We live in an age of renewed space exploration, colloquially known as Space Age 2.0. Unlike the previous one, this new space age is characterized by inter-agency cooperation and collaboration between space agencies and the commercial space industry (aka. NewSpace). In addition to sending crews back to the Moon and onto Mars, a major objective of the current space age is the commercialization of Low Earth Orbit (LEO). That means large constellations of satellites, debris mitigation, and plenty of commercial space stations.
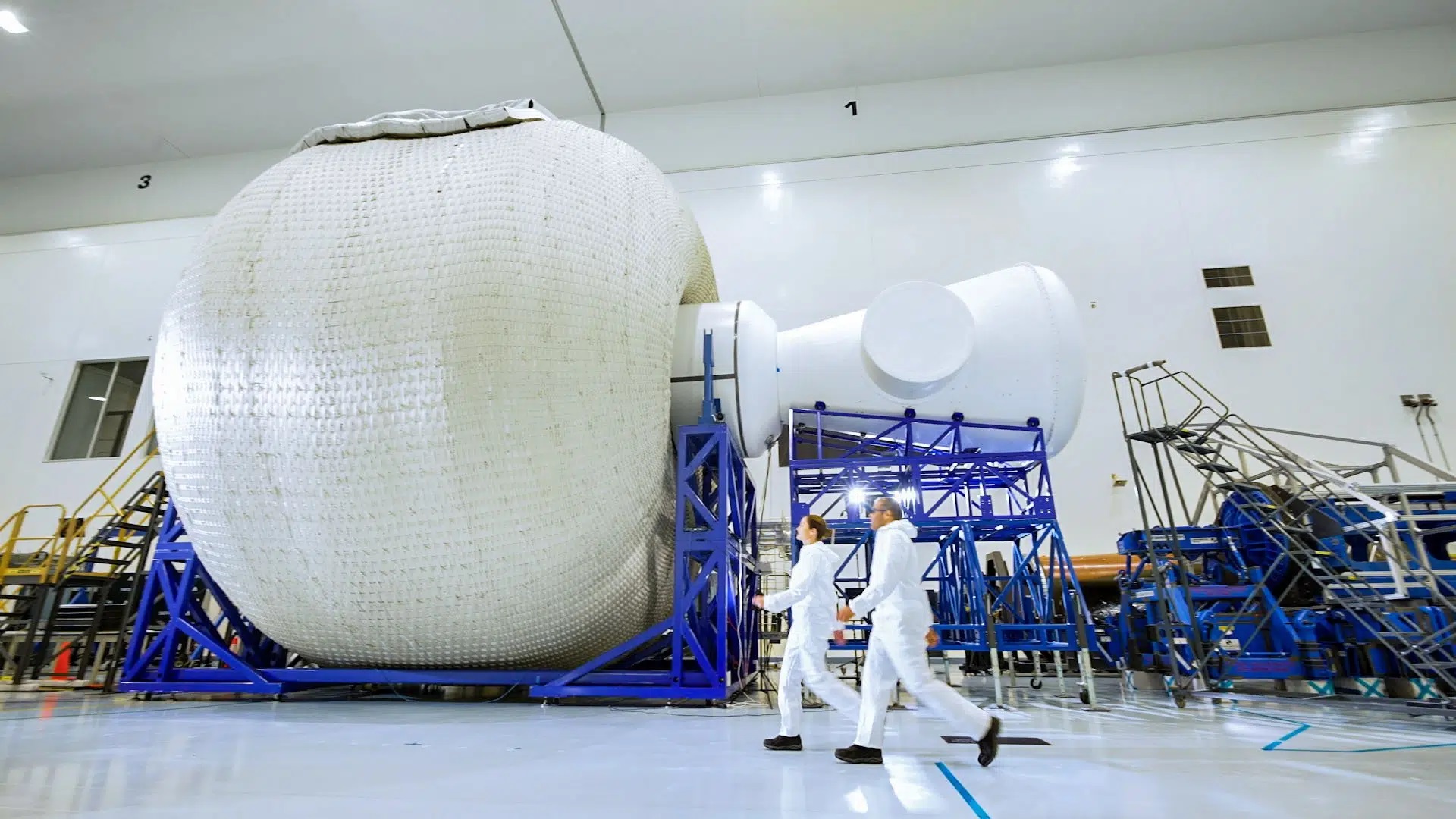
To accommodate this commercial presence in LEO, Sierra Space has developed the Large Integrated Flexible Environment (LIFE) habitat, an inflatable module that can be integrated into future space stations. As part of the Commercial Low Earth Orbit Development Program, NASA, Sierra Space, and ILC Dover (the Delaware-based engineering manufacturing company) recently conducted a full-scale burst pressure test of their LIFE habitat. The test occurred at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, and was caught on video (see below).
Continue reading “Watch a House-Sized Space Habitat (Intentionally) Burst”