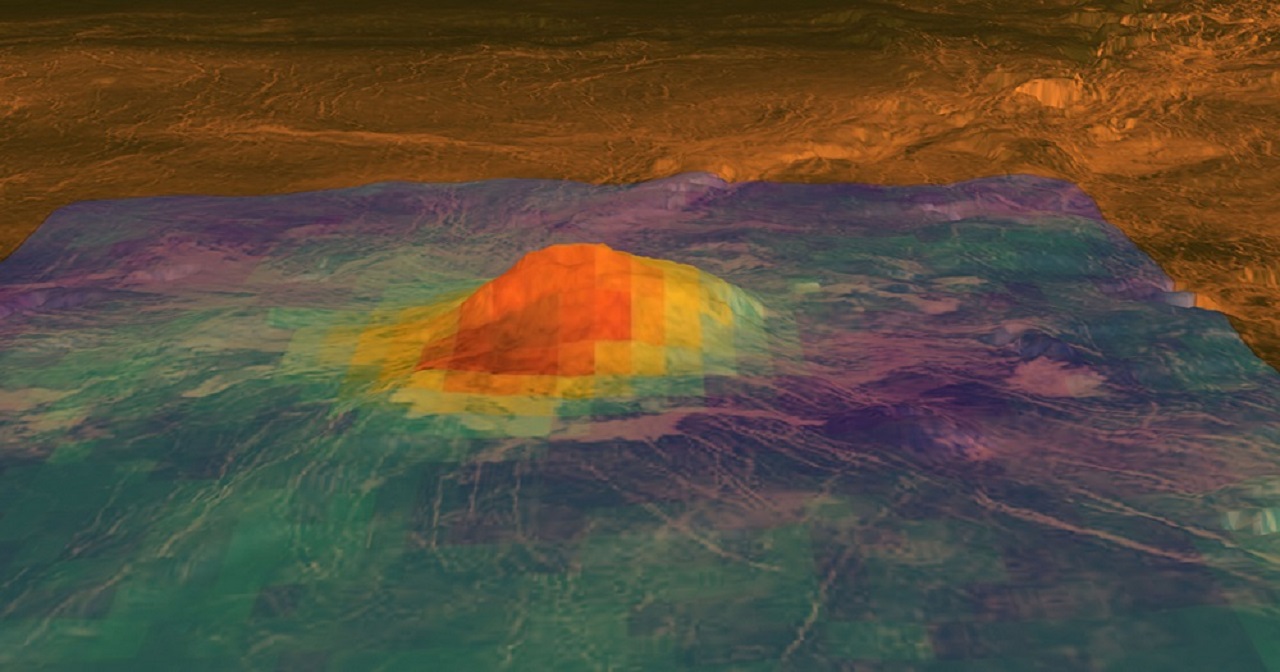
Despite the similarities our world has with Venus, there is still much don’t know about Earth’s “Sister planet” and how it came to be. Thanks to its super-dense and hazy atmosphere, there are still unresolved questions about the planet’s geological history. For example, despite the fact that Venus’ surface is dominated by volcanic features, scientists have remained uncertain whether or not the planet is still volcanically active today.
While the planet is known to have been volcanically active as recent as 2.5 million years ago, no concrete evidence has been found that there are still volcanic eruptions on Venus’ surface. However, new research led by the USRA’s Lunar and Planetary Institute (LPI) has shown that Venus may still have active volcanoes, making it the only other planet in the Solar System (other than Earth) that is still volcanically active today.
Continue reading “The Surprising Possibility That There are Still Active Volcanoes on Venus”