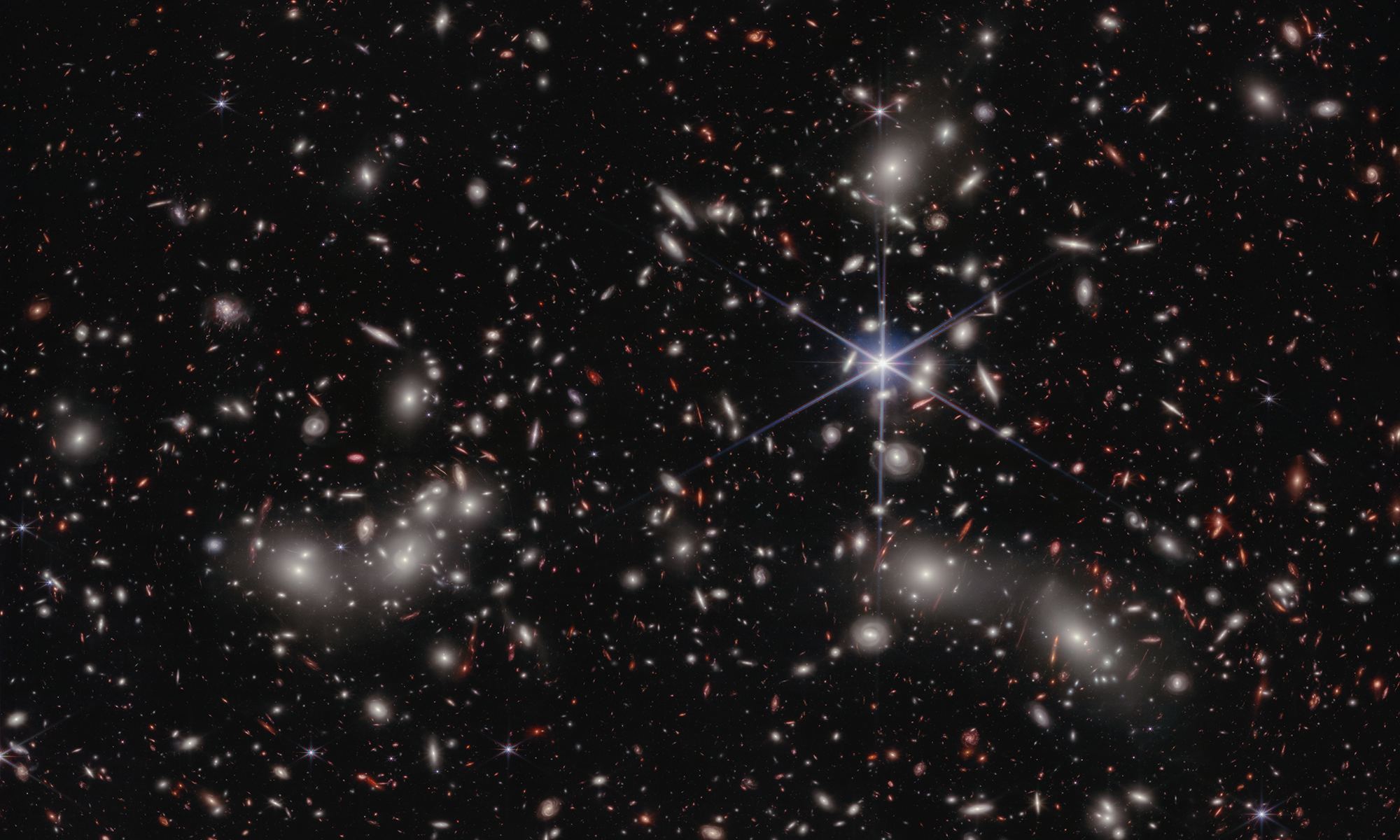
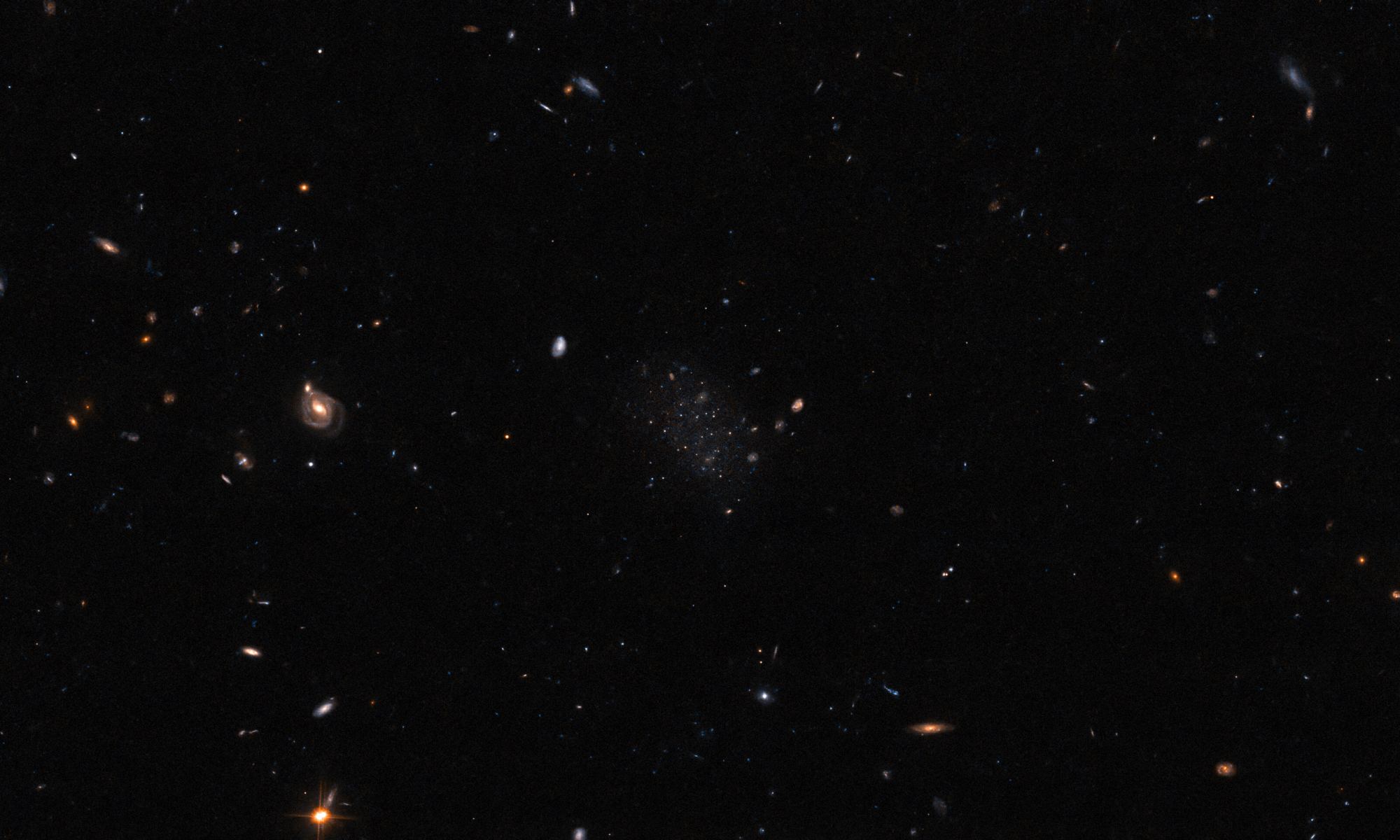
As the successor to the venerable Hubble Space Telescope, one of the main duties of the James Webb Space Telescope has been to take deep-field images of iconic cosmic objects and structures. The JWST’s next-generation instruments and improved resolution provide breathtakingly detailed images, allowing astronomers to learn more about the cosmos and the laws that govern it. The latest JWST deep-field is of a region of space known as Abell 7244 – aka. Pandora’s Cluster – where three galaxy clusters are in the process of coming together to form a megacluster.
Continue reading “Webb Sees Three Galaxy Clusters Coming Together to Form a Megacluster”Webb Sees Three Galaxy Clusters Coming Together to Form a Megacluster