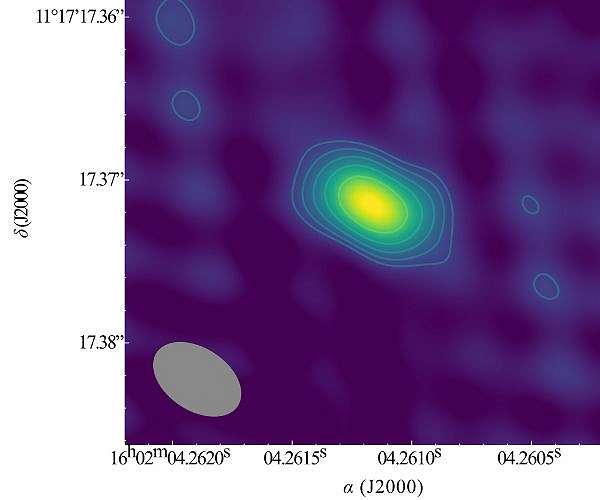
If nothing else catches your attention in the title then surely ‘hypernebula’ does! There are some amazing processes scattered around the cosmos, of particular interest are the fast radio bursts (FRB). These brief flashes of radiation happen without warning…until now. A team in the Netherlands have identified a second FRB as coming from within a hyper nebula – a dense and highly magnetised cloud of plasma that is illuminated by a powerful but unknown source!
Continue reading “Another Fast Radio Burst is Coming from a Hypernebula. Also, Hypernebulae are a Thing”Now Astronomers have Discovered “Ultra-Fast Radio Bursts” Lasting Millionths of a Second

A recent study published in Nature Astronomy examines the discovery of what astronomers are dubbing “ultra-fast radio bursts”, a new type of fast radio bursts (FRBs) that the team determined lasts for a mind-boggling ten millionths of a second or less. Traditionally, FRBs have been found to last only thousandths of a second, but this study builds on a 2021 study that hypothesized FRBs could possibly last for millionths of a second. This also comes after astronomers recently announced the discovery of the oldest and farthest FRB ever observed, approximately 8 billion light-years from Earth.
Continue reading “Now Astronomers have Discovered “Ultra-Fast Radio Bursts” Lasting Millionths of a Second”A magnetar has been discovered throwing off bizarre blasts of radiation. Is this where fast radio bursts come from?
Magnetars are the ultimate aggressive star: intense magnetic fields, massive outbursts, the works. We’ve known that magnetars are capable of producing some of the most powerful blasts in the cosmos, but new observations reveal a different kind of radiation: radio waves. This could potentially solve the long-standing puzzle of the origins of the mysterious Fast Radio Bursts.
Continue reading “A magnetar has been discovered throwing off bizarre blasts of radiation. Is this where fast radio bursts come from?”Astronomers Have Detected the Brightest Fast Radio Burst Ever Seen. Still No Idea What’s Causing Them
Fast Radio Bursts (FRBs) have been one of the more puzzling and fascinating areas of astronomical study ever since the first was detected in 2007 (known as the Lorimer Burst). Much like gravitational waves, the study of these short-lived radio pulses (which last only a few milliseconds) is still in its infancy, and only a 33 events have been detected. What’s more, scientists are still not sure what accounts for them.
While some believe that they are entirely natural in origin, others have speculated that they could be evidence of extra-terrestrial activity. Regardless of their cause, according to a recent study, three FRBs were detected this month in Australia by the Parkes Observatory radio telescope in remote Australia. Of these three, one happened to be the most powerful FRB recorded to date.
The signals were detected on March 1st, March 9th, and March 11th, and were designated as FRB 180301, FRB 180309 and FRB 180311. Of these, the one recorded on March 9th (FRB 180309) was the brightest ever recorded, having a signal-to-noise ratio that was four times higher than the previous brightest FRB. This event, known as FRB 170827, was detected on August 27th, 2017, by the UTMOST array in Australia.

All three of these events were detected by the Parkes radio telescope, which is located in New South Wales about 380 kilometers (236 mi) from Sydney. As one of three telescopes that makes up the Australia Telescope National Facility, this telescope has been studying pulsars, rapidly spinning neutron stars, and conducting large-scale surveys of the sky since 1961. In recent years, it has been dedicated to the detection of FRBs in our Universe.
Considering how rare and short-lived FRBs are, recording three in the space of one month is quite the achievement. What’s more, the fact that the detections happened in real-time, rather than being discovered in archival data, is also impressive. Shortly after the event, Stefan Oslowski (of the Swinburne University of Technology) tweeted about this rather fortunate discovery (see below).
At present, none of the three events are believed to be “repeaters” – aka. Repeating Fast Radio Bursts. So far, only one FRB has been found to be repeating. This was none other than FRB 121102, which was first detected by the Arecibo radio telescope in Puerto Rico on November 2nd, 2012. In 2015, several more bursts were detected from this some source which had properties that were consistent with the original signal.
The Parkes Pulsar Timing Array just discovered the highest signal-to-noise ratio Fast Radio Burst ever! https://t.co/MNOIGjM8MS via @astronomerstel @frbcatalogue
— Stefan Oslowski (@StefanOslowski) March 9, 2018
As noted, and in spite of all the events that have been detected, scientists are still not sure what causes these strange bursts. But with three more events detected, and the possibility that they could repeat in the near-future, scientists now have more events to pore over and base their theories on. And with next-generation arrays being constructed, a great many more events (and repeaters) are likely to be detected in the coming years.
These include the the Square Kilometer Array currently being built across Australia, New Zealand and South Africa, and the Five hundred meter Aperture Spherical Telescope (FAST) being build in China. With these telescopes joining observatories like the Very Large Telescope (VLT), the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) and venerated observatories like Arecibo, FRBs may not be mysterious for much longer!
Further Reading: The Astronomer’s Telegram, Science Alert
What Are Fast Radio Bursts?
You might think you’re reading an educational website, where I explain fascinating concepts in space and astronomy, but that’s not really what’s going on here.
What’s actually happening is that you’re tagging along as I learn more and more about new and cool things happening in the Universe. I dig into them like a badger hiding a cow carcass, and we all get to enjoy the cache of knowledge I uncover.
Okay, that analogy got a little weird. Anyway, my point is. Squirrel!
Fast radio bursts are the new cosmic whatzits confusing and baffling astronomers, and now we get to take a front seat and watch them move through all stages of process of discovery.
Stage 1: A strange new anomaly is discovered that doesn’t fit any current model of the cosmos. For example, strange Boyajian’s Star. You know, that star that probably doesn’t have an alien megastructure orbiting around it, but astronomers can’t rule that out just yet?
Stage 2: Astronomers struggle to find other examples of this thing. They pitch ideas for new missions and scientific instruments. No idea is too crazy, until it’s proven to be too crazy. Examples include dark matter, dark energy, and that idea that we’re living in a
Stage 3: Astronomers develop a model for the thing, find evidence that matches their predictions, and vast majority of the astronomical community comes to a consensus on what this thing is. Like quasars and gamma ray bursts. YouTuber’s make their videos. Textbooks are updated. Balance is restored.
Today we’re going to talk about Fast Radio Bursts. They just moved from Stage 1 to Stage 2. Let’s dig in.
Fast radio bursts, or FRBs, or “Furbys” were first detected in 2007 by the astronomer Duncan Lorimer from West Virginia University.
He was looking through an archive of pulsar observations. Pulsars, of course, are newly formed neutron stars, the remnants left over from supernova explosions. They spin rapidly, blasting out twin beams of radiation. Some can spin hundreds of times a second, so precisely you could set your watch to them.

In this data, Lorimer made a “that’s funny” observation, when he noticed one blast of radio waves that squealed for 5 milliseconds and then it was gone. It didn’t match any other observation or prediction of what should be out there, so astronomers set out to find more of them.
Over the last 10 years, astronomers have found about 25 more examples of Fast Radio Bursts. Each one only lasts a few milliseconds, and then fades away forever. A one time event that can appear anywhere in the sky and only last for a couple milliseconds and never repeats is not an astronomer’s favorite target of study.
Actually, one FRB has been found to repeat, maybe.
The question, of course, is “what are they?”. And the answer, right now is, “astronomers have no idea.”
In fact, until very recently, astronomers weren’t ever certain they were coming from space at all. We’re surrounded by radio signals all the time, so a terrestrial source of fast radio bursts seems totally logical.
About a week ago, astronomers from Australia announced that FRBs are definitely coming from outside the Earth. They used the Molonglo Observatory Synthesis Telescope (or MOST) in Canberra to gather data on a large patch of sky.
Then they sifted through 1,000 terabytes of data and found just 3 fast radio bursts. Three.
Since MOST is farsighted and can’t perceive any radio signals closer than 10,000 km away, the signals had to be coming outside planet Earth. They were “extraterrestrial” in origin.
Right now, fast radio bursts are infuriating to astronomers. They don’t seem to match up with any other events we can see. They’re not the afterglow of a supernova, or tied in some way to gamma ray bursts.
In order to really figure out what’s going on, astronomers need new tools, and there’s a perfect instrument coming. Astronomers are building a new telescope called the Canadian Hydrogen Intensity Mapping Experiment (or CHIME), which is under construction near the town of Penticton in my own British Columbia.
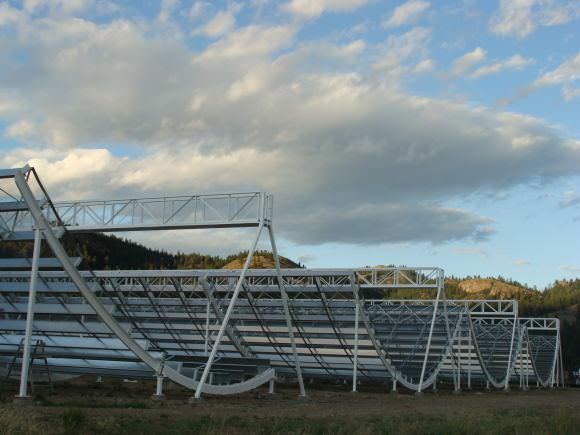

It looks like a bunch of snowboard halfpipes, and its job will be to search for hydrogen emission from distant galaxies. It’ll help us understand how the Universe was expanding between 7 and 11 billion years ago, and create a 3-dimensional map of the early cosmos.
In addition to this, it’s going to be able to detect hundreds of fast radio bursts, maybe even a dozen a day, finally giving astronomers vast pools of signals to study.
What are they? Astronomers have no idea. Seriously, if you’ve got a good suggestion, they’d be glad to hear it.
In these kinds of situations, astronomers generally assume they’re caused by exploding stars in some way. Young stars or old stars, or maybe stars colliding. But so far, none of the theoretical models match the observations.

Another idea is black holes, of course. Specifically, supermassive black holes at the hearts of distant galaxies. From time to time, a random star, planet, or blob of gas falls into the black hole. This matter piles upon the black hole’s event horizon, heats up, screams for a moment, and disappears without a trace. Not a full on quasar that shines for thousands of years, but a quick snack.
The next idea comes with the only repeating fast radio burst that’s ever been found. Astronomers looked through the data archive of the Arecibo Observatory in Puerto Rico and found a signal that had repeated at least 10 times in a year, sometimes less than a minute apart.
Since the quick blast of radiation is repeating, this rules out a one-time collision between exotic objects like neutron stars. Instead, there could be a new class of magnetars (which are already a new class of neutron stars), that can release these occasional shrieks of radio.
Or maybe this repeating object is totally different from the single events that have been discovered so far.
Here’s my favorite idea. And honestly, the one that’s the least realistic. What I’m about to say is almost certainly not what’s going on. And yet, it can’t be ruled out, and that’s good enough for my fertile imagination.
Avi Loeb and Manasvi Lingam at Harvard University said the following about FRBs:
“Fast radio bursts are exceedingly bright given their short duration and origin at distances, and we haven’t identified a possible natural source with any confidence. An artificial origin is worth contemplating and checking.”
Artificial origin. So. Aliens. Nice.
Loeb and Lingam calculated how difficult it would be to send a signal that strong, that far across the Universe. They found that you’d need to build a solar array with twice the surface area of Earth to power the radio wave transmitter.
And what would you do with a transmission of radio or microwaves that strong? You’d use it to power a spacecraft, of course. What we’re seeing here on Earth is just the momentary flash as a propulsion beam sweeps past the Solar System like a lighthouse.
But in reality, this huge solar array would be firing out a constant beam of radiation that would propel a massive starship to tremendous speeds. Like the Breakthrough Starshot spacecraft, but for million tonne spaceships.
In other words, we could be witnessing alien transportation systems, pushing spacecraft with beams of energy to other worlds.
And I know that’s probably not what’s happening. It’s not aliens. It’s never aliens. But in my mind, that’s what I’m imagining.
So, kick back and enjoy the ride. Join us as we watch astronomers struggle to understand what fast radio bursts are. As they invalidate theories, and slowly unlock one of the most thrilling mysteries in modern astronomy. And as soon as they figure it out, I’ll let you know all about it.
What do you think? Which explanation for fast radio bursts seems the most logical to you? I’d love to hear your thoughts and wild speculation in the comments.
Into The Black? Maybe Radio Bursts Are From Outside The Galaxy After All, Study Says
Where are these radio bursts coming from? Astronomers have heard these signals from the sky several times, but always with the same telescope (Parkes Observatory in Australia). There was debate about whether these were coming from inside or outside the galaxy, or even from Earth itself (given only the one observatory was detecting them.)
A new study with a different telescope, the Arecibo Observatory in Puerto Rico, concludes that the bursts are from outside the galaxy. This is the first time one of these bursts have been found in the northern hemisphere of the sky.
“Our result is important because it eliminates any doubt that these radio bursts are truly of cosmic origin,” stated Victoria Kaspi, an astrophysics researcher at McGill University who participated in the research. “The radio waves show every sign of having come from far outside our galaxy – a really exciting prospect.”
Fast radio bursts are a flurry of radio waves that last a few thousandths of a second, and at any given minute there are only seven of these in the sky on average, according to the Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy. Their cause is unknown. They could be anything from black holes, to neutron stars coming together, to the magnetic field of pulsars (a type of neutron star) flaring up — or something else.

The pulse was found Nov. 2, 2012 in the constellation Auriga. Astronomers believe it is from quite far away from measuring its plasma dispersion, or the slowdown of radio waves as they crash into interstellar electrons. This particular source had triple the maximum dispersion than what would be found inside the galaxy, astronomers stated.
“The brightness and duration of this event, and the inferred rate at which these bursts occur, are all consistent with the properties of the bursts previously detected by the Parkes telescope in Australia,” stated Laura Spitler, who led the research. (She was at Cornell University when the study began, but is now at the Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy in Bonn, Germany.)
But other research has been back-and-forth on whether these are actually extragalactic bursts. One 2013 paper supposed it could be colliding neutron stars from far away, while another said it could instead be nearby stars flaring up.
The research was published in the Astrophysical Journal and is also available in preprint version on Arxiv.
Source: McGill University and the Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy