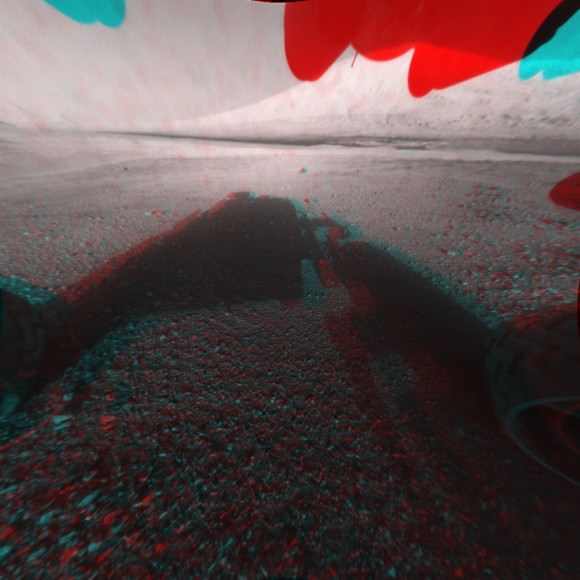
Image Caption: Rover’s Self Portrait -This Picasso-like self portrait of NASA’s Curiosity rover was taken by its Navigation cameras, located on the now-upright mast. The camera snapped pictures 360-degrees around the rover, while pointing down at the rover deck, up and straight ahead. Those images are shown here in a polar projection. Most of the tiles are thumbnails, or small copies of the full-resolution images that have not been sent back to Earth yet. Two of the tiles are full-resolution. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech.
See below the 1st 360 degree panorama from Curiosity and an enhanced Sol 2 mosaic of the full resolution view of the north rim of Gale Crater by this author
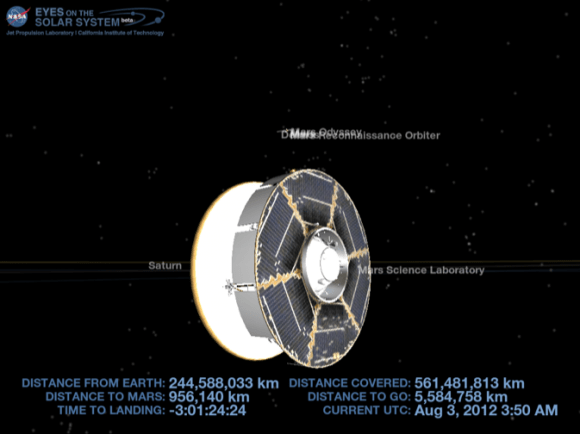
The rover Curiosity continues her marathon run of milestone achievements – snapping her 1st self portrait and 1st 360 degree panorama since touchdown inside Gale Crater barely over 2 sols, or Martian days ago.
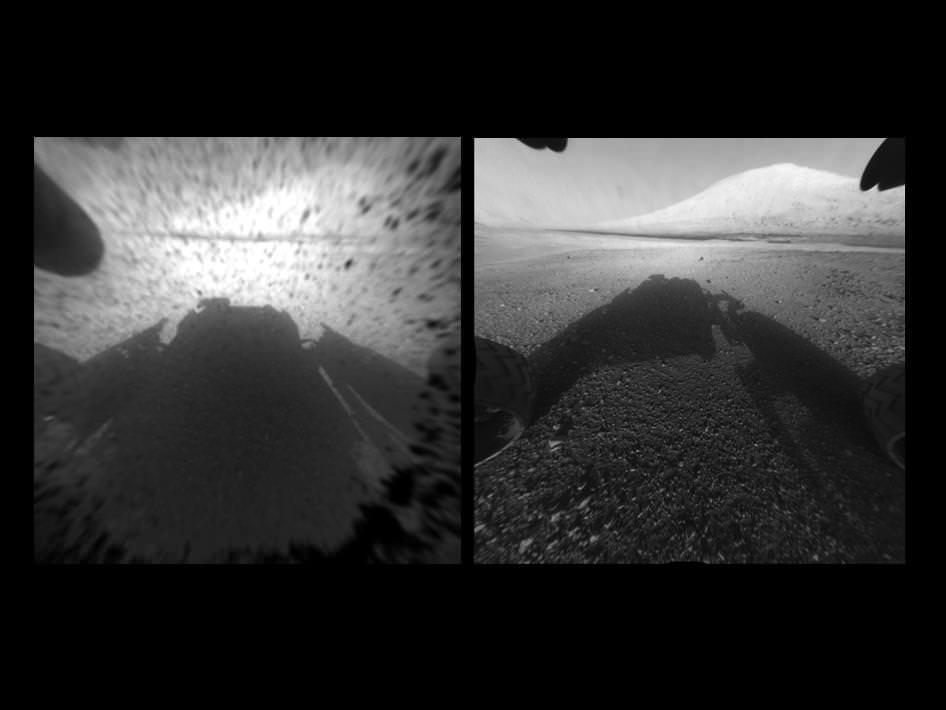
To take all these new images, Curiosity used a new camera, the just-activated higher resolution navigation cameras (Navcam) positioned on the mast. Several of the new images provide the best taste yet of the stupendous vistas coming soon. See our enhanced Sol 2 mosaic below.
The 3.6 foot-tall (1.1 meter) camera mast on the rover deck was just raised and activated earlier today, Wednesday, Aug. 8.
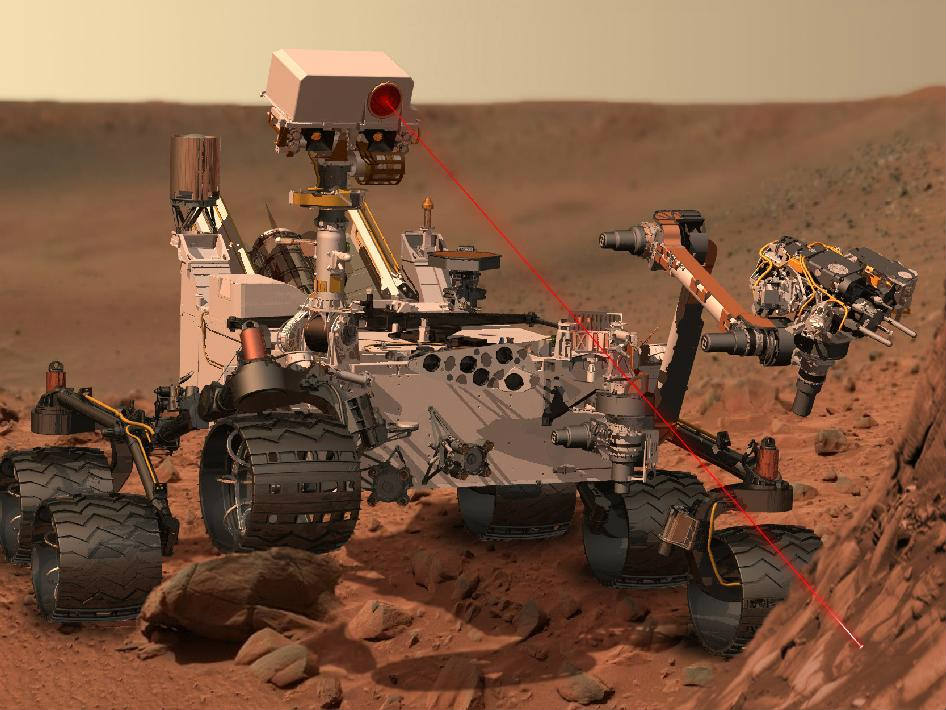
The mast deployment is absolutely crucial to Curiosity’s science mission. It is also loaded with the high resolution MastCam cameras and the ChemCam instrument with the laser rock zapper.
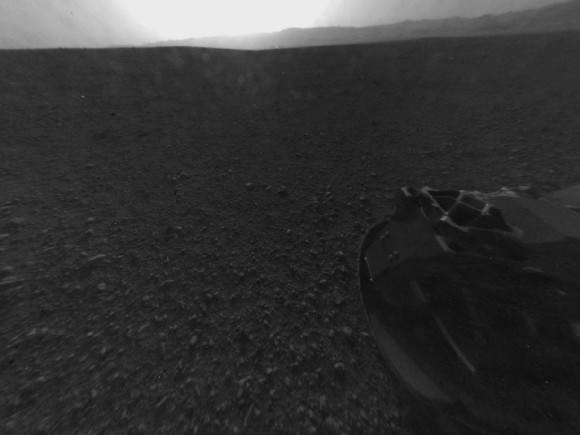
Most of the images Navcam images beamed back today were lower-resolution thumbnails. But 2 high-resolution Navcams from the panorama and the self portrait were also downlinked and provide the clearest view yet of the breathtaking terrain surrounding Curiosity in every direction.
“The full frame navcams show the north rim of Gale Crater,” said Justin Maki, MSL navcam lead, at a briefing today at JPL. “The Navcam’s are identical to the MER Navcam’s.”
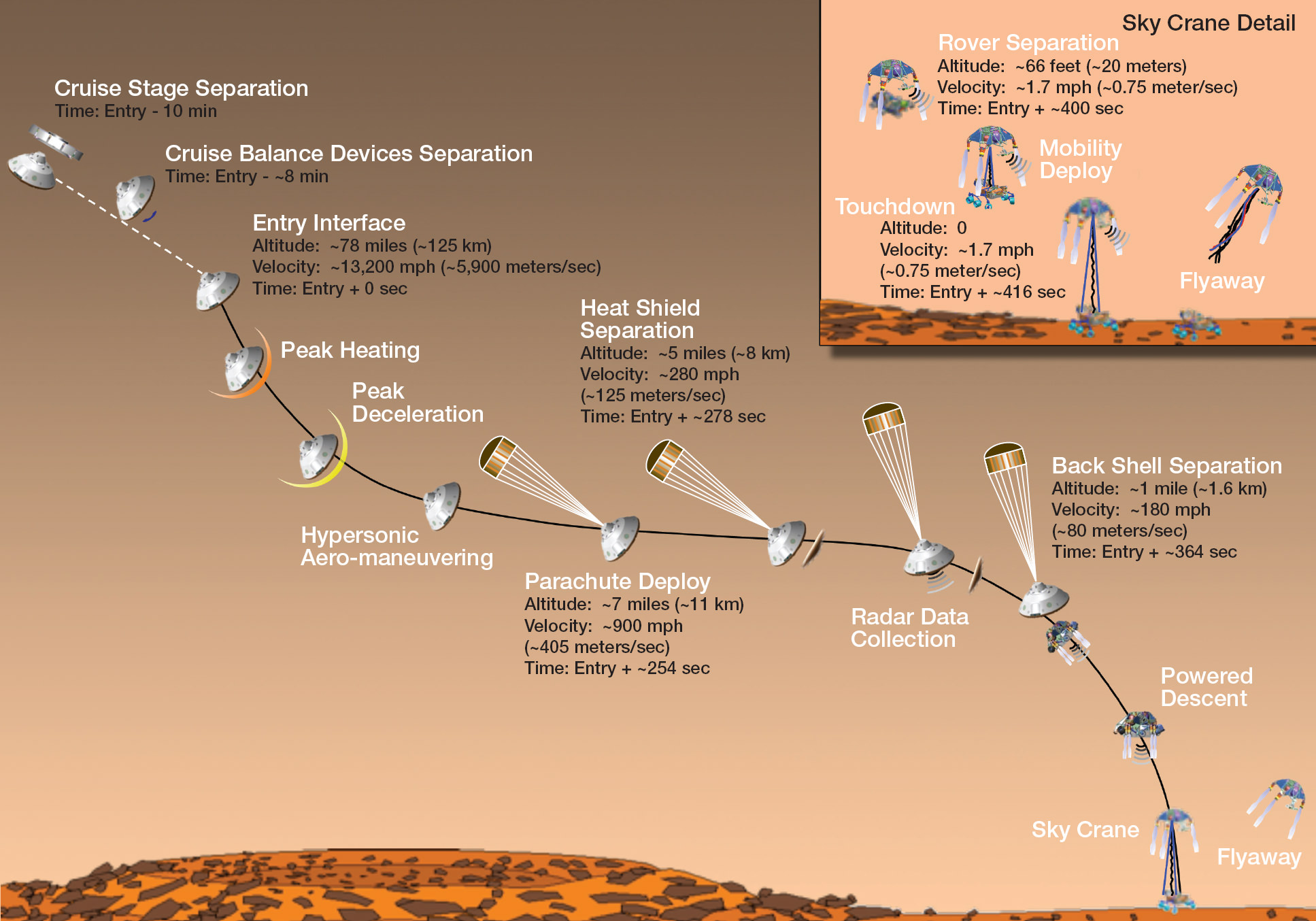
The hi res images also show how the descent thruster excavated the topsoil like Phoenix.
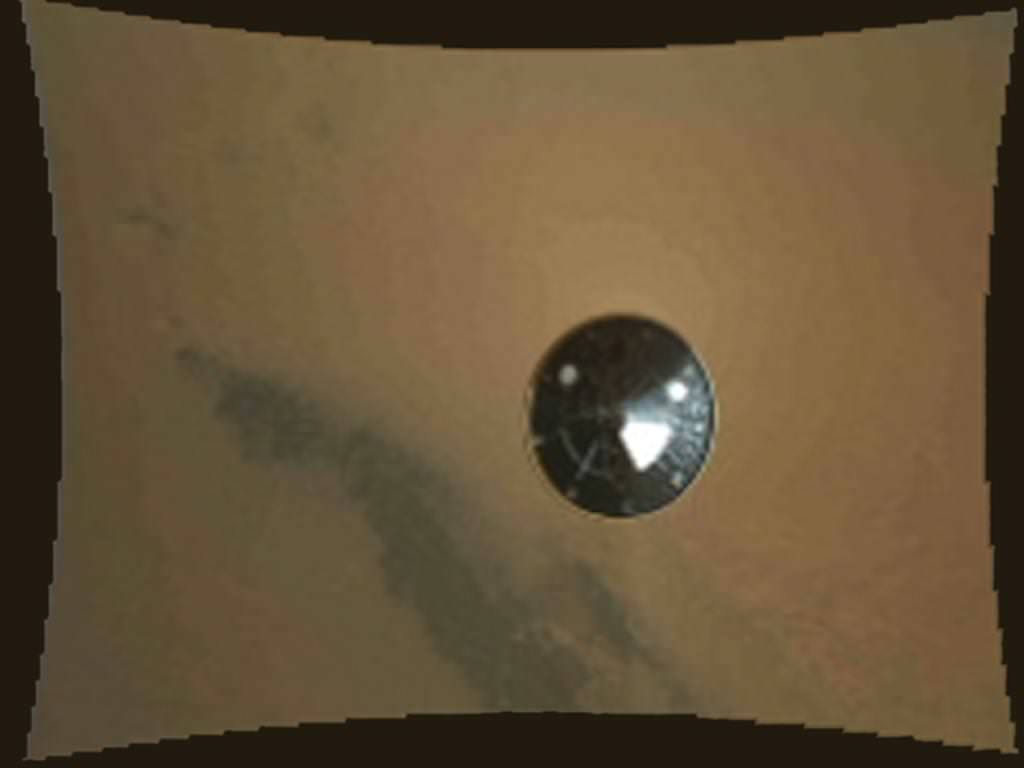
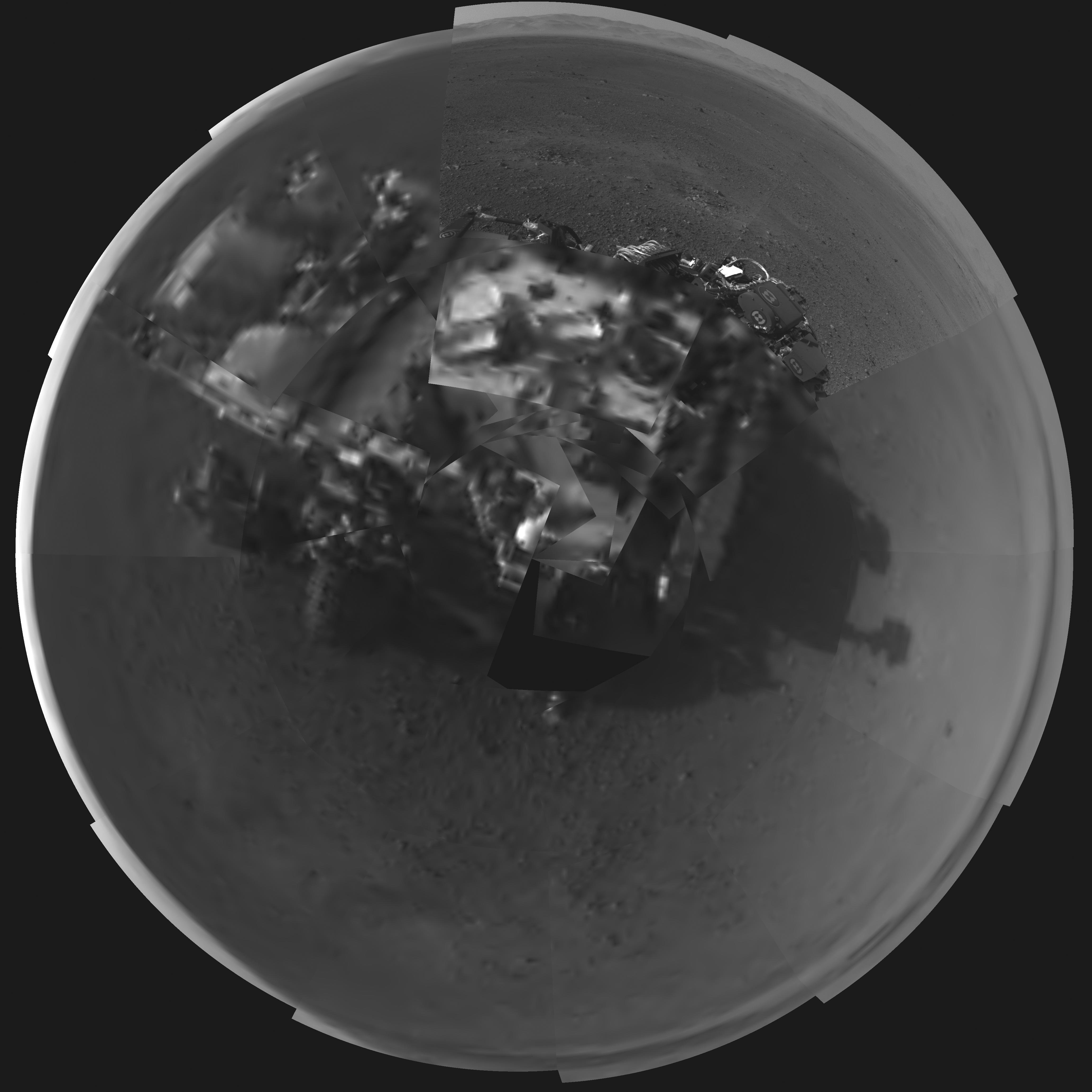
Image Caption: Curiosity Looks Away from the Sun – This is the first 360-degree panoramic view from NASA’s Curiosity rover, taken with the Navigation cameras. Most of the tiles are thumbnails, or small copies of the full-resolution images that have not been sent back to Earth yet. Two of the tiles near the center are full-resolution. Mount Sharp is to the right, and the north Gale Crater rim can be seen at center. The rover’s body is in the foreground, with the shadow of its head, or mast, poking up to the right. These images were acquired at 3:30 pm on Mars, or the night of Aug. 7 PDT (early morning Aug. 8 EDT). Thumbnails are 64 by 64 pixels in size; and full-resolution images are 1024 by 1024 pixels. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
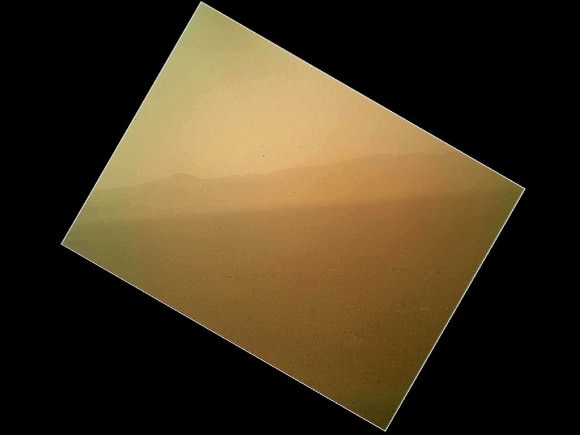
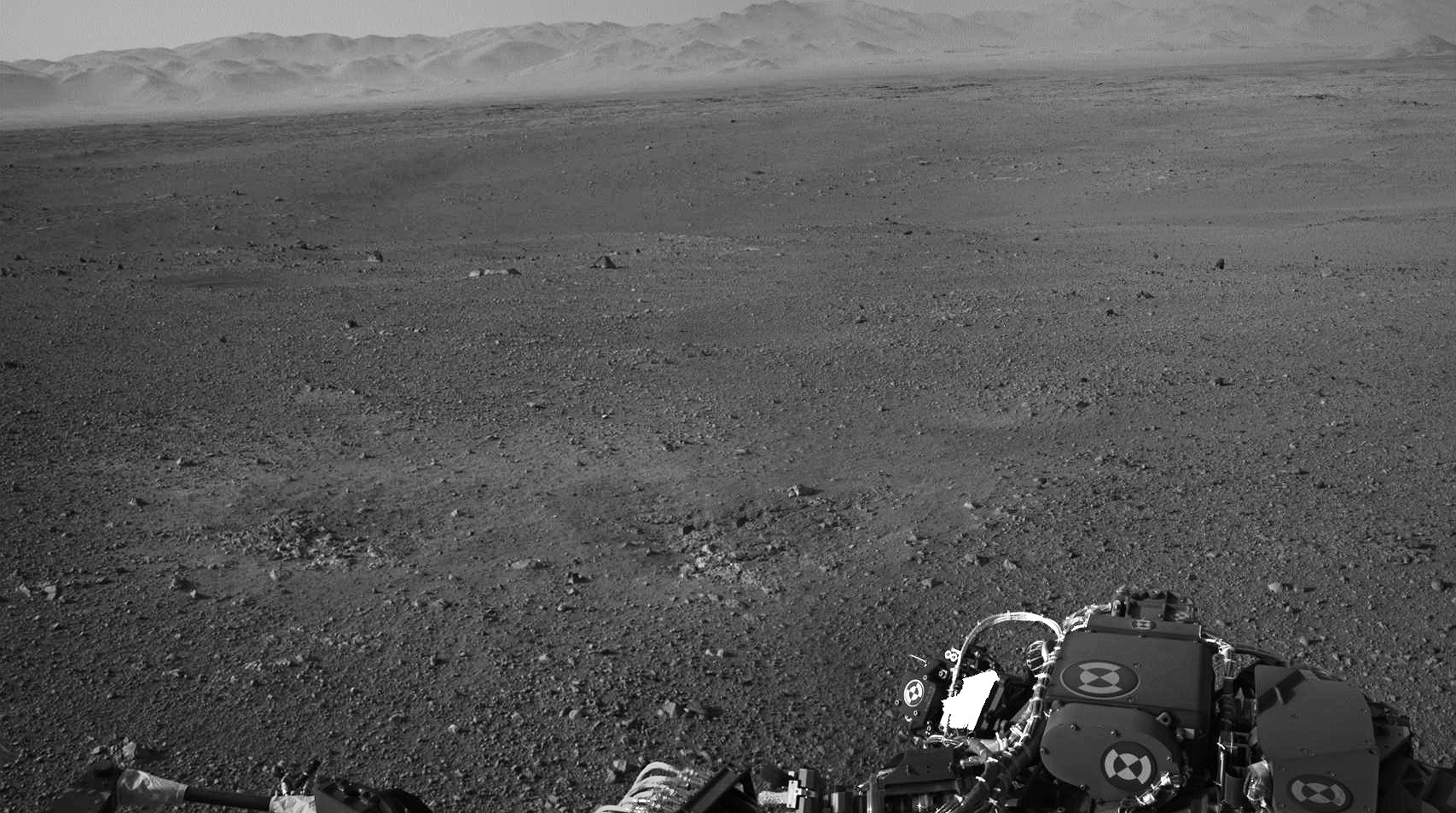
Image Caption: Looking to Martian bedrock and Gale Carter North Rim, Enhanced Mosaic- This mosaic was assembled from the first two full resolution Navcam images returned by Curiosity on Sol 2 (Aug 8) and enhanced to bring out further details. Processing by Ken Kremer and Marco Di Lorenzo. Topsoil in the foreground has been excavated by the descent landing thrusters to expose what the team believes is bedrock. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Ken Kremer/Marco di Lorenzo
“These Navcam images indicate that our powered descent stage did more than give us a great ride, it gave our science team an amazing freebie,” said John Grotzinger, project scientist for the mission from the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena. “The thrust from the rockets actually dug a one-and-a-half-foot-long [0.5-meter] trench in the surface. It appears we can see Martian bedrock on the bottom. Its depth below the surface is valuable data we can use going forward.”
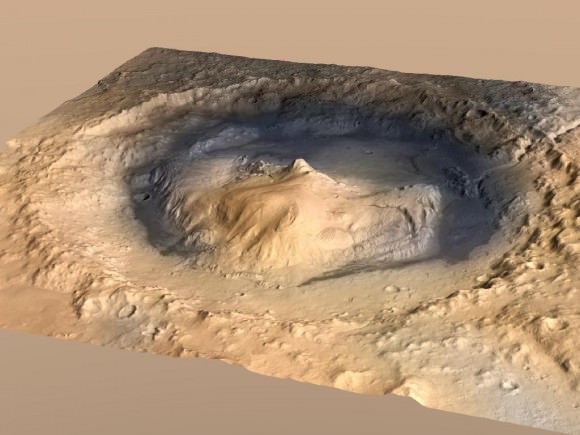
Gale Crater is unlike anything we’ve seen before on Mars.
It also distinctly reminded Grotzinger of Earth and looked to him like the rover set down in the Mojave desert. “The thing that’s amazing about this is to a certain extent the first impression you get is how earth-like this seems, looking at that landscape.”
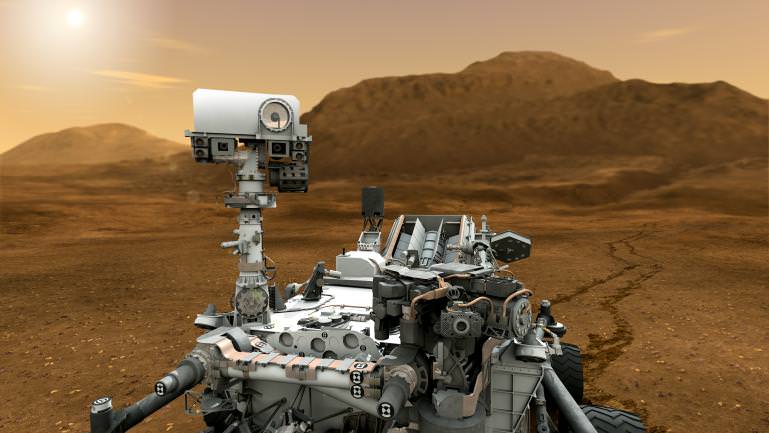
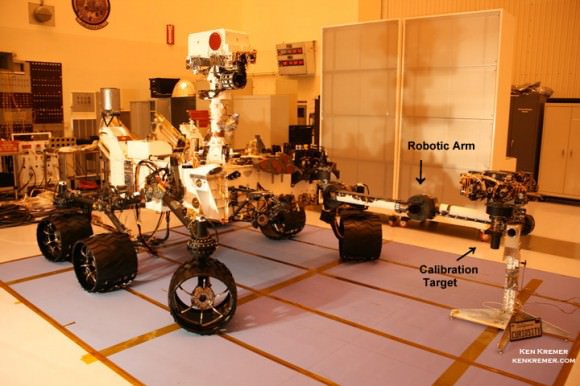
Curiosity carries 10 science instruments with a total mass 15 times as large as the science payloads on NASA’s Mars rovers Spirit and Opportunity. Some of the tools, such as a laser-firing instrument for checking rocks’ elemental composition from a distance, are the first of their kind on Mars. Curiosity will use a drill and scoop, which are located at the end of its robotic arm, to gather soil and powdered samples of rock interiors, then sieve and parcel out these samples into the rover’s analytical laboratory instruments.
So far everything is going very well with Curiosity’s mechanical and instrument checkout. And there is even more power than expected from the RTG nuclear power source.
“We have more power than we expected and that’s going to be fantastic for being able to keep the rover awake longer,” said Mission manager Jennifer Trosper of JPL.
Looking to Martian bedrock and Gale Carter North Rim, Enhanced Mosaic with False Color- This mosaic was assembled from the first two full resolution Navcam images returned by Curiosity on Sol 2 (Aug 8) and enhanced and colorized to bring out further details. Processing by Ken Kremer and Marco Di Lorenzo. Topsoil in the foreground has been excavated by the descent landing thrusters to expose what the team believes is bedrock. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Ken Kremer/Marco di Lorenzo


![PIA16011[1]](https://www.universetoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/08/PIA160111-580x74.jpg)




![673969main_PIA15993-43_full[1]](https://www.universetoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/08/673969main_PIA15993-43_full1-580x435.jpg)