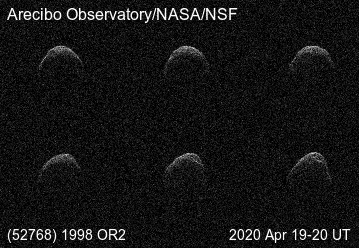
A fascinating asteroid named 1998 OR2 pays our neck of the inner solar system a visit early Wednesday morning, and if skies are clear, you might just get a chance to watch it slide by.
Continue reading “Watch Asteroid 1998 OR2 Zip Past Earth This Week”A Star is Orbiting the Milky Way’s Black Hole and Moving Exactly How Einstein Predicted it Should
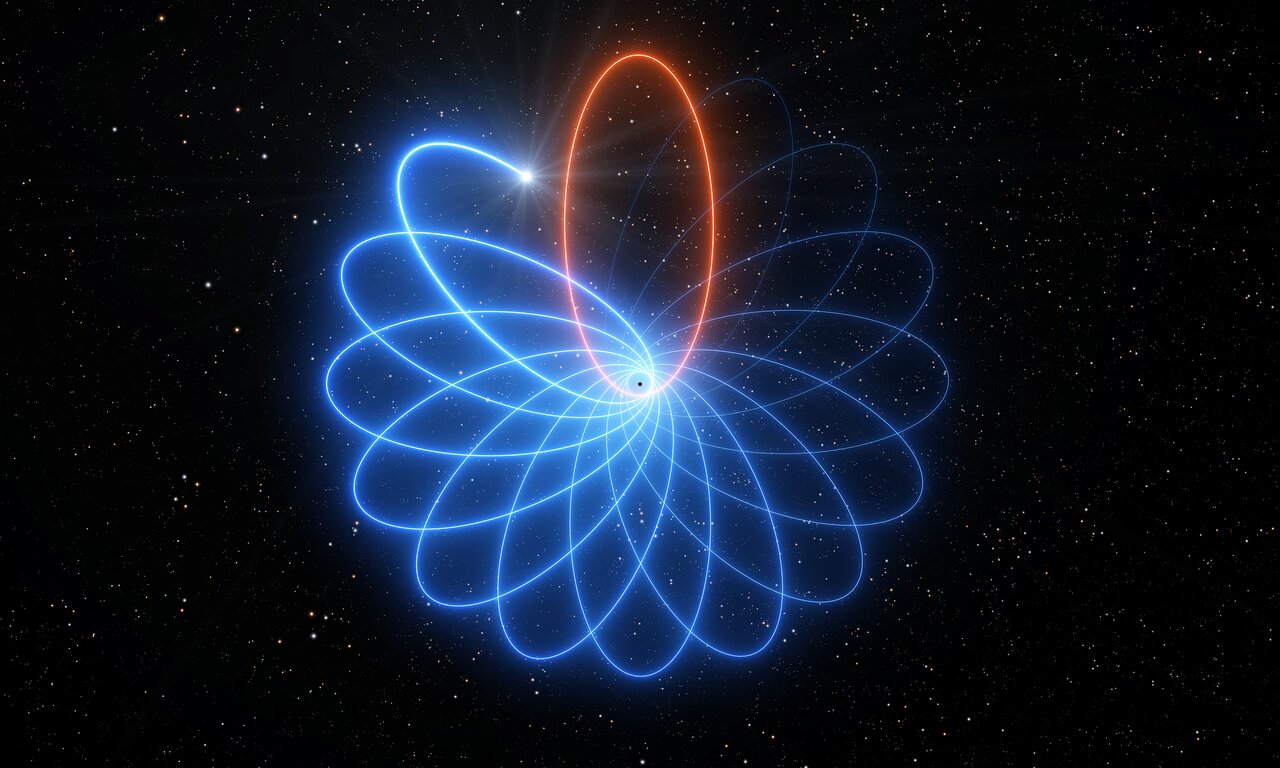
At the center of our galaxy, roughly 26,000 light-years from Earth, is the Supermassive Black Hole (SMBH) known as Sagittarius A*. The powerful gravity of this object and the dense cluster of stars around it provide astronomers with a unique environment for testing physics under the most extreme conditions. In particular, it offers them a chance to test Einstein’s Theory of General Relativity (GR).
For example, in the past thirty years, astronomers have been observing a star in the vicinity of Sagittarius A* (S2) to see if its orbit conforms to what is predicted by General Relativity. Recent observations made with the ESO’s Very Large Telescope (VLT) have completed an observation campaign that confirmed that the star’s orbit is rosette-shaped, once again proving that Einstein theory was right on the money!
Continue reading “A Star is Orbiting the Milky Way’s Black Hole and Moving Exactly How Einstein Predicted it Should”This is the Final Picture NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope
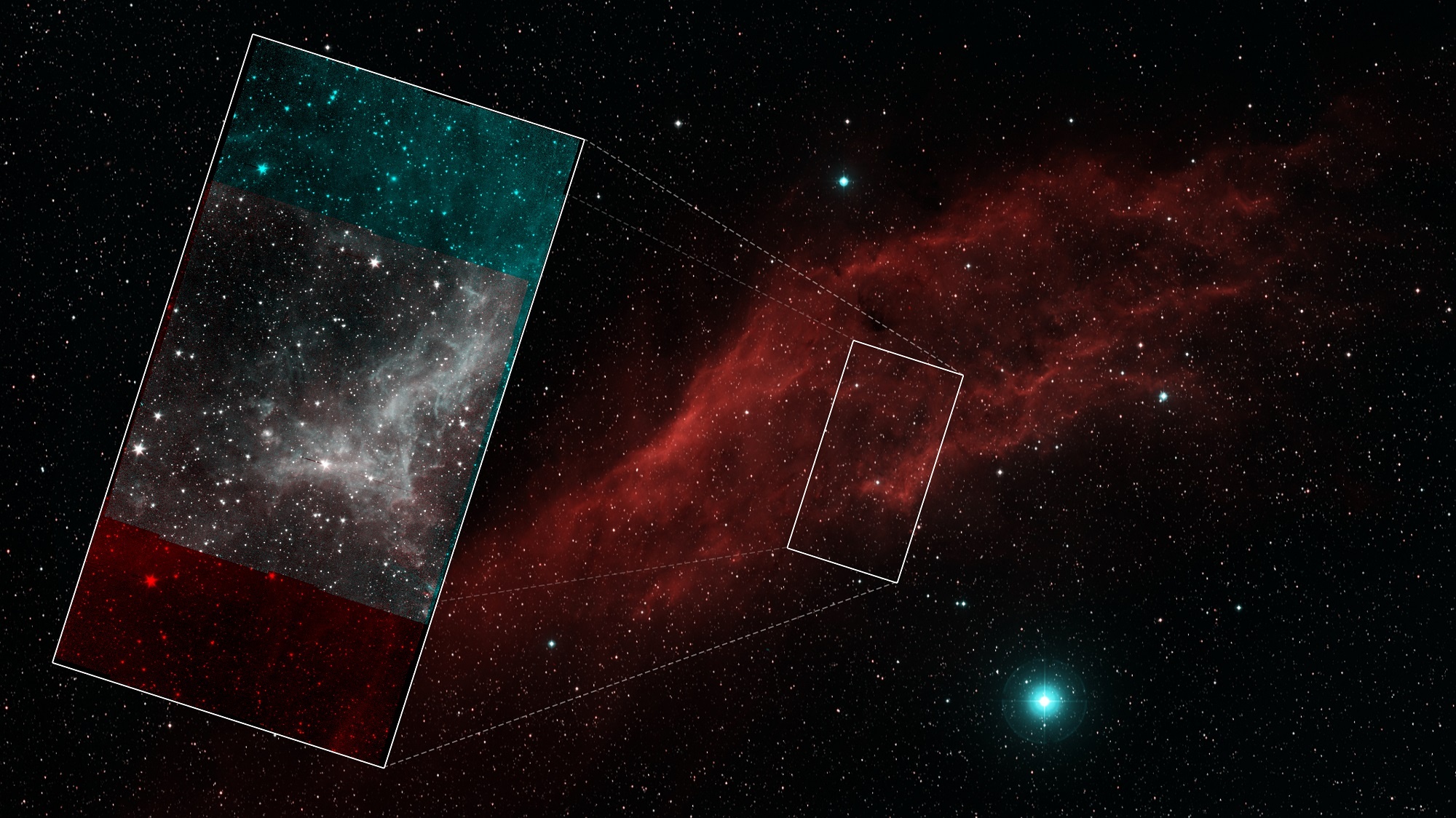

On Jan. 30th, 2020, NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope was retired after sixteen years of faithful service. As one of the four NASA Great Observatories – alongside Hubble, Chandra, and Compton space telescopes – Spitzer was dedicated to studying the Universe in infrared light. In so doing, it provided new insights into our Universe and enabled the study of objects and phenomena that would otherwise be impossible.
For instance, Spitzer was the first telescope to see light from an exoplanet and made important discoveries about comets, stars, and distant galaxies. It is therefore fitting that mission scientists decided to spend the last five days before the telescope was to be decommissioned capturing breathtaking images of the California Nebula, which were stitched into a mosaic and recently released to the public.
Continue reading “This is the Final Picture NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope”Astronomers Find a Six-Planet System Which Orbit in Lockstep With Each Other
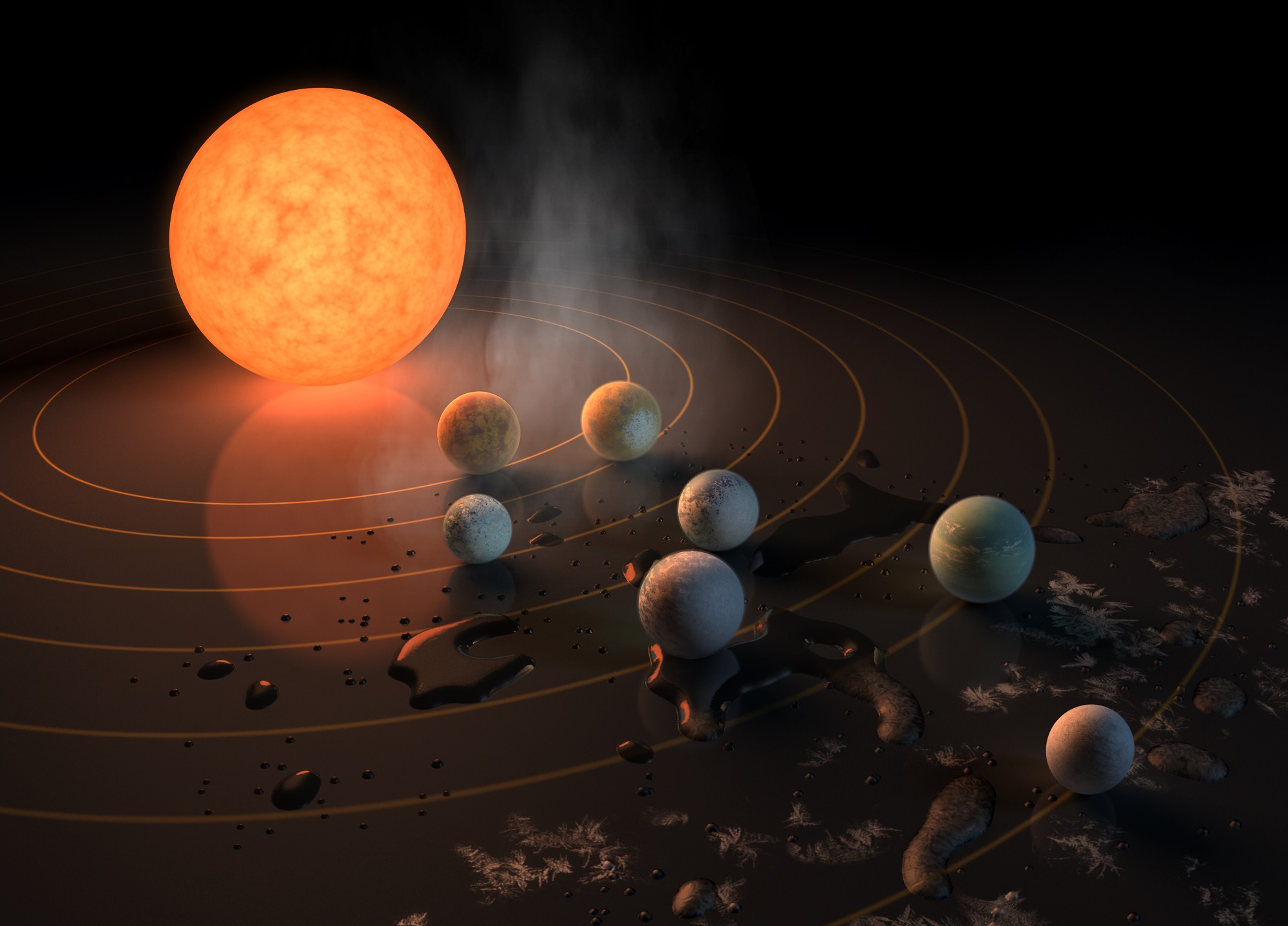

To date, astronomers have confirmed the existence of 4,152 extrasolar planets in 3,077 star systems. While the majority of these discoveries involved a single planet, several hundred star systems were found to be multi-planetary. Systems that contain six planets or more, however, appear to be rarer, with only a dozen or so cases discovered so far.
This is what astronomers found after observing HD 158259, a Sun-like star located about 88 light-years from Earth, for the past seven years using the SOPHIE spectrograph. Combined with new data from the Transiting Exoplanet Space Satellite (TESS), an international team reported the discovery of a six planet system where all were in near-perfect rhythm with each other.
Continue reading “Astronomers Find a Six-Planet System Which Orbit in Lockstep With Each Other”Astronomers Detected a Black Hole Merger With Very Different Mass Objects
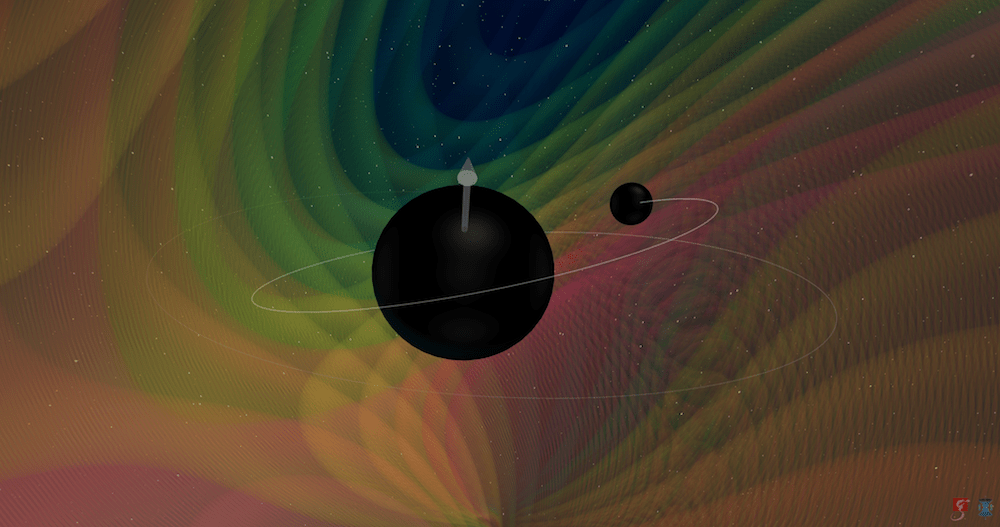
In another first, scientists at the LIGO and Virgo gravitational wave detectors announced a signal unlike anything they’ve ever seen before. While many black hole mergers have been detected thanks to LIGO and Virgo’s international network for detectors, this particular signal (GW190412) was the first where the two black holes had distinctly different masses.
Continue reading “Astronomers Detected a Black Hole Merger With Very Different Mass Objects”Hubble Sees a Galaxy With Spiral Arms, Surrounded by Other Spiral Arms
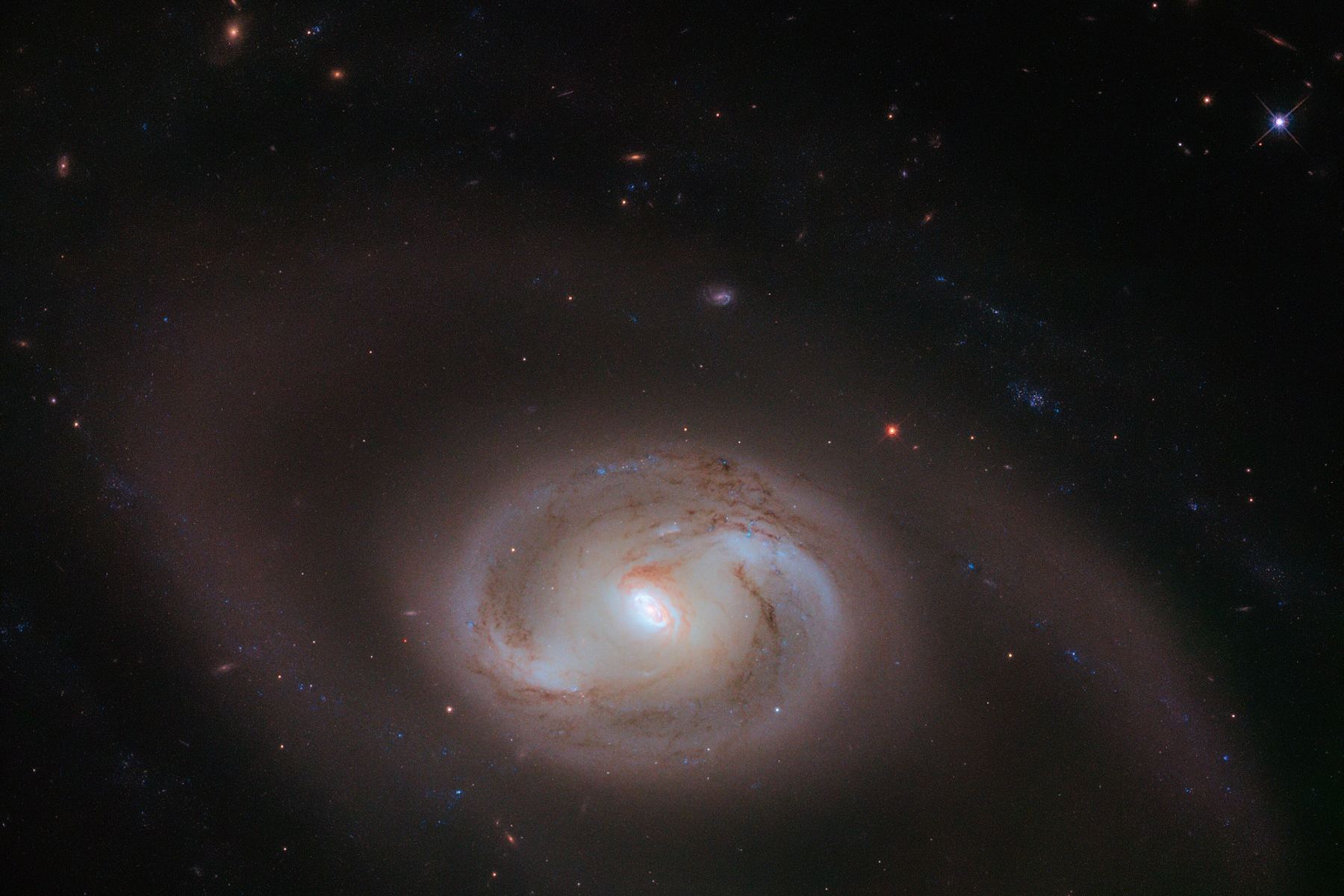
Even after thirty years of faithful service, the Hubble Space Telescope continues to reveal truly fascinating things about our Universe. This includes the image (shown at top) taken of the astronomical feature known as NGC 2273, a barred spiral galaxy similar to the Milky Way. However, upon closer inspection, the image reveals that the spiral arms of this galaxy contain a second set of spiral arms.
Continue reading “Hubble Sees a Galaxy With Spiral Arms, Surrounded by Other Spiral Arms”Interstellar Comet 2I/Borisov Formed in a Very Cold Environment
In the summer of 2019, a team of astronomers from NASA, the ESA, and the International Scientific Optical Network (ISON) announced the detection of the comet 2I/Borisov. This comet was the only second interstellar visitor observed passed through our Solar System, coming on the heels of the mysterious ‘Oumuamua. For this reason, astronomers from all over the world watched this comet intently as it made its closest pass to the Sun.
One such group, led by Martin Cordiner and Stefanie Milam of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, observed 2I/Borisov using the ESO’s Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) in the Chilean Andes. This allowed them to observe the gases 2I/Borisov released as it moved closer to our Sun, thus providing the first-ever chemical composition readings of an interstellar object.
Continue reading “Interstellar Comet 2I/Borisov Formed in a Very Cold Environment”Rocket Lab was Able to Catch Falling Inert Rocket Stage With a Helicopter, Continuing Their Path to Reusability
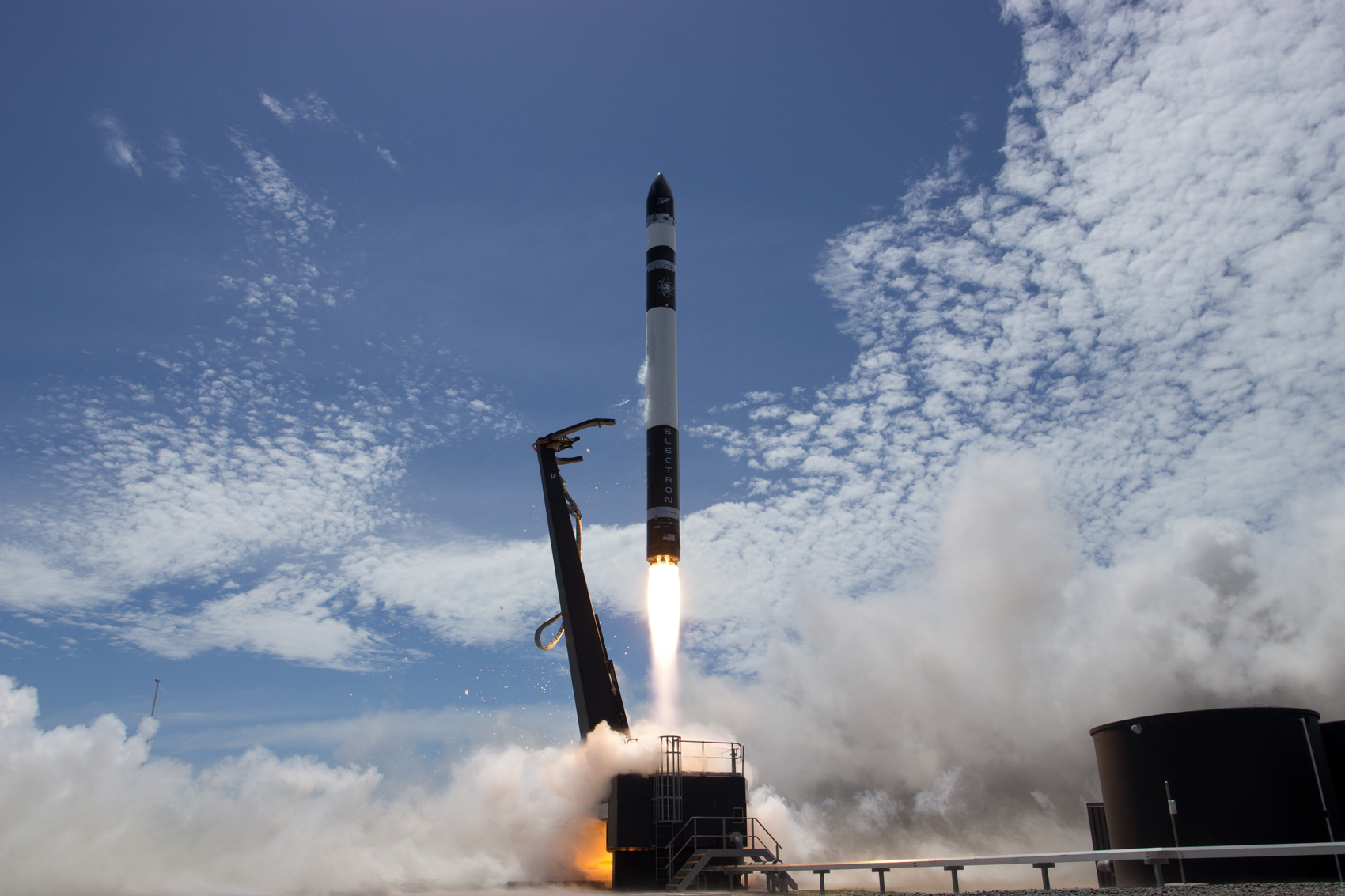
In the summer of 2017, the company Rocket Lab officially tossed its hat into the commercial aerospace (aka. NewSpace) ring with the first test flights of their two-stage Electron Rocket. Dedicated to providing cost-effective launch services for the small satellite market, the company began conducting commercial launches from their complexes in New Zealand and California using the lightweight Electron.
Looking to cut the costs associated with individual launches further, Rocket Lab has decided to pursue reusability as well. In early March, before the isolation orders were issued, the company achieved a major milestone when it conducted a successful mid-air recovery of the test stage of an Electron Rocket – which involved a helicopter catching the test stage after its parachute deployed.
Continue reading “Rocket Lab was Able to Catch Falling Inert Rocket Stage With a Helicopter, Continuing Their Path to Reusability”Catching the Peak of the 2020 April Lyrids
Stuck at home with clear skies? We’re all in a similar situation, as the ongoing pandemic sees most of the worldwide amateur astronomy community observing from home or from their backyard. One astronomical sure-fire event coming up this week requires no special equipment, just a set of working ‘Mk-1 eyeballs’ and a clear sky: the April Lyrids.
Continue reading “Catching the Peak of the 2020 April Lyrids”Astronomers Might Have Imaged a Second Planet Around Nearby Proxima Centauri – and it Might Have a Huge Set of Rings
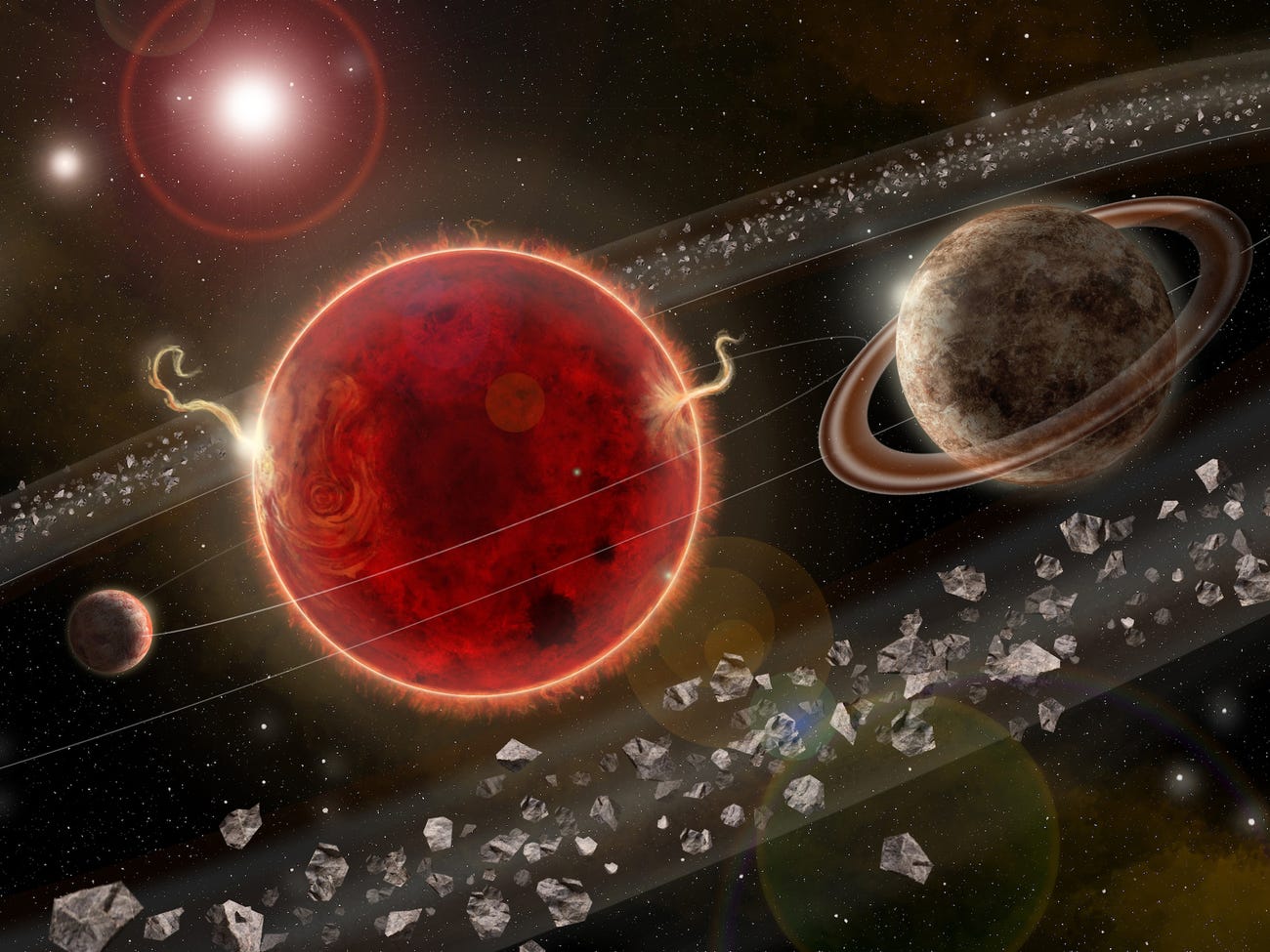
In 2016, astronomers working for the European Southern Observatory (ESO) confirmed the existence of a terrestrial planet around Earth’s closest stellar neighbor – Proxima Centauri. The discovery of this nearby extrasolar planet (Proxima b) caused no shortage of excitement because, in addition to being similar in size to Earth, it was found to orbit within the star’s habitable zone (HZ).
Thanks to an INAF-led team, a second exoplanet (a super-Earth) was found early this year around Proxima Centauri using the Radial Velocity Method. Based on the separation between the two planets, another INAF-led team attempted to observe this planet using the Direct Imaging Method. While not entirely successful, their observations raise the possibility that this planet has a system of rings around it, much like Saturn.
Continue reading “Astronomers Might Have Imaged a Second Planet Around Nearby Proxima Centauri – and it Might Have a Huge Set of Rings”