The invention of the rocket changed space science forever. The Universe could only be inspected from the surface of the Earth, with all that atmosphere in the way, until rockets were invented. And as far as the modern age of rocketry goes, it all started 90 years ago with Robert Goddard’s liquid-fuelled rocket.
Goddard was a dreamer. He envisioned rocket-powered spacecraft plying the solar system. Obviously, he passed away before interplanetary travel materialized, but his work on rocketry certainly laid the groundwork for that eventual achievement. The Goddard Space Flight Center is named after him, and it’s doubtful that any engineering or technology student in the world doesn’t know who he is.
Goddard’s first liquid-fuelled rocket was modest by today’s standards, of course. But he had to solve several technical challenges to achieve it, and his ability to solve these challenges led to not only this first flight, but to a total of 34 rocket flights in 15 years, from 1926 to 1941. His rockets reached the altitude of 2.6 km (1.6 miles) and speeds of 885 km/h (550 mph.) He also patented 214 inventions.
Goddard is considered the father of modern rocket science, but he is actually one of three men who are considered the main contributors to modern rocketry. Russian Konstantin Tsiolkovsky (1858-1935) and German Hermann Oberth (1894-1989) are the other founding fathers of modern rocketry.
Goddard didn’t invent rocketry, of course. The Chinese used rockets as far back as the 13th century, and rockets made appearances throughout history as weapons and fireworks. But Goddard’s success at liquid-fuelled rocketry, and the capabilities that came with it, is when rocketry really got off the ground. (Sorry.)
Nowadays, Goddard is understood to be a driven and highly-intelligent person, the type of person who is responsible for advancing science and technology. But back in his time, before he had successful flights, he and his ideas were ridiculed. Check out this criticism from the New York Times, January 13th, 1920:
“That Professor Goddard, with his ‘chair’ in Clark College and the countenancing of the Smithsonian Institution, does not know the relation of action to reaction, and of the need to have something better than a vacuum against which to react — to say that would be absurd. Of course he only seems to lack the knowledge ladled out daily in high schools.”
Stinging words, to be sure, but people who know anything about the history of science are familiar with this kind of condemnation of brilliant people, coming from those who lack vision.
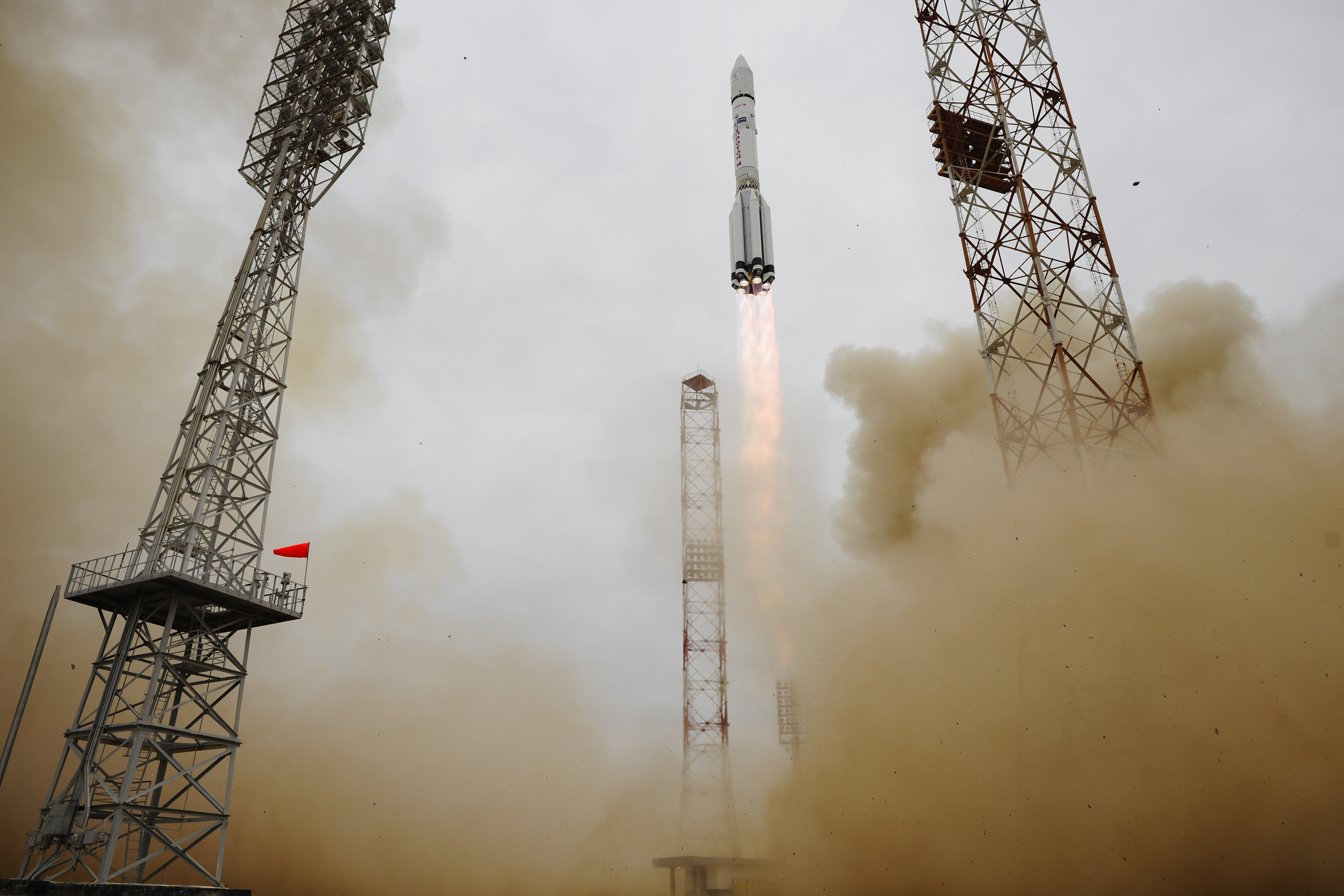
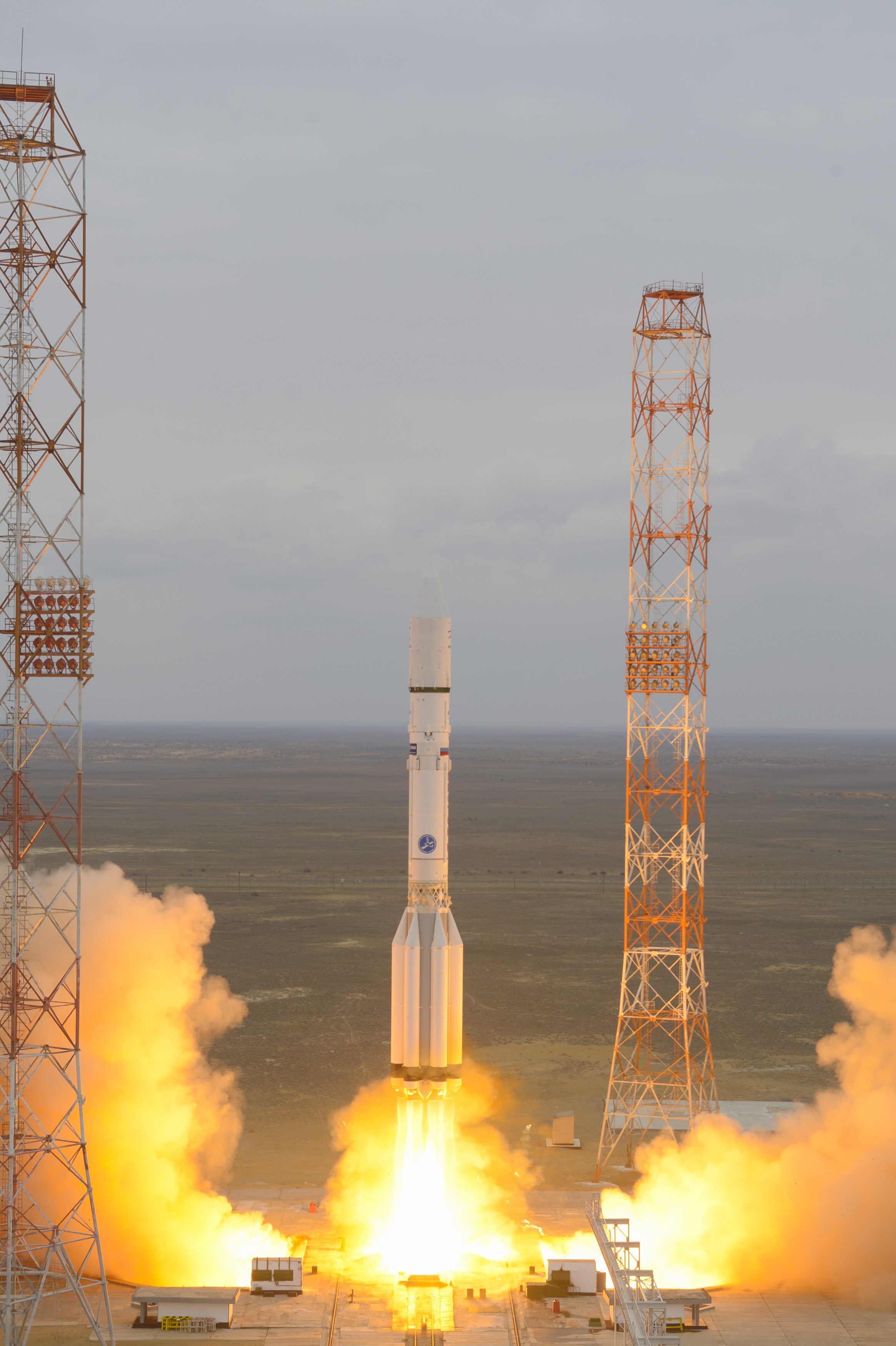
Now of course, we have huge rockets. Great thundering beasts that lift enormous loads out of Earth’s gravity well. And we’re so accustomed to rocket launches now that they barely make news. But I always get a kick out of imagining what people like Goddard would feel if they were able to view a launch of one of today’s behemoths, like the Ariane 5. I’m sure his chest would swelled with pride, and he would be amazed at what people have accomplished.
But his vindication wouldn’t just come from the huge leaps we’ve made in rocket technology, and the huge rockets we now routinely launch. It would also come from this retraction, delivered decades too late but with class, by the New York Times, on July 17 1969, the day after Apollo 11 launched:
Further investigation and experimentation have confirmed the findings of Isaac Newton in the 17th Century and it is now definitely established that a rocket can function in a vacuum as well as in an atmosphere. The Times regrets the error.