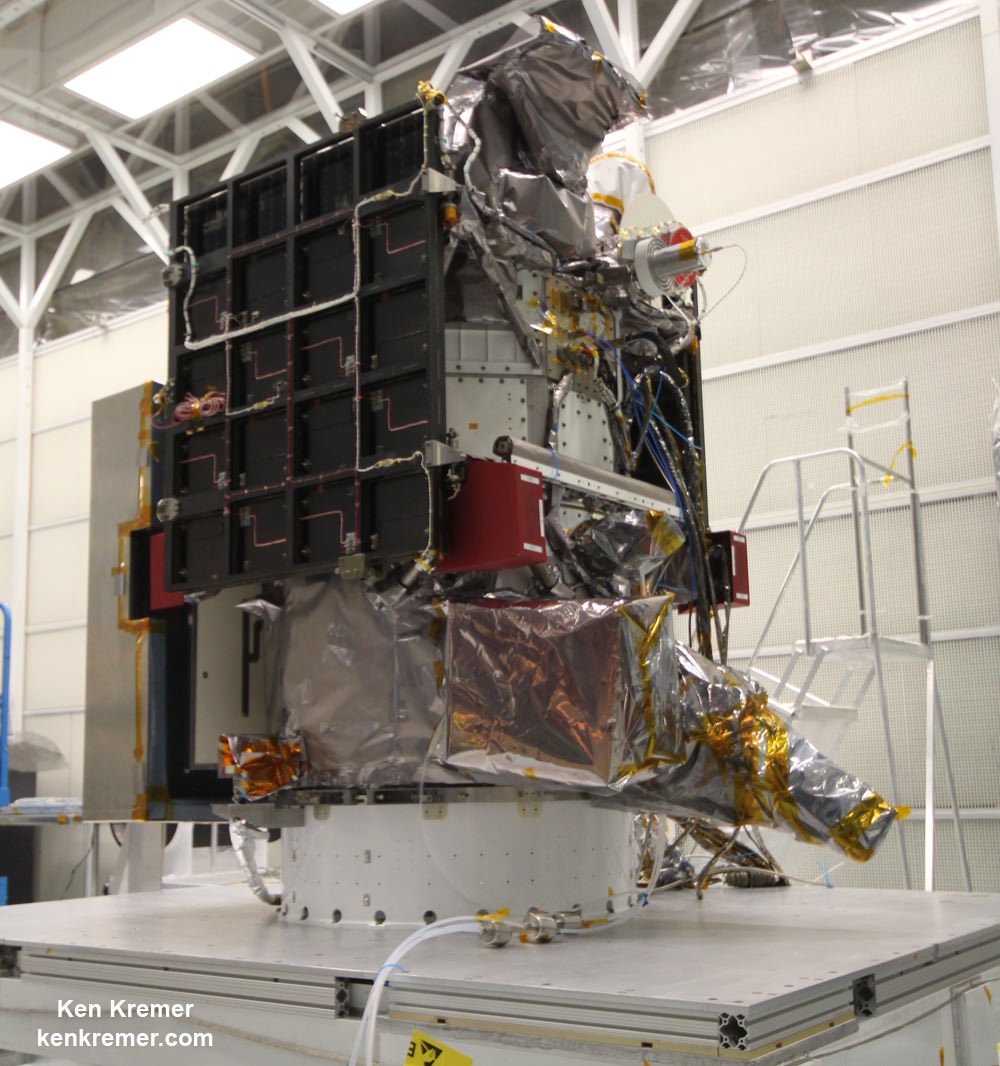
EPIC is a four megapixel CCD camera and telescope mounted on DSCOVR and orbiting at the L1 Lagrange Point – a neutral gravity point that lies on the direct line between Earth and the sun.
The goal of the $340 million DSCOVR is to monitor the solar wind and aid very important forecasts of space weather at Earth from L1.
EPIC will capture “a constant view of the fully illuminated Earth as it rotates, providing scientific observations of ozone, vegetation, cloud height and aerosols in the atmosphere.”
L1 is located 1.5 million kilometers (932,000 miles) sunward from Earth. At L1 the gravity between the sun and Earth is perfectly balanced and the DSCOVR satellite orbits about that spot just like a planet.
The EPIC images “were taken between 3:50 p.m. and 8:45 p.m. EDT on July 16, showing the moon moving over the Pacific Ocean near North America,” NASA said.

You can see Earth’s North Pole at the upper left side of the images which results from the orbital tilt of Earth from the vantage point of the spacecraft at the L1 Lagrange Point.
EPIC will take full disk color images of the sunlit side of Earth at least six times per day.
They will be made publically available by NASA at a dedicated website, when the camera starts its regular daily science observation campaign of the home planet in about a month during September.
NASA says the images will show varying views of the rotating Earth and they will be posted online some 12 to 36 hours after they are acquired.
Each image is actually a composite of three images taken in the red, green and blue channels of the EPIC camera to provide the final “natural color” image of Earth. Since the images are taken about 30 seconds apart as the moon is moving there is a slight but noticeable artifact on the right side of the moon, NASA explained.
Altogether, “ EPIC takes a series of 10 images using different narrowband spectral filters — from ultraviolet to near infrared — to produce a variety of science products. The red, green and blue channel images are used in these color images.”
EPIC should capture these Earth-Moon transits about twice per year as the orbit of DSCOVR crosses the orbital plane of the moon.
The closest analog according to NASA came in May 2008 when NASA’s Deep Impact spacecraft “captured a similar view of Earth and the moon from a distance of 31 million miles away. The series of images showed the moon passing in front of our home planet when it was only partially illuminated by the sun.”
We never see the far side of the moon from Earth since the bodies are tidally locked. And its quite apparent from the images, that the moon’s far side looks completely different from the side facing Earth. The far side lacks the large, dark, basaltic plains, or maria, that are so prominent on the Earth-facing side.
“It is surprising how much brighter Earth is than the moon,” said Adam Szabo, DSCOVR project scientist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, in a statement.
“Our planet is a truly brilliant object in dark space compared to the lunar surface.”
DSCOVR is a joint mission between NOAA, NASA, and the U.S Air Force (USAF) that is managed by NOAA. The satellite and science instruments were provided by NASA and NOAA.

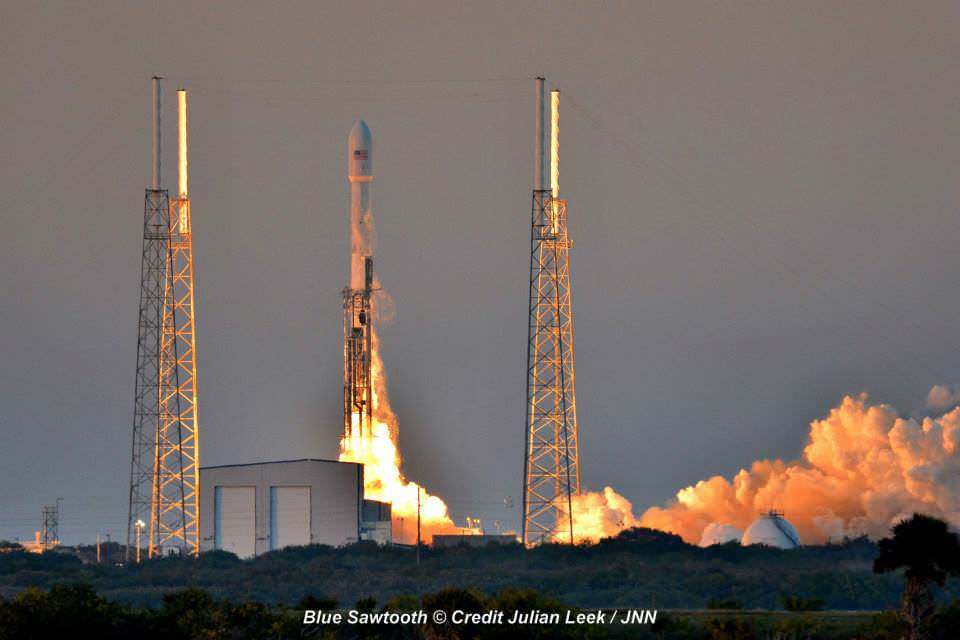
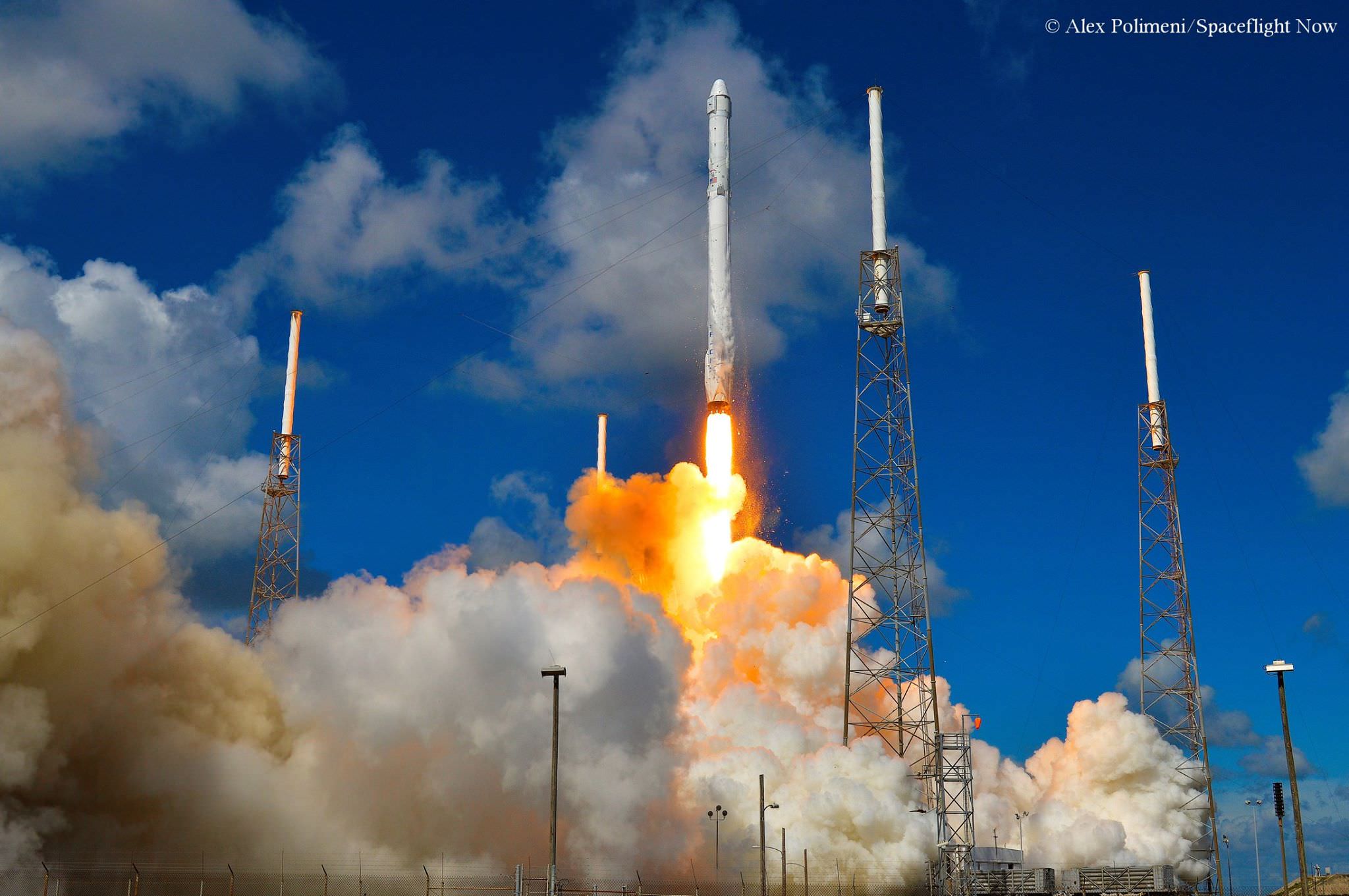
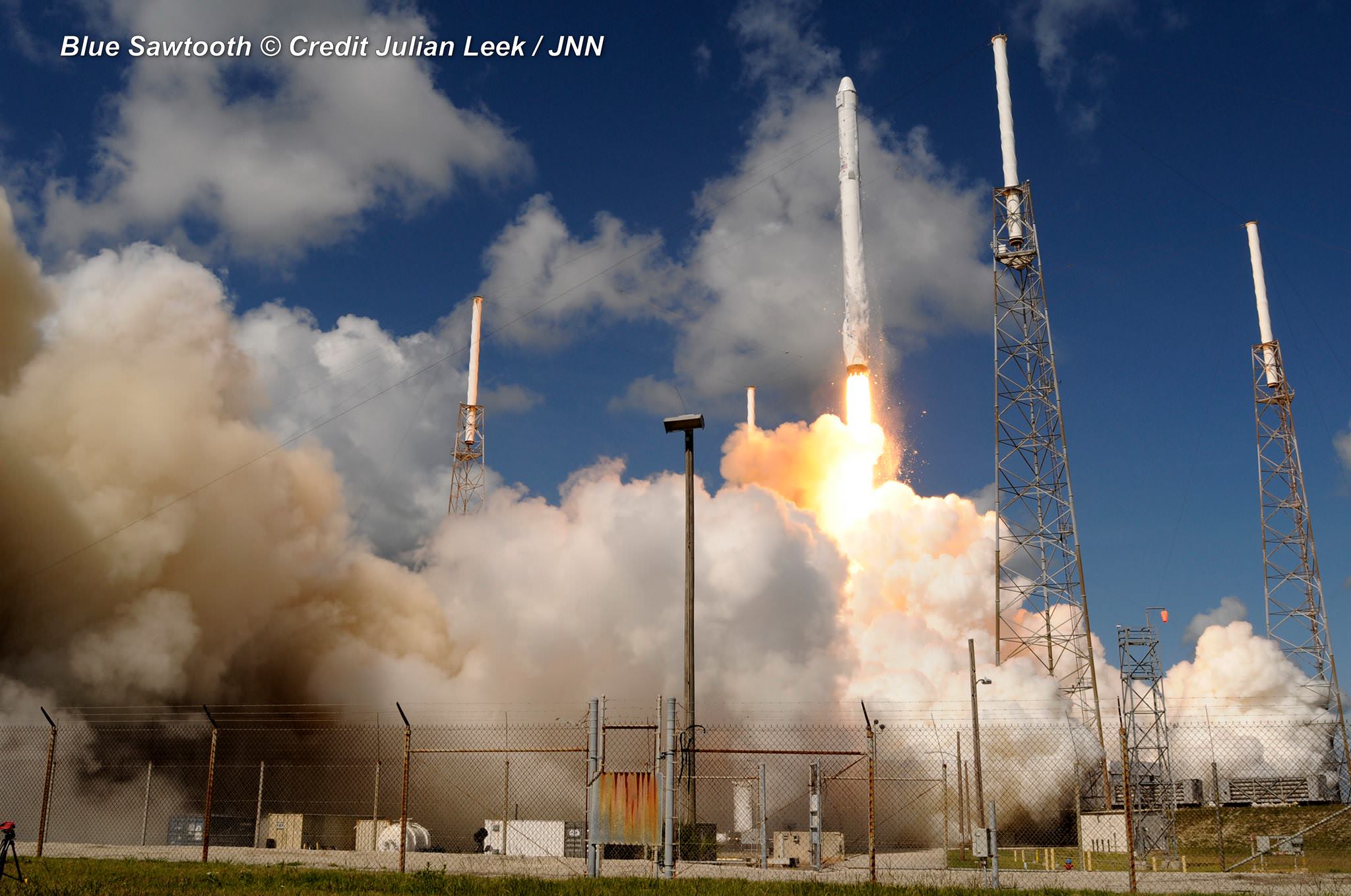
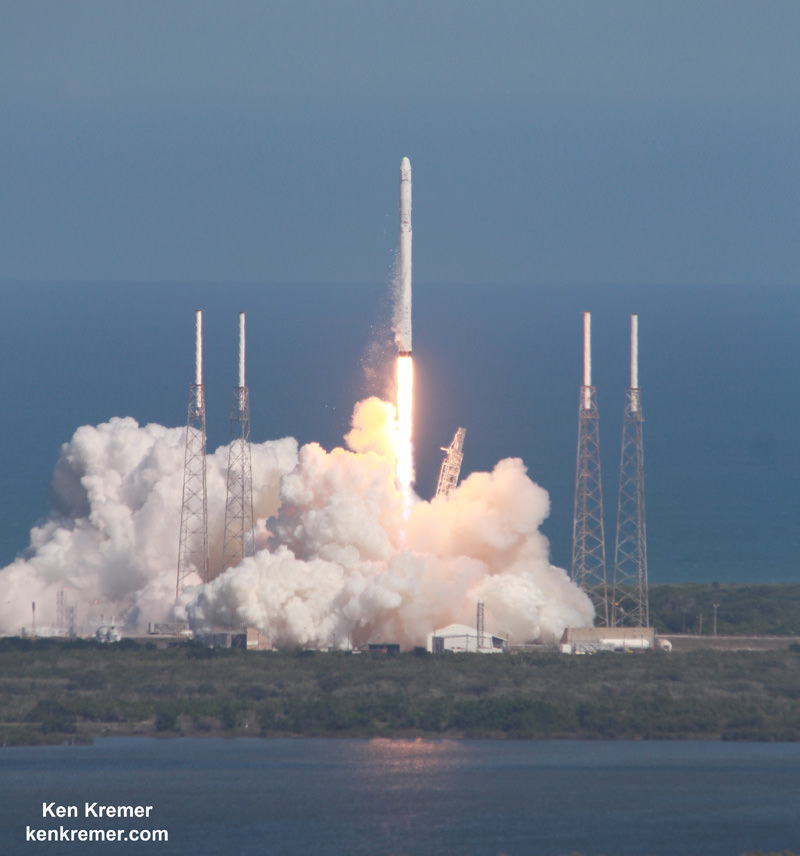
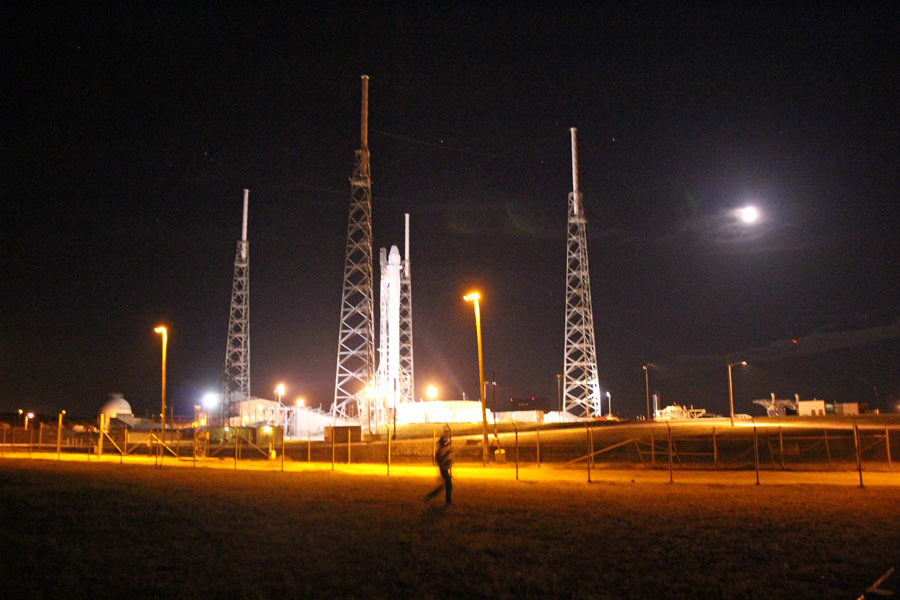
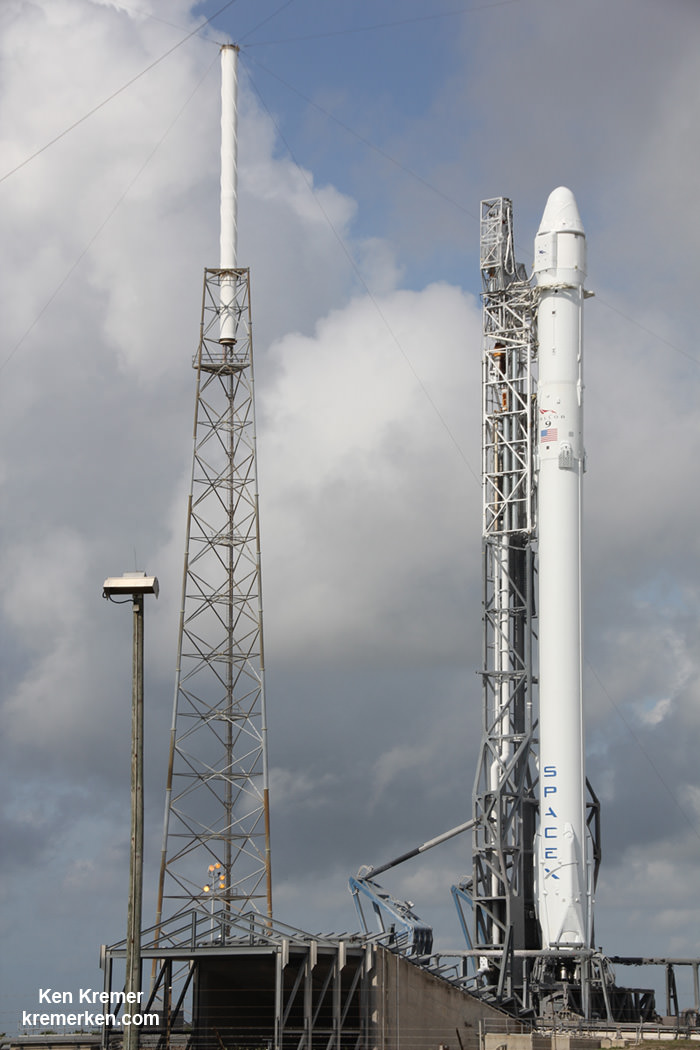
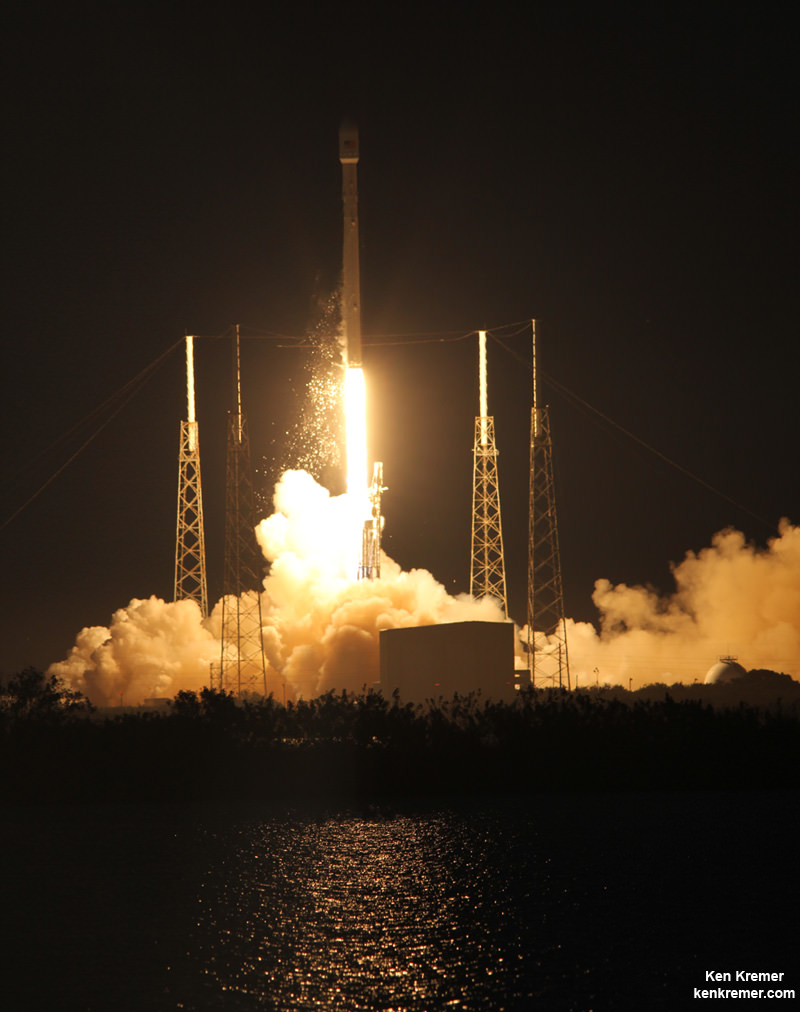
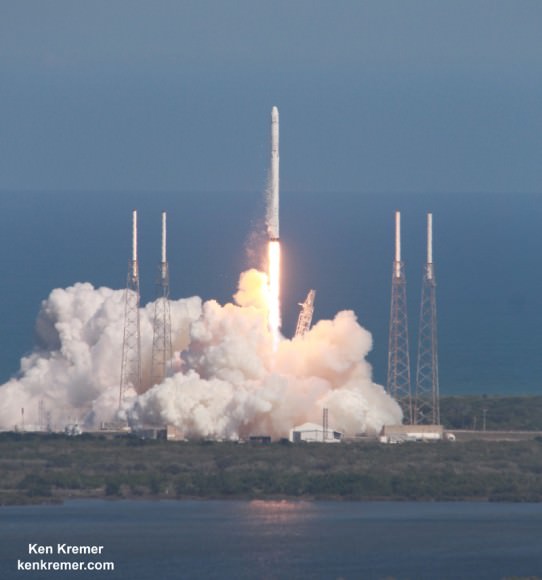
The couch sized probe was launched atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 on Feb. 11, 2015 from Cape Canaveral, Florida, to start a million mile journey to its deep space observation post. The rocket was funded by the USAF.
DSCOVR was first proposed in 1998 by then US Vice President Al Gore as the low cost ‘Triana’ satellite to take near continuous views of the Earth’s entire globe to feed to the internet as a means of motivating students to study math and science. It was eventually built as a much more capable Earth science satellite that would also conduct the space weather observations.
But Triana was shelved for purely partisan political reasons and the satellite was placed into storage at NASA Goddard and the science was lost until now.
It was also dubbed “Goresat.’
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.
Video caption: This animation shows images of the far side of the moon, illuminated by the sun, as it crosses between the DISCOVR spacecraft’s Earth Polychromatic Imaging Camera (EPIC) camera and telescope, and the Earth – one million miles away. Credit: NASA/NOAA