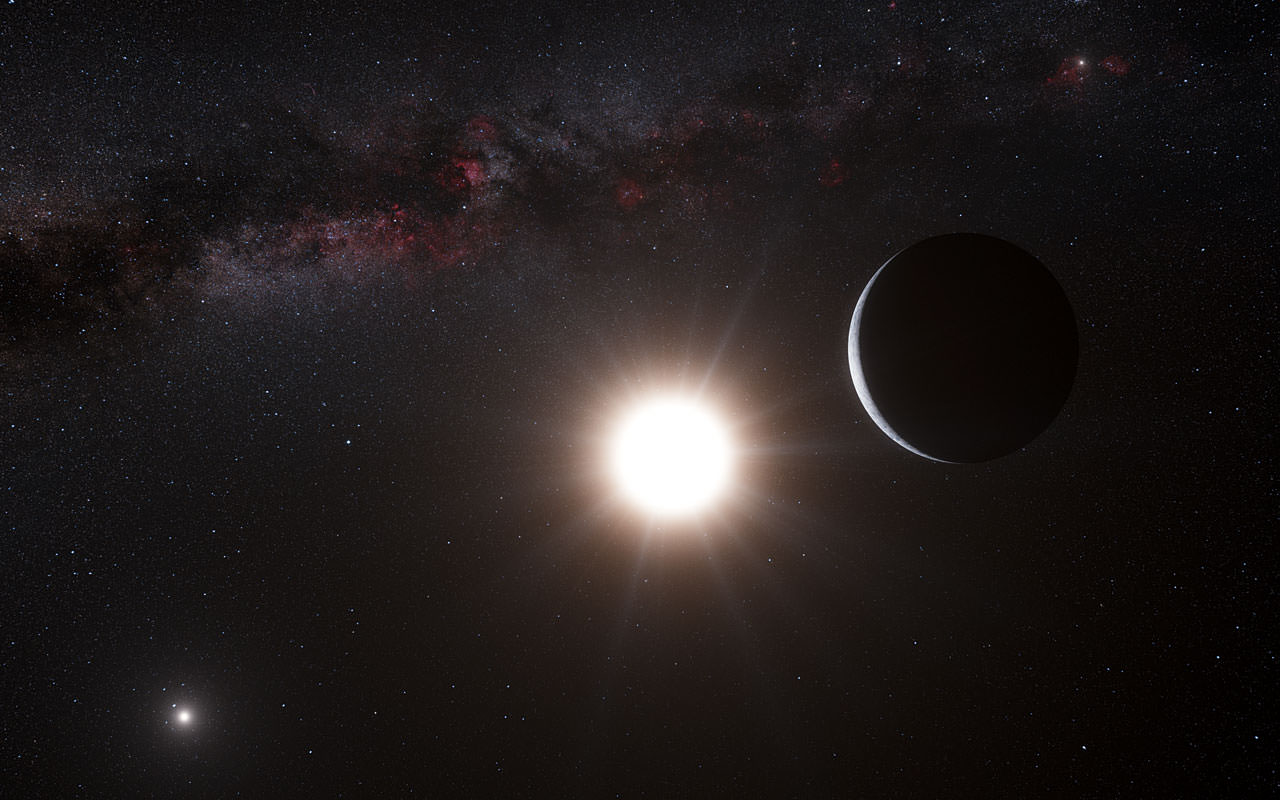
In the past, the number of known exoplanets has exploded, with 4093 confirmed detections so far (and another 4,727 candidates awaiting confirmation). With the discovery of so many planets that are dozens, hundreds, or even thousands of light years away, a great deal of attention has understandably been directed to our nearest stellar neighbors. Could planets be right next door, with the possibility of life being there as well?
While a potentially-habitable planet was recently discovered around Proxima Centauri (Proxima b), Alpha Centauri remains something of a question mark. But thanks to a recent study from the Georgia Institute of Technology (GIT), we might be getting closer to determining if this neighboring system supports life. In a twist, the study revealed that one of the stars in the binary system is more likely to be habitable than the other.
Continue reading “Of the Two Stars in Alpha Centauri, One is Probably More Habitable than the Other”