The early moments of the universe were turbulent and filled with hot and dense matter. Fluctuations in the early universe could have been great enough that stellar-mass pockets of matter collapsed under their own weight to create primordial black holes. Although we’ve never detected these small black holes, they could have played a vital role in cosmic evolution, perhaps growing into the supermassive black holes we see today. A new study shows how this could work, but also finds the process is complicated.
Continue reading “Primordial Black Holes Could Have Triggered the Formation of Supermassive Black Holes”Supermassive Black Holes Shut Down Star Formation

One of the key aspects of galactic evolution is star production. On a basic level, stars form within a galaxy’s gas and dust all the time, and where they form can help determine a galaxy’s shape and size. But there seems to be a sweet point when star production in a galaxy is particularly strong. Galaxies often have a period of rapid star production which then drops off. Astronomers are still trying to understand what causes this drop-off.
Continue reading “Supermassive Black Holes Shut Down Star Formation”The Milky Way’s Most Recent Meal was a Galaxy it Gobbled up 8-10 Billion Years ago

A central aspect of galactic evolution is that they must eat or be eaten. Dark energy strives to push galaxies apart, but gravity tries to pull them together. As a result, galaxies tend to form into local groups. As these superclusters of galaxies become more isolated due to cosmic expansion, they gravitationally turn on each other, and in time the largest galaxies of the group will consume the smaller ones. The Milky Way is one of the larger galaxies in our local group, and so it has consumed smaller galaxies in the past. But piecing together the history of these galactic meals is a real challenge.
Continue reading “The Milky Way’s Most Recent Meal was a Galaxy it Gobbled up 8-10 Billion Years ago”The Milky Way Hasn’t Been Evenly Mixed

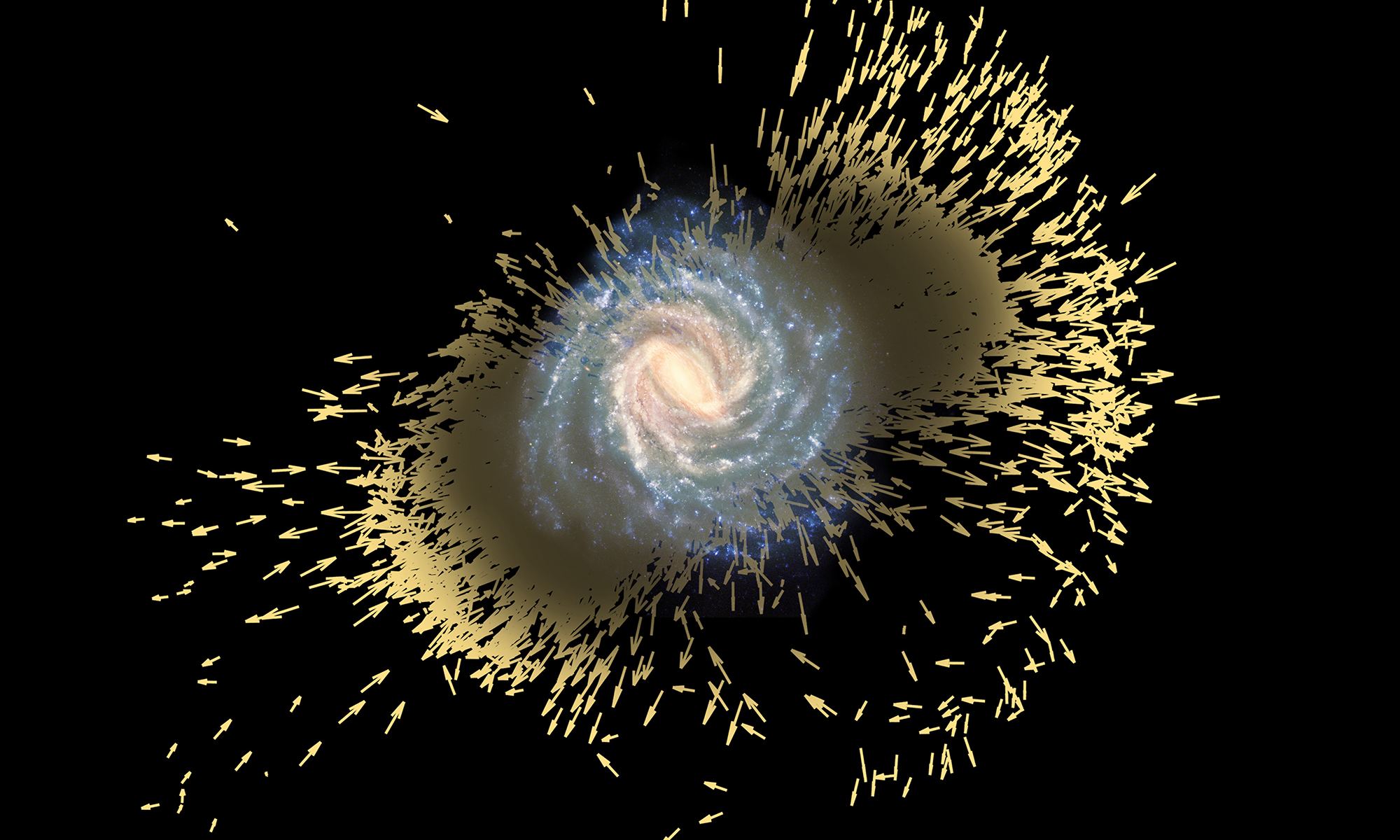
Gas from the intergalactic medium constantly rains down on galaxies, fueling continued star formation. New research has shown that this gas is not evenly mixed, and stars are not equal across the galaxy. This result means that solar systems are not the same within the Milky Way.
Continue reading “The Milky Way Hasn’t Been Evenly Mixed”Supermassive Black Hole Winds Were Already Blowing Less Than a Billion Years After the Big Bang

At the heart of most galaxies is a supermassive black hole. These beasts of gravity can play a crucial role in the formation and evolution of their galaxy. But astronomers still don’t fully understand when the influence of black holes becomes significant. Did large black holes form early in the universe, causing galaxies to form around them? Or did black holes grow after its primordial galaxy had begun to form? You might call this the chicken or egg problem. But a recent study suggests that galaxies and their supermassive black holes can have a mutual interaction that allows them to co-evolve.
Continue reading “Supermassive Black Hole Winds Were Already Blowing Less Than a Billion Years After the Big Bang”Nearby Ancient Dwarf Galaxies Have a Surprising Amount of Dark Matter

Around the Milky Way, there are literally dozens of dwarf galaxies that continue to be slowly absorbed into our own. These galaxies are a major source of interest for astronomers because they can teach us a great deal about cosmic evolution, like how smaller galaxies merged over time to create larger structures. Since they are thought to be relics of the very first galaxies in the Universe, they are also akin to “galactic fossils.”
Recently, a team of astrophysicists from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) observed one of the most ancient of these galaxies (Tucana II) and noticed something unexpected. At the edge of the galaxy, they observed stars in a configuration that suggest that Tucana II has an extended Dark Matter halo. These findings imply that the most ancient galaxies in the Universe had more Dark Matter than previously thought.
Continue reading “Nearby Ancient Dwarf Galaxies Have a Surprising Amount of Dark Matter”Some of the Milky Way’s oldest stars aren’t where they’re expected to be
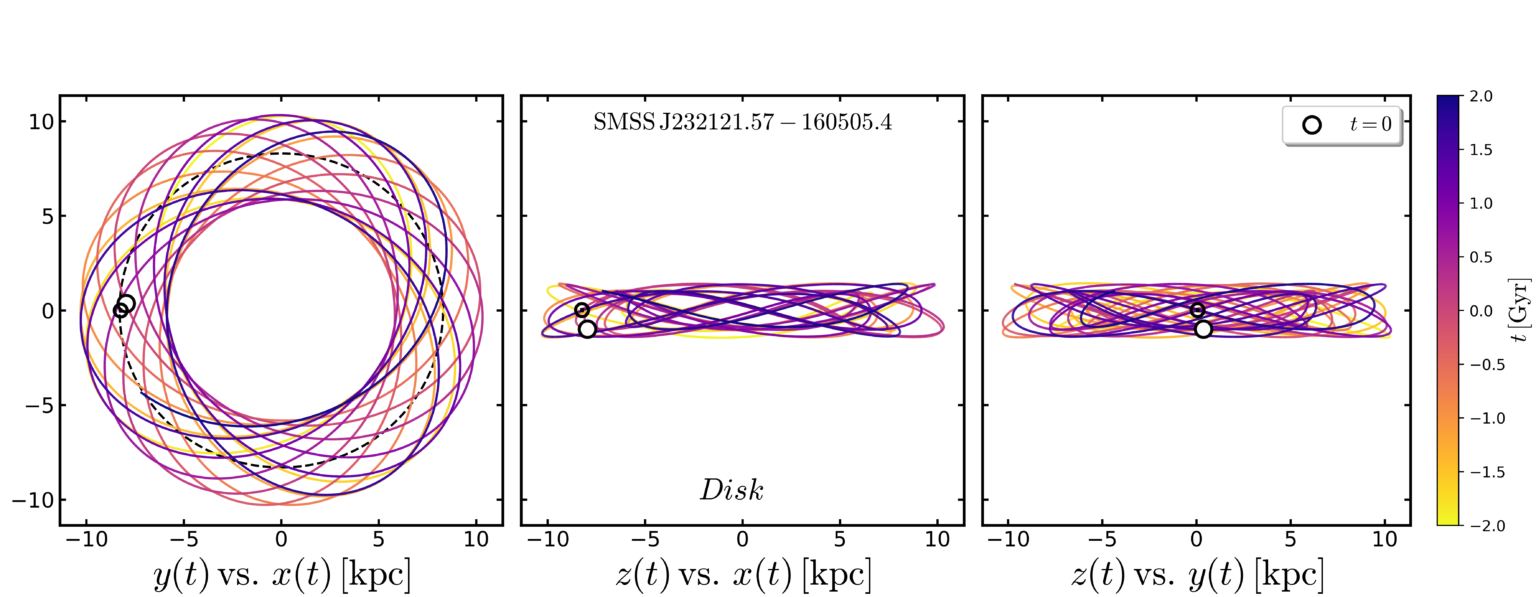
One of the ways we categorize stars is by their metallicity. That is the fraction of heavier elements a star has compared to hydrogen and helium. It’s a useful metric because the metallicity of a star is a good measure of its age.
Continue reading “Some of the Milky Way’s oldest stars aren’t where they’re expected to be”The family tree of the Milky Way. The mergers that gave us the galaxy we see today
Galaxies build themselves up slowly over time by cannibalizing their neighbors. Using an advanced suite of computer simulations, researchers have now traced back the evolutionary history of our own Milky Way.
Continue reading “The family tree of the Milky Way. The mergers that gave us the galaxy we see today”7% of the Stars in the Milky Way’s Center Came From a Single Globular Cluster That Got Too Close and Was Broken Up
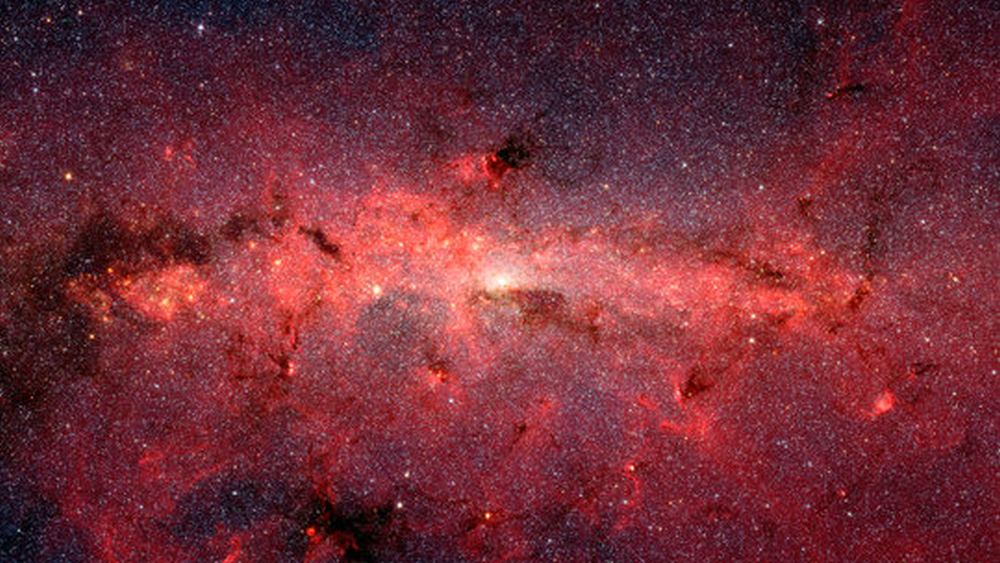

The heart of the Milky Way can be a mysterious place. A gigantic black hole resides there, and it’s surrounded by a retinue of stars that astronomers call a Nuclear Star Cluster (NSC). The NSC is one of the densest populations of stars in the Universe. There are about 20 million stars in the innermost 26 light years of the galaxy.
New research shows that about 7% of the stars in the NSC came from a single source: a globular cluster of stars that fell into the Milky Way between 3 and 5 billion years ago.
Continue reading “7% of the Stars in the Milky Way’s Center Came From a Single Globular Cluster That Got Too Close and Was Broken Up”What Shuts Down a Galaxy’s Star Formation?

In the 1920s, Edwin Hubble studied hundreds of galaxies. He found that they tended to fall into a few broad types. Some contained elegant spirals of bright stars, while others were spherical or elliptical with little or no internal structure. In 1926 he developed a classification scheme for galaxies, now known as Hubble’s Tuning Fork.
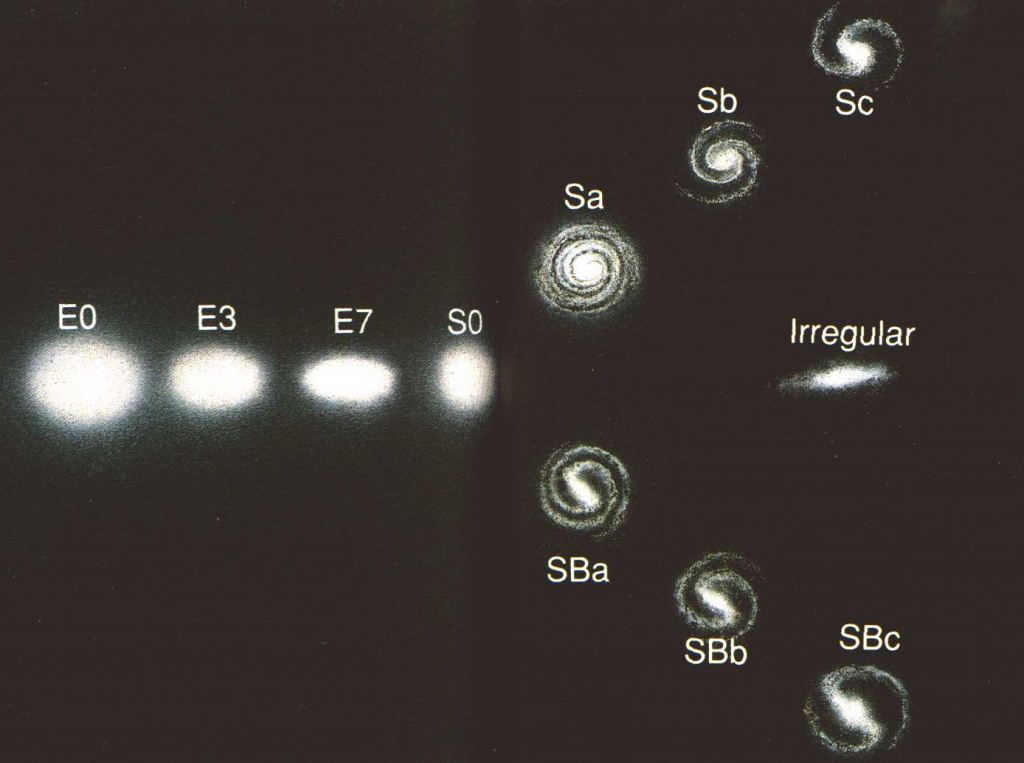
When you look at Hubble’s scheme, it suggests an evolution of galaxies, beginning as an elliptical galaxy, then flattening and shifting into a spiral galaxy. While many saw this as a reasonable model, Hubble cautioned against jumping to conclusions. We now know ellipticals do not evolve into spirals, and the evolution of galaxies is complex. But Hubble’s scheme marks the beginning of the attempt to understand how galaxies grow, live, and die.
Continue reading “What Shuts Down a Galaxy’s Star Formation?”