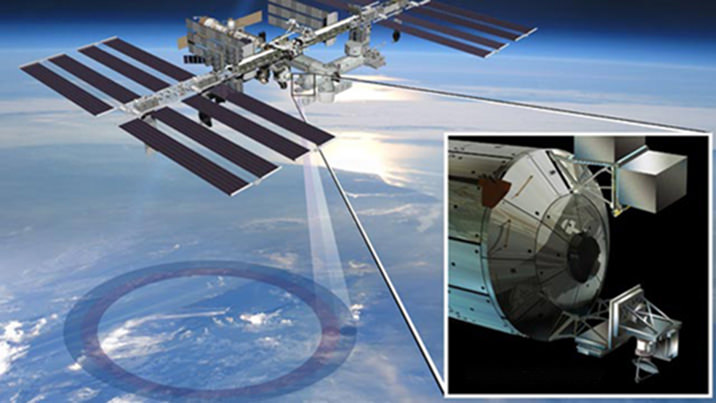
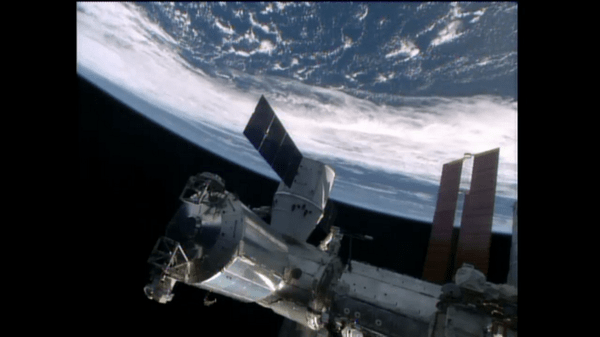
NASA inaugurated a new era of research for the International Space Station (ISS) as an Earth observation platform following the successful installation and activation of the ISS-RapidScat science instrument on the outposts exterior at Europe’s Columbus module.
The ISS Rapid Scatterometer, or ISS-RapidScat, is NASA’s first research payload aimed at conducting near global Earth science from the station’s exterior and will be augmented with others in coming years.
RapidScat is designed to monitor ocean winds for climate research, weather predictions, and hurricane monitoring.
The 1280 pound (580 kilogram) experimental instrument is already collecting its first science data following its recent power-on and activation at the station.
“Its antenna began spinning and it started transmitting and receiving its first winds data on Oct.1,” according to a NASA statement.
The first image from RapidScat was released by NASA on Oct. 6, shown below, and depicts preliminary measurements of global ocean near-surface wind speeds and directions.
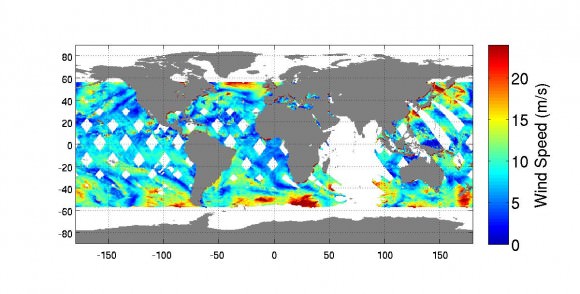
The $26 million remote sensing instrument uses radar pulses to observe the speed and direction of winds over the ocean for the improvement of weather forecasting.
“Most satellite missions require weeks or even months to produce data of the quality that we seem to be getting from the first few days of RapidScat,” said RapidScat Project Scientist Ernesto Rodriguez of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, which built and manages the mission.
“We have been very lucky that within the first days of operations we have already been able to observe a developing tropical cyclone.
“The quality of these data reflect the level of testing and preparation that the team has put in prior to launch,” Rodriguez said in a NASA statement. “It also reflects the quality of the spare QuikScat hardware from which RapidScat was partially assembled.”
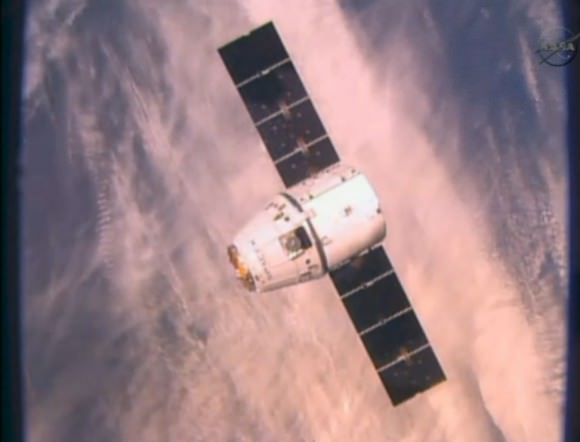
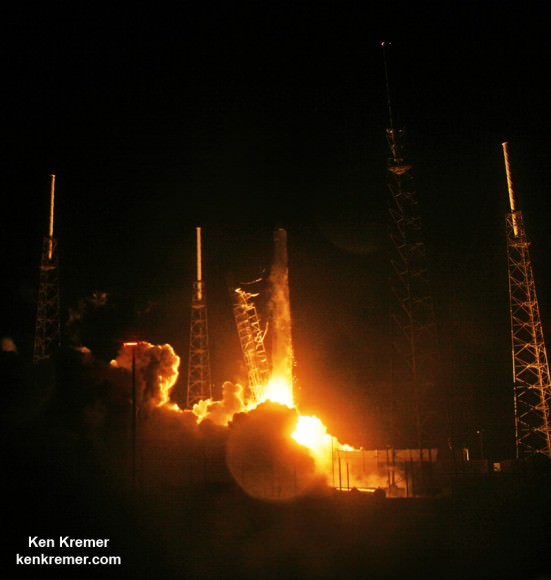
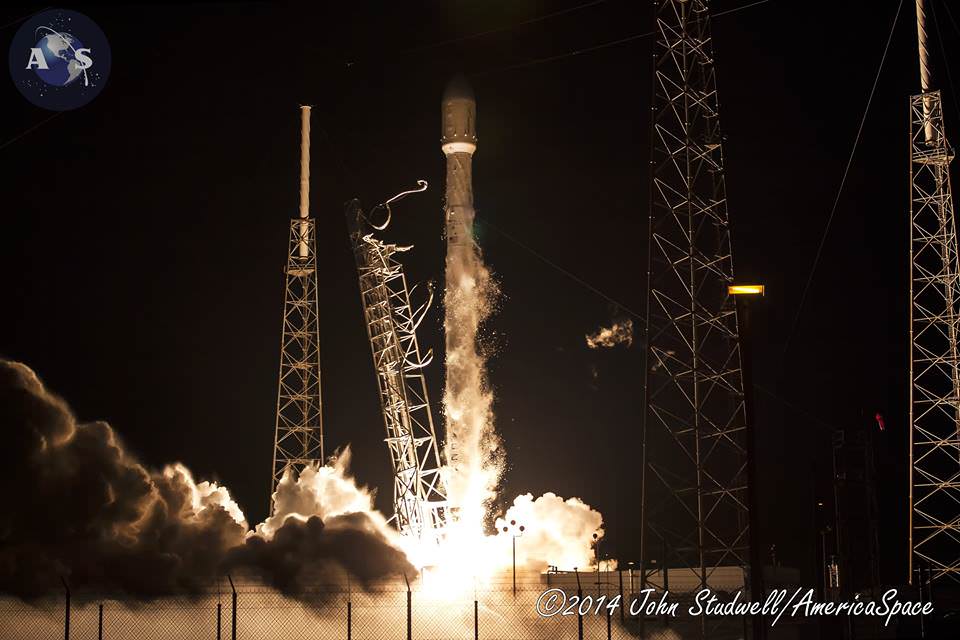
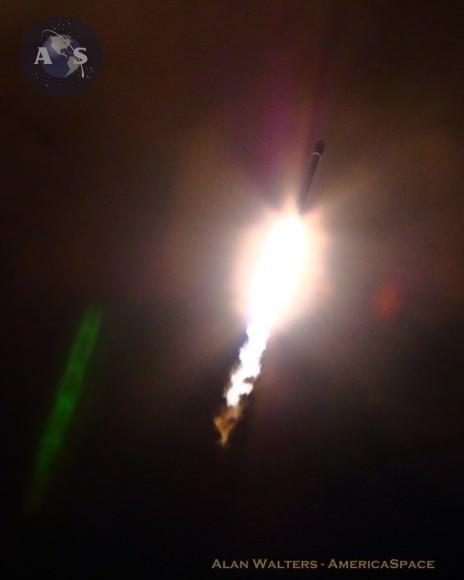
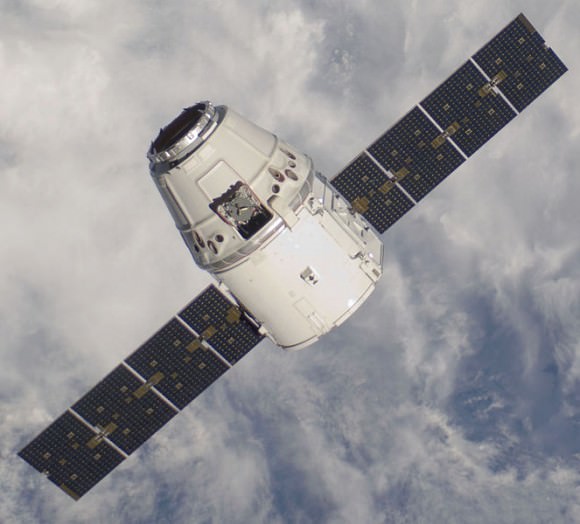
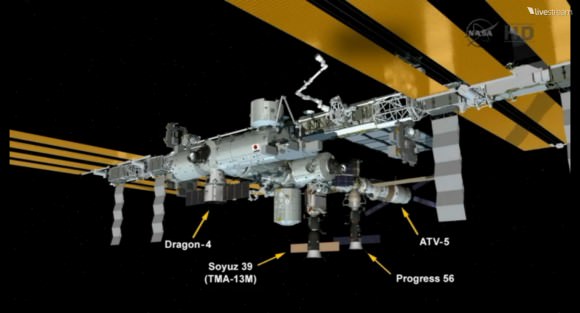
RapidScat, payload was hauled up to the station as part of the science cargo launched aboard the commercial SpaceX Dragon CRS-4 cargo resupply mission that thundered to space on the company’s Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex-40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Sept. 21.
Dragon was successfully berthed at the Earth-facing port on the station’s Harmony module on Sept 23, as detailed here.
It was robotically assembled and attached to the exterior of the station’s Columbus module using the station’s robotic arm and DEXTRE manipulator over a two day period on Sept 29 and 30.
Ground controllers at Johnson Space Center intricately maneuvered DEXTRE to pluck RapidScat and its nadir adapter from the unpressurized trunk section of the Dragon cargo ship and attached it to a vacant external mounting platform on the Columbus module holding mechanical and electrical connections.

The nadir adapter orients the instrument to point at Earth.
The couch sized instrument and adapter together measure about 49 x 46 x 83 inches (124 x 117 x 211 centimeters).
Engineers are in the midst of a two week check out process that is proceeding normally so far. Another two weeks of calibration work will follow.
Thereafter RapidScat will begin a mission expected to last at least two years, said Steve Volz, associate director for flight programs in the Earth Science Division, NASA Headquarters, Washington, at a prelaunch media briefing at the Kennedy Space Center.
RapidScat is the forerunner of at least five more Earth science observing instruments that will be added to the station by the end of the decade, Volz explained.
The second Earth science instrument, dubbed CATS, could be added by year’s end.
The Cloud-Aerosol Transport System (CATS) is a laser instrument that will measure clouds and the location and distribution of pollution, dust, smoke, and other particulates in the atmosphere.
CATS is slated to launch on the next SpaceX resupply mission, CRS-5, currently targeted to launch from Cape Canaveral, FL, on Dec. 9.

This has been a banner year for NASA’s Earth science missions. At least five missions will be launched to space within a 12 month period, the most new Earth-observing mission launches in one year in more than a decade.
ISS-RapidScat is the third of five NASA Earth science missions scheduled to launch over a year.
NASA has already launched the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory, a joint mission with the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency in February, and the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) carbon observatory in July 2014.

Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.
…………….
Learn more about Commercial Space Taxis, Orion and NASA Human and Robotic Spaceflight at Ken’s upcoming presentations:
Oct 14: “What’s the Future of America’s Human Spaceflight Program with Orion and Commercial Astronaut Taxis” & “Antares/Cygnus ISS Rocket Launches from Virginia”; Princeton University, Amateur Astronomers Assoc of Princeton (AAAP), Princeton, NJ, 7:30 PM
Oct 23/24: “Antares/Cygnus ISS Rocket Launch from Virginia”; Rodeway Inn, Chincoteague, VA