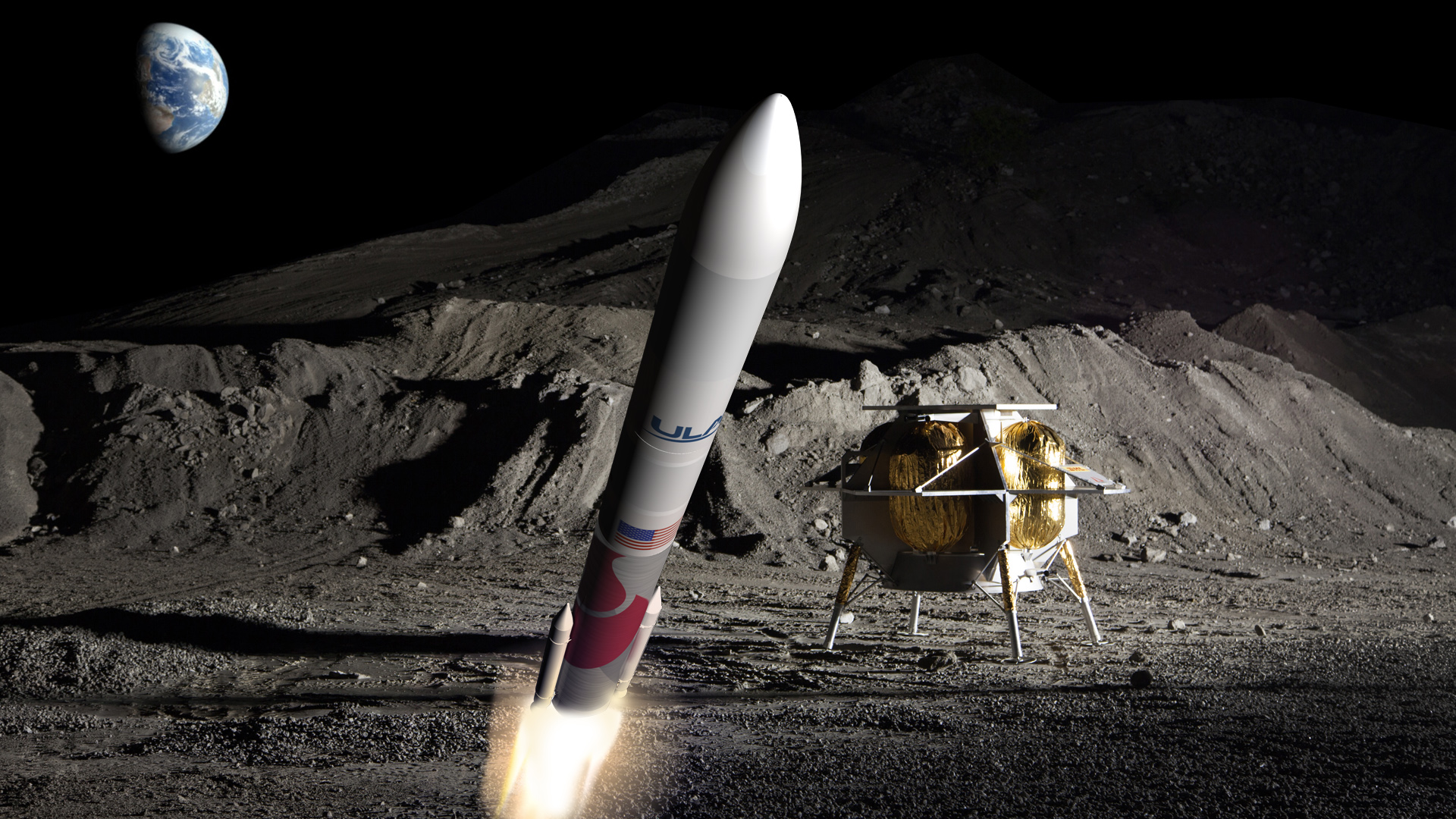
In May of 2019, NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) selected Astrobotic to fulfill a contract to deliver 14 payloads to the Moon by 2021. The Pittsburg-based aerospace company plans to do this using their Peregrine Lander, a robotic lunar spacecraft that is capable of delivering payloads to the Moon for the competitive price of $1.2 million per kilogram (~$544,300 per lbs).
To get the Peregrine lander and NASA’s payloads to the Moon, Astrobiotic recently announced that it would be relying on United Launch Alliance (ULA) to provide launch services. ULA will do this using their next-generation heavy-lift launch system known as the Vulcan Centaur rocket, which will also be the inaugural launch of this new vehicle.
Continue reading “Astrobotic is Going to Use a Vulcan Rocket For its Lunar Lander in 2021”