In the past century, astronomers have learned a great deal about the cosmos and our place in it. From discovering that the Universe is in a constant state of expansion to the discovery of the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) and the Big Bang cosmological model, our perception of the cosmos has expanded immensely. And yet, many of the most profound astronomical discoveries still occur within our cosmic backyard – the Milky Way Galaxy.
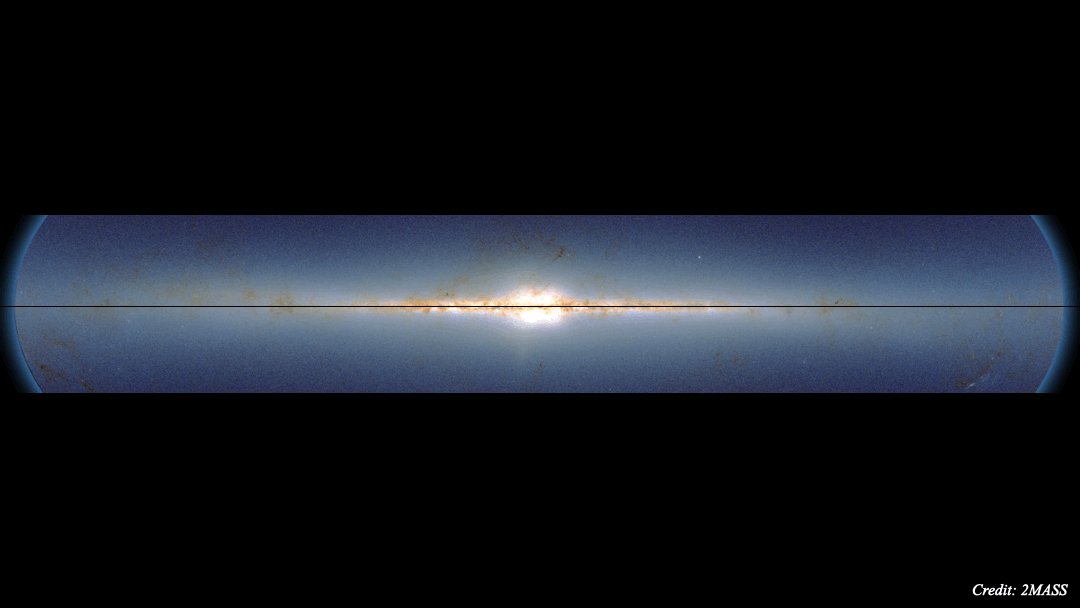
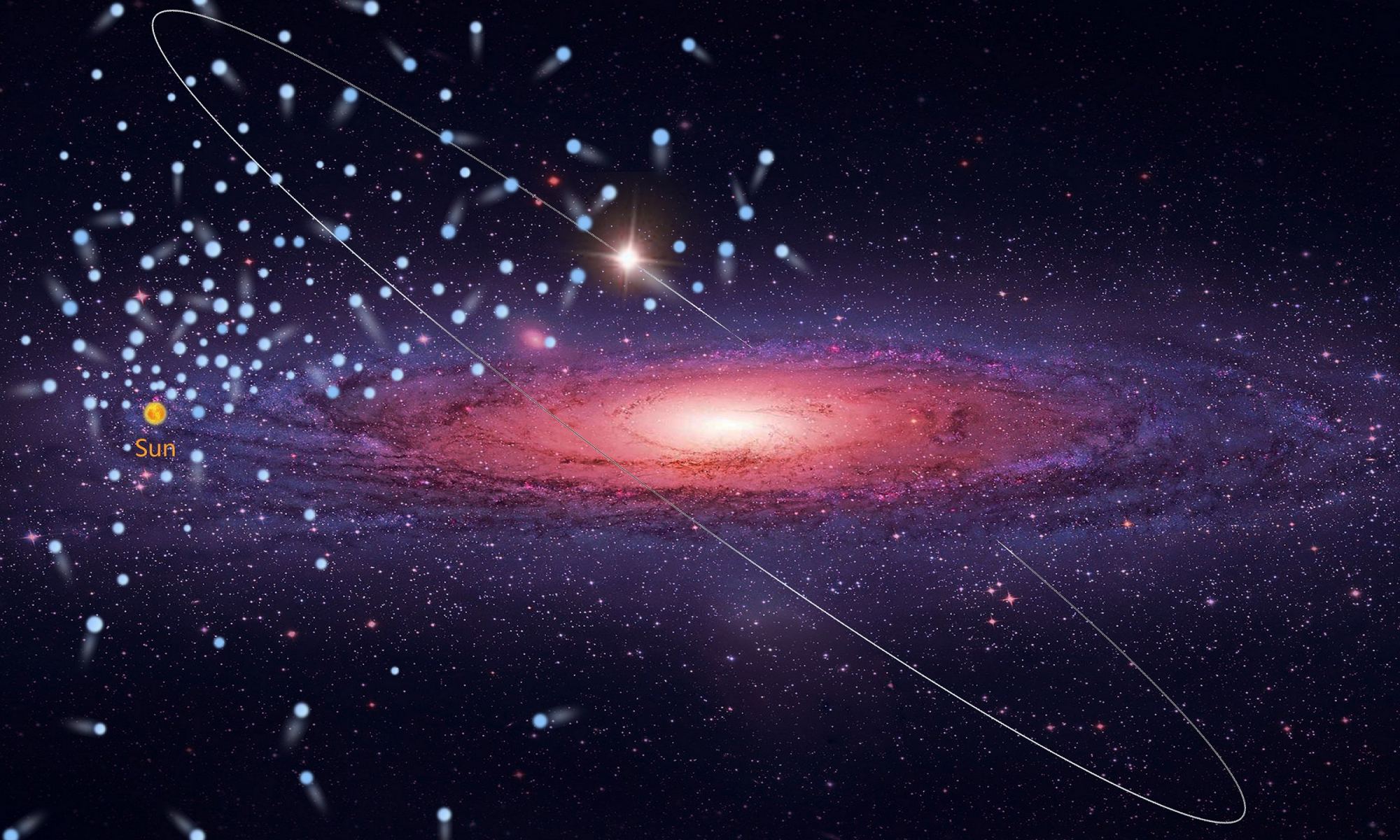
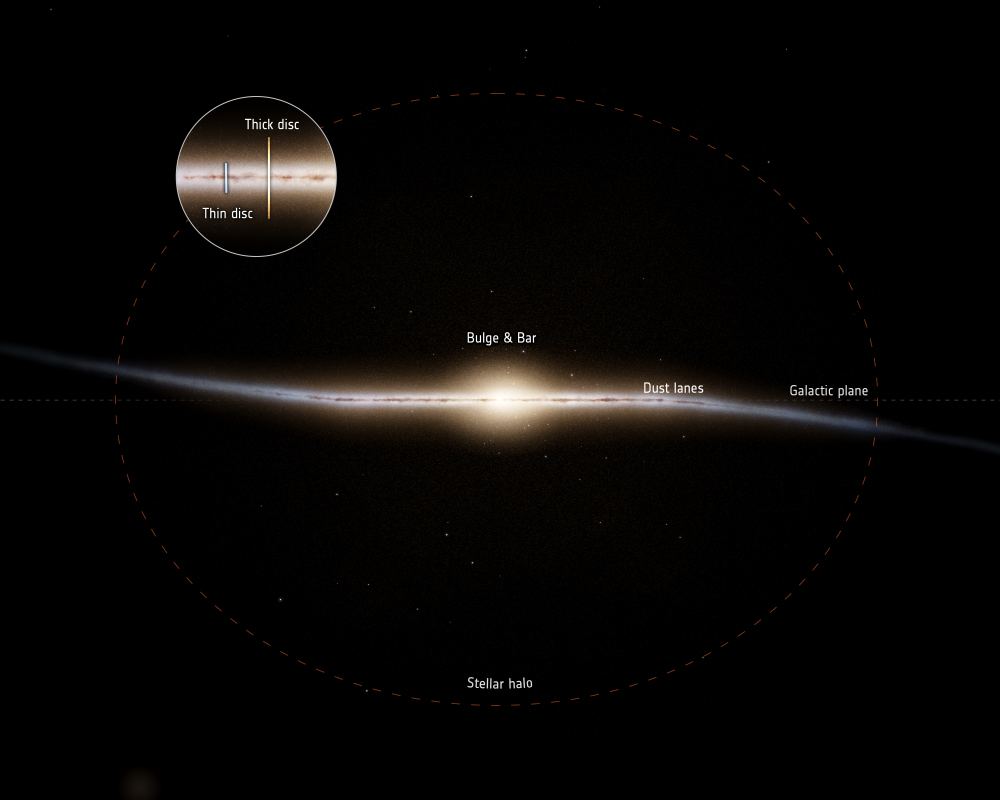
Compared to other galaxies, which astronomers can resolve with relative ease, the structure and size of the Milky Way have been the subject of ongoing discovery. The most recent comes from the Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics (MPE), where scientists have found a previously undiscovered inner ring of metal-rich stars just outside the Galactic Bar. The existence of this ring has revealed new insights into star formation in this region of the galaxy during its early history.
Continue reading “The Milky Way has an Inner Ring, Just Outside the Core”