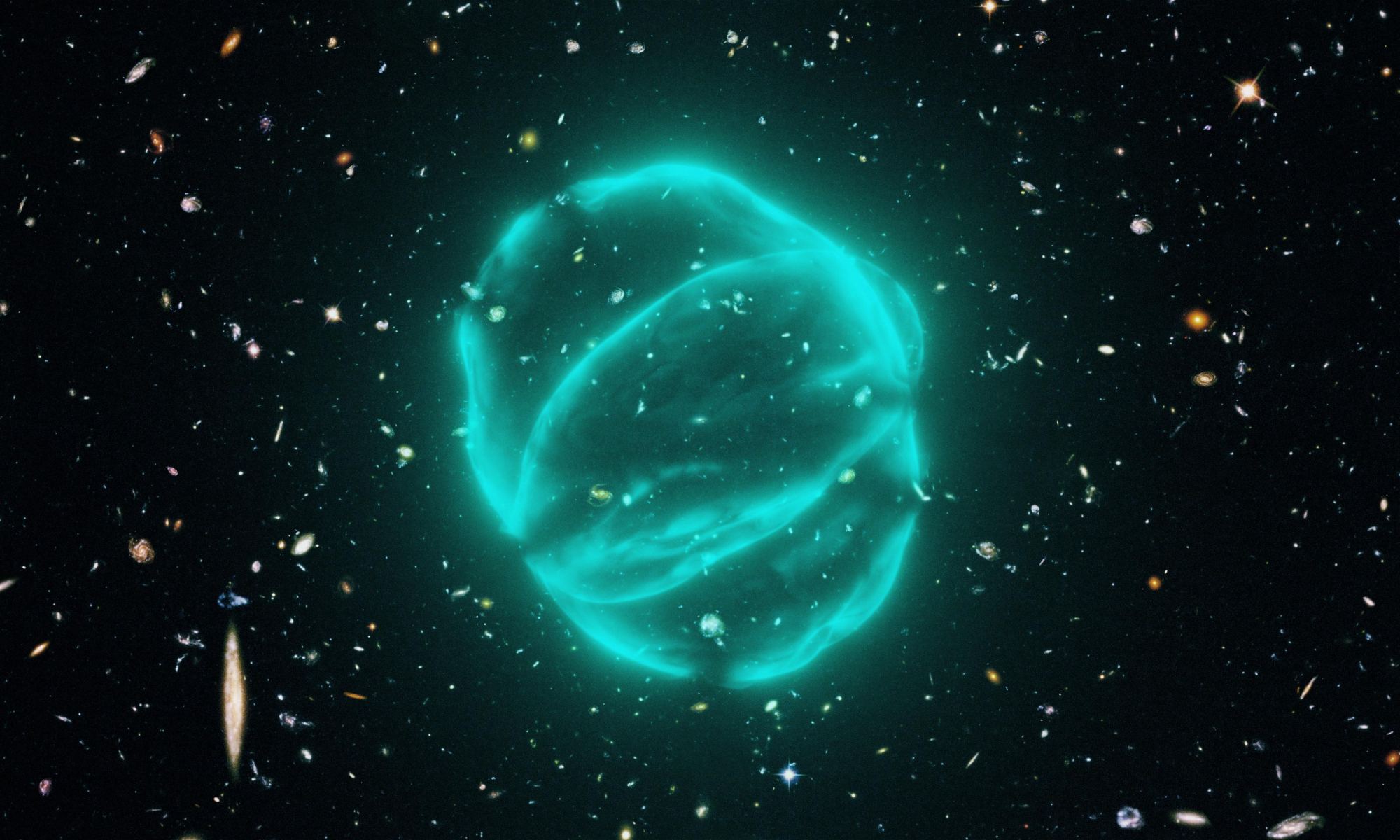
In radio astronomy, circle-shaped objects are fairly common. Since diffuse ionized gas often emits radio light, objects such as supernova remnants, planetary nebulae, and even star-forming regions can create circular arcs of diffuse gas. But in 2019 astronomers began to discover radio circles they couldn’t explain, in part because they are so large.
Continue reading “New Radio Images of Bizarre “Odd Radio Circles” Which are Vastly Bigger Than the Milky Way”Exploding Material From a Gamma-ray Burst Scrambled Nearby Magnetic Fields
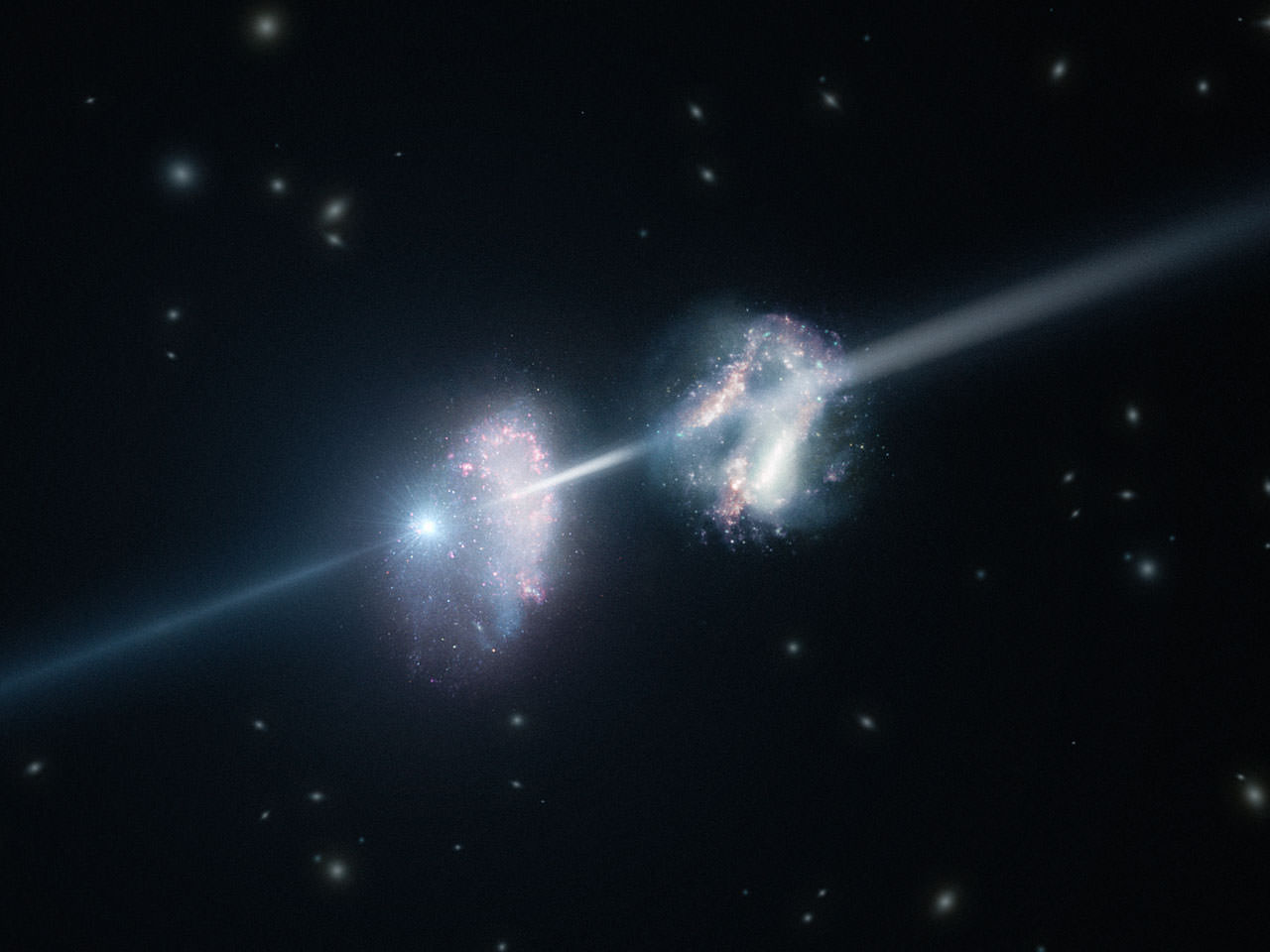

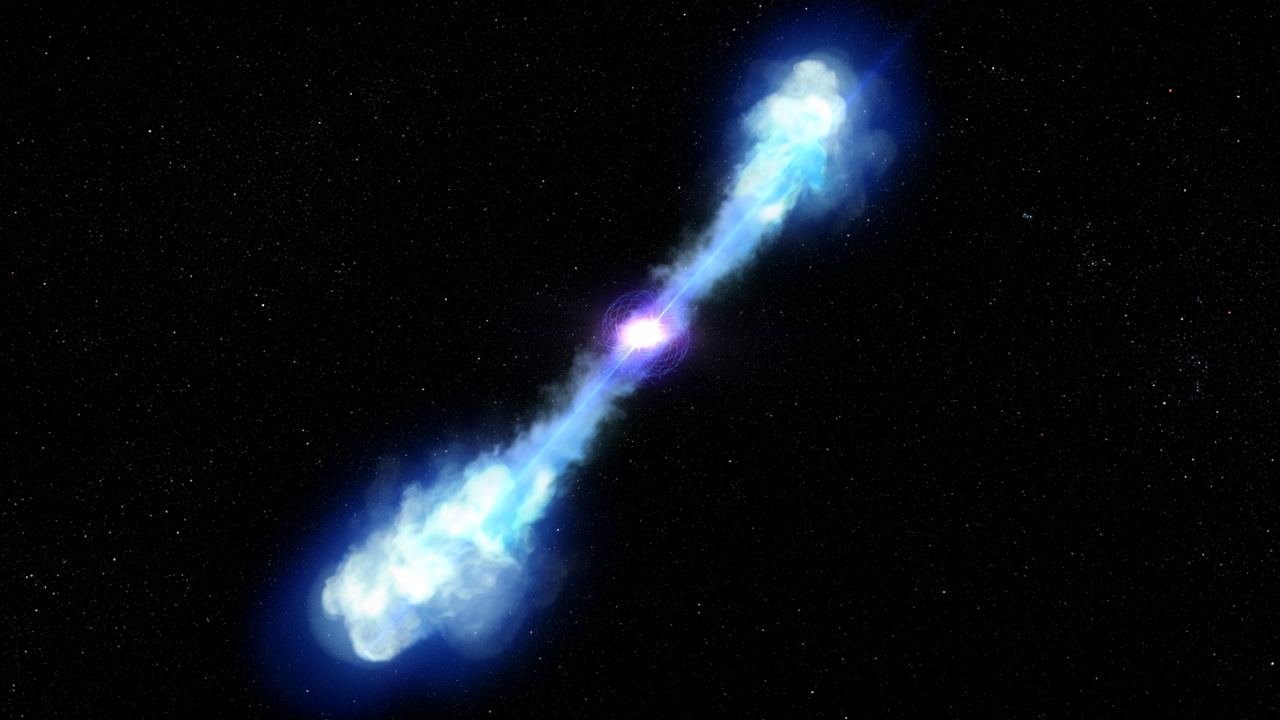
A team of astronomers has found that giant, organized magnetic fields can help drive some of the most powerful explosions in the universe. But when all is said and done, the shock wave from that blast scrambles any magnetic fields in a matter of minutes.
Continue reading “Exploding Material From a Gamma-ray Burst Scrambled Nearby Magnetic Fields”An Intermediate-Mass Black Hole Discovered Through the Gravitational Lensing of a Gamma-ray Burst
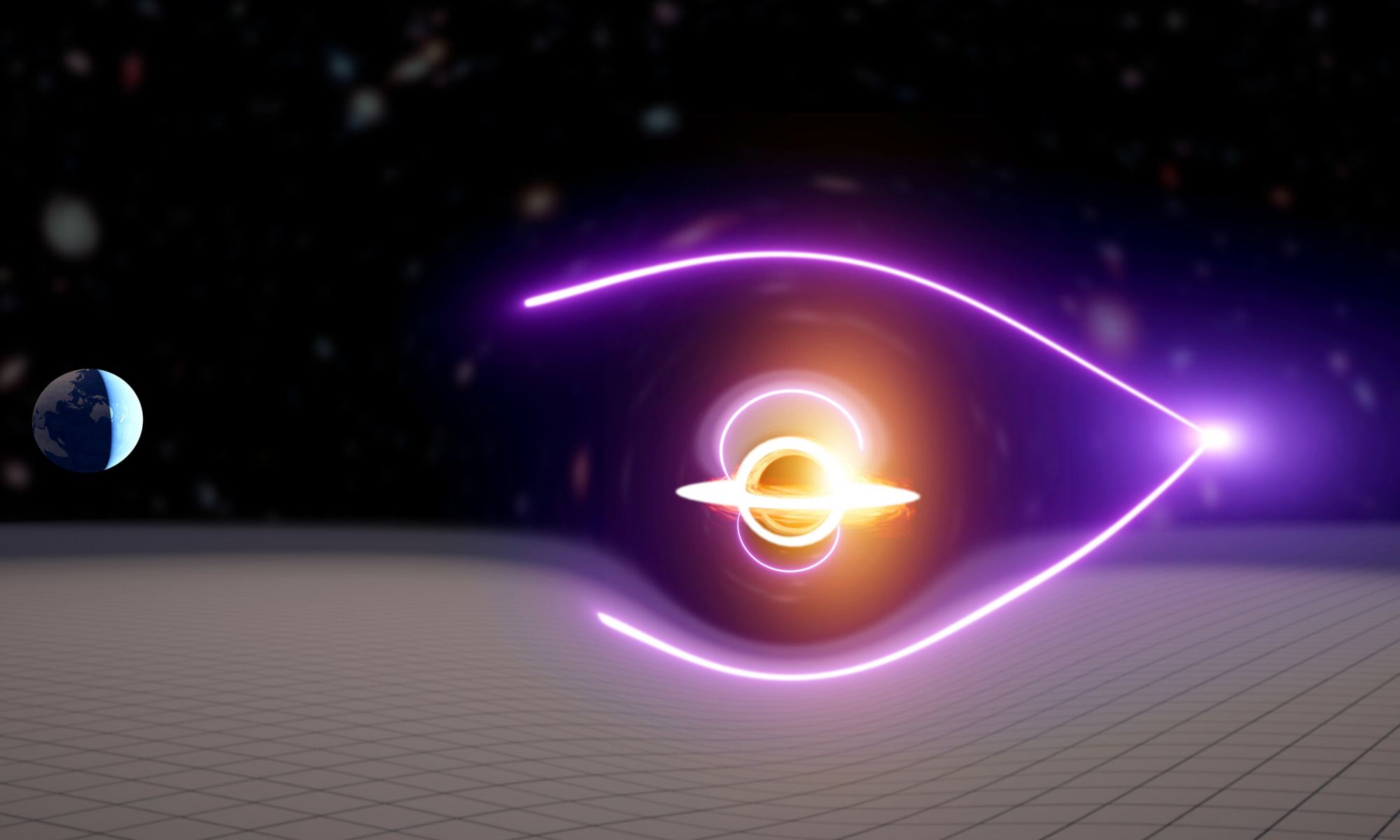
Black holes come in three sizes: small, medium, and large. Small black holes are of stellar mass. They form when a large star collapses at the end of its life. Large black holes lurk in the centers of galaxies and are millions or billions of solar masses. Middle-sized black holes are those between 100 to 100,000 solar masses. They are known as Intermediate Mass Black Holes (IMBHs), and they are the kind we least understand.
Continue reading “An Intermediate-Mass Black Hole Discovered Through the Gravitational Lensing of a Gamma-ray Burst”Astronomers think they’ve seen a magnetar form for the first time; the collision of two neutron stars
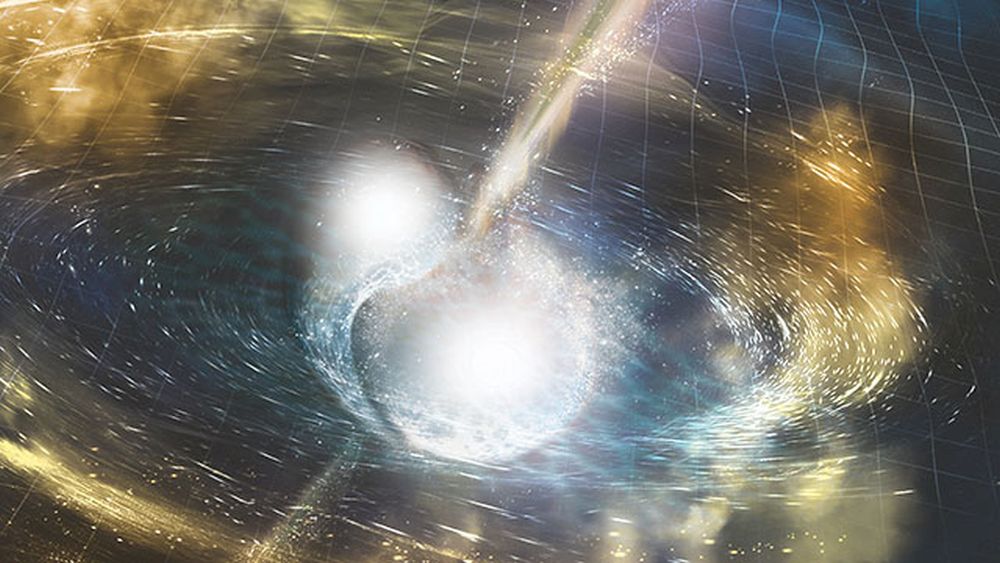
A magnetar is a neutron star with a magnetic field thousands of times more powerful than those of typical neutron stars. Their fields are so strong that they can generate powerful, short-duration events such as soft gamma repeaters and fast radio bursts. While we have learned quite a bit about magnetars in recent years, we still don’t understand how neutron stars can form such intense magnetic fields. But that could soon change thanks to a new study.
Continue reading “Astronomers think they’ve seen a magnetar form for the first time; the collision of two neutron stars”Beyond “Fermi’s Paradox” X: What is the Firstborn Hypothesis?
Welcome back to our Fermi Paradox series, where we take a look at possible resolutions to Enrico Fermi’s famous question, “Where Is Everybody?” Today, we examine the possibility that the reason for the Great Silence is that we are “early to the party”!
In 1950, Italian-American physicist Enrico Fermi sat down to lunch with some of his colleagues at the Los Alamos National Laboratory, where he had worked five years prior as part of the Manhattan Project. According to various accounts, the conversation turned to aliens and the recent spate of UFOs. Into this, Fermi issued a statement that would go down in the annals of history: “Where is everybody?“
This became the basis of the Fermi Paradox, which refers to the disparity between high probability estimates for the existence of extraterrestrial intelligence (ETI) and the apparent lack of evidence. Since Fermi’s time, there have been several proposed resolutions to his question, which includes the Firstborn Hypothesis that states that humanity could be the first intelligent life to emerge in our galaxy.
Continue reading “Beyond “Fermi’s Paradox” X: What is the Firstborn Hypothesis?”A New Kind of Supernova Explosion has been Discovered: Fast Blue Optical Transients
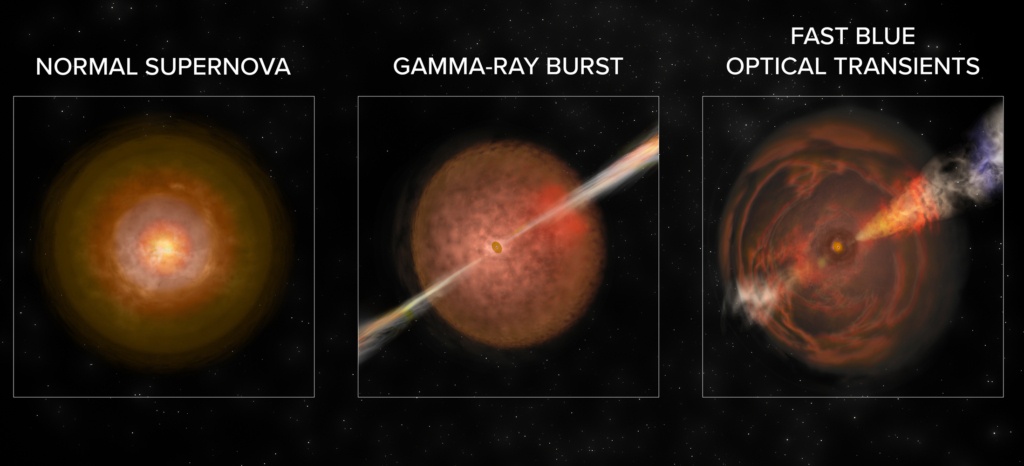
For the child inside all of us space-enthusiasts, there might be nothing better than discovering a new type of explosion. (Except maybe bigger rockets.) And it looks like that’s what’s happened. Three objects discovered separately—one in 2016 and two in 2018—add up to a new type of supernova that astronomers are calling Fast Blue Optical Transients (FBOT).
Continue reading “A New Kind of Supernova Explosion has been Discovered: Fast Blue Optical Transients”NASA Chooses 4 New Astronomy Space Missions for Additional Study

Since 1958, the NASA Explorer Program has conducted low-cost missions that were deemed relevant to the goals of the Science Mission Directorate (SMD), particularly where the study of our Sun and the deeper cosmic mysteries are concerned. Recently, the Explorer Program selected four missions that they considered to be well-suited to these goals, two of which will be selected for launch in the coming years.
Consisting of two astrophysics Small Explorer (SMEX) and two Missions of Opportunity (MO) proposals, these missions are designed to study cosmic explosions and the debris they leave behind, as well as monitor how nearby stellar flares may affect the atmospheres of orbiting planets. After detailed evaluations, two of these missions will be selected next year and will take to space sometime in 2025.
Continue reading “NASA Chooses 4 New Astronomy Space Missions for Additional Study”It Takes Two Stars to Make a Gamma Ray Burst
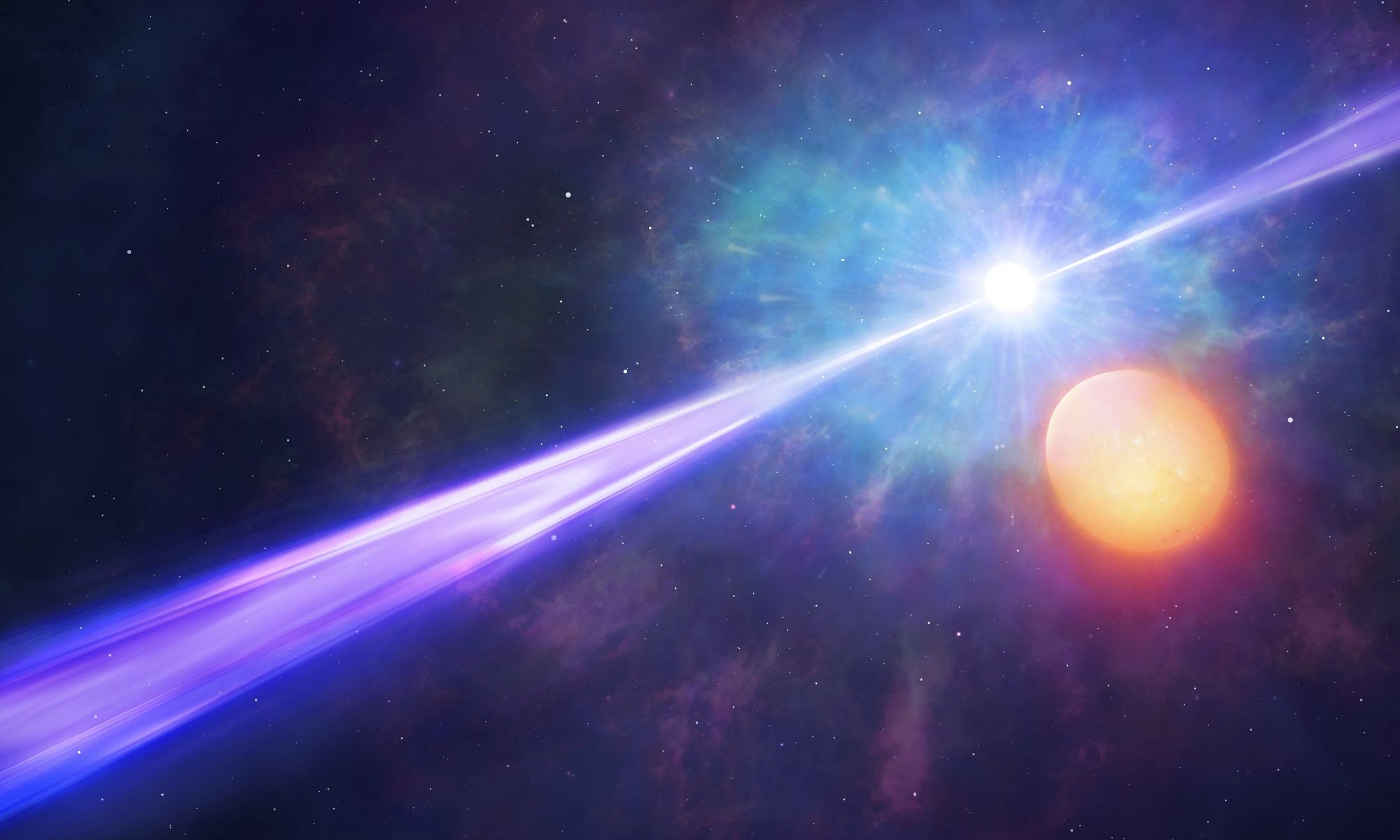

In 1967, NASA scientists noticed something they had never seen before coming from deep space. In what has come to be known as the “Vela Incident“, multiple satellites registered a Gamma-Ray Burst (GRB) that was so bright, it briefly outshined the entire galaxy. Given their awesome power and the short-lived nature, astronomers have been eager to determine how and why these bursts take place.
Decades of observation have led to the conclusion that these explosions occur when a massive star goes supernova, but astronomers were still unsure why it happened in some cases and not others. Thanks to new research by a team from the University of Warwick, it appears that the key to producing GRBs lies with binary star systems – i.e. a star needs a companion in order to produce the brightest explosion in the Universe.
Continue reading “It Takes Two Stars to Make a Gamma Ray Burst”Hubble Has Looked at the 2017 Kilonova Explosion Almost a Dozen Times, Watching it Slowly Fade Away
In 2017, LIGO (Laser-Interferometer Gravitational Wave Observatory) and Virgo detected gravitational waves coming from the merger of two neutron stars. They named that signal GW170817. Two seconds after detecting it, NASA’s Fermi satellite detected a gamma ray burst (GRB) that was named GRB170817A. Within minutes, telescopes and observatories around the world honed in on the event.
The Hubble Space Telescope played a role in this historic detection of two neutron stars merging. Starting in December 2017, Hubble detected the visible light from this merger, and in the next year and a half it turned its powerful mirror on the same location over 10 times. The result?
The deepest image of the afterglow of this event, and one chock-full of scientific detail.
Continue reading “Hubble Has Looked at the 2017 Kilonova Explosion Almost a Dozen Times, Watching it Slowly Fade Away”Massive Triple Star System Creates this Bizarre Swirling Pinwheel of Dust. And it Could be the Site of a Gamma Ray Burst
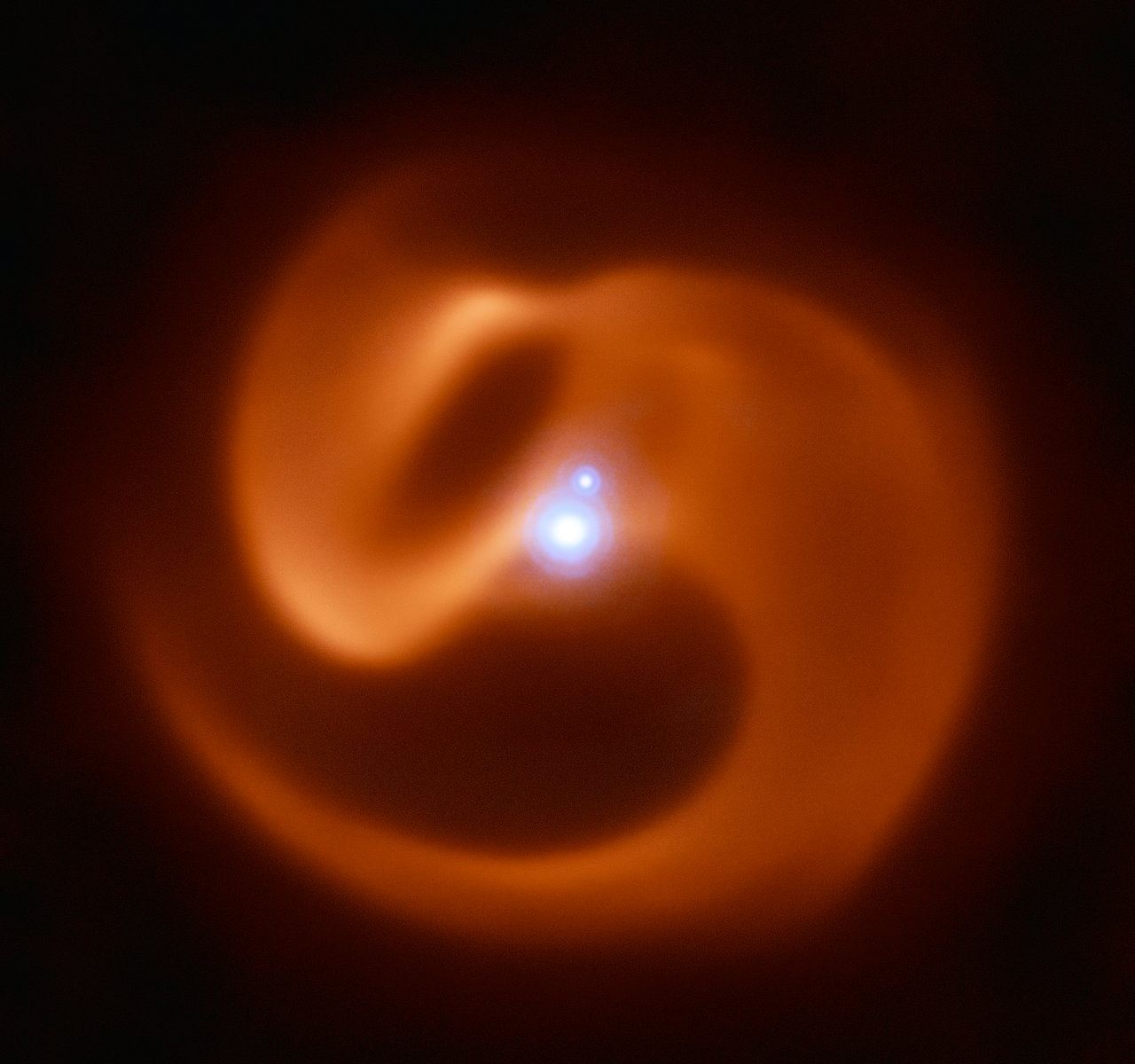

When stars reach the end of their lifespan, many undergo gravitational collapse and explode into a supernova, In some cases, they collapse to become black holes and release a tremendous amount of energy in a short amount of time. These are what is known as gamma-ray bursts (GRBs), and they are one of the most powerful events in the known Universe.
Recently, an international team of astronomers was able to capture an image of a newly-discovered triple star system surrounded by a “pinwheel” of dust. This system, nicknamed “Apep”, is located roughly 8,000 light years from Earth and destined to become a long-duration GRB. In addition, it is the first of its kind to be discovered in our galaxy.