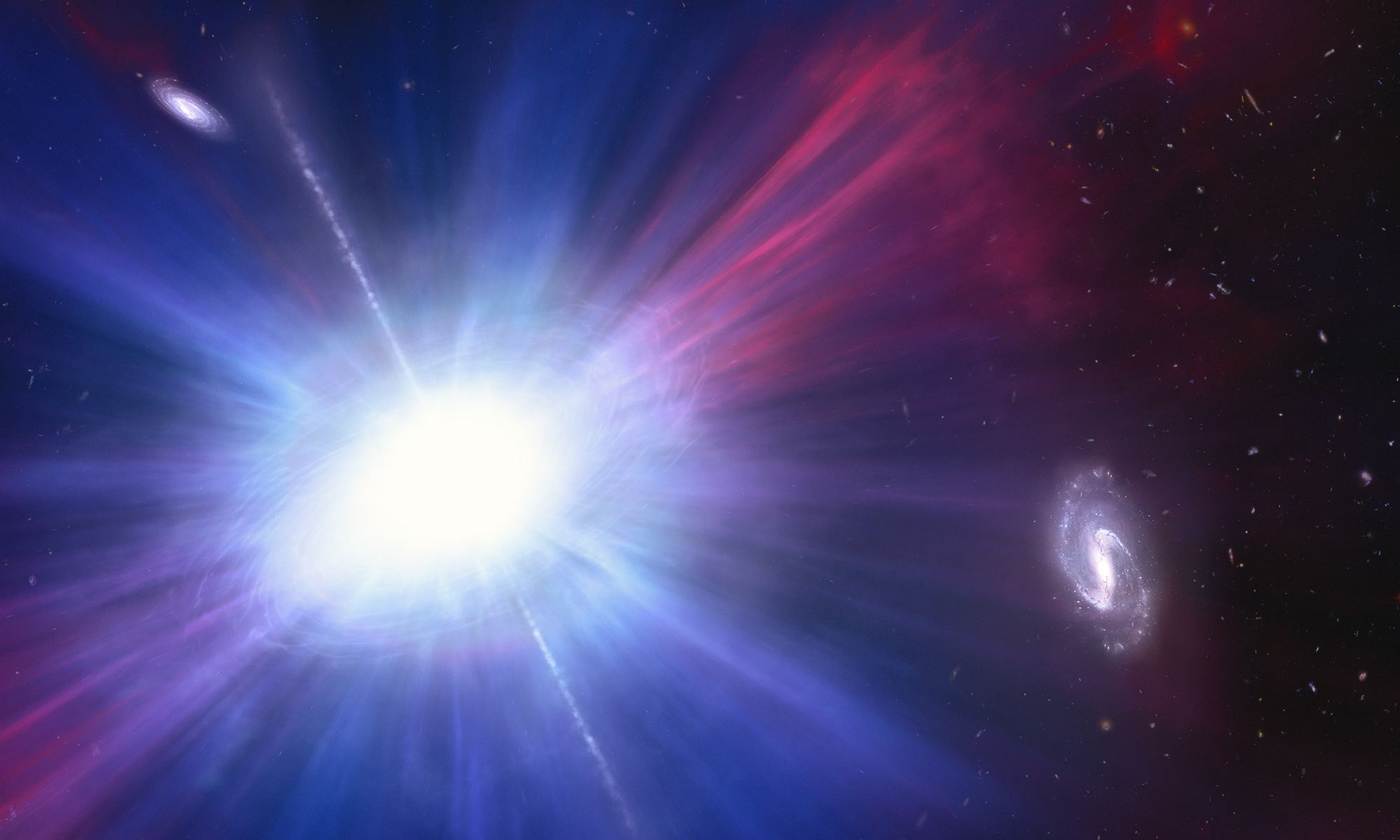
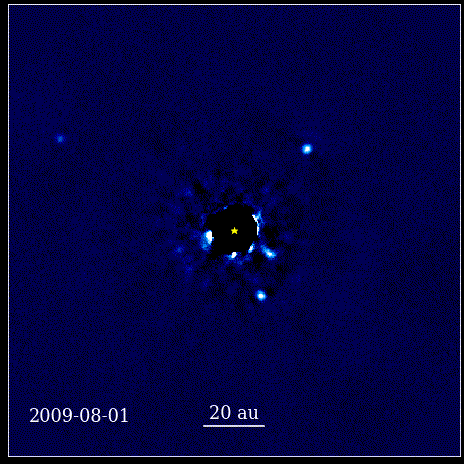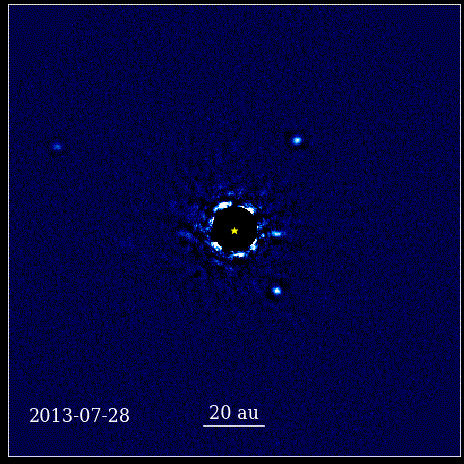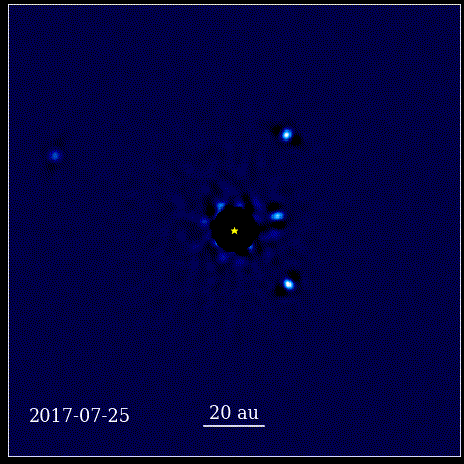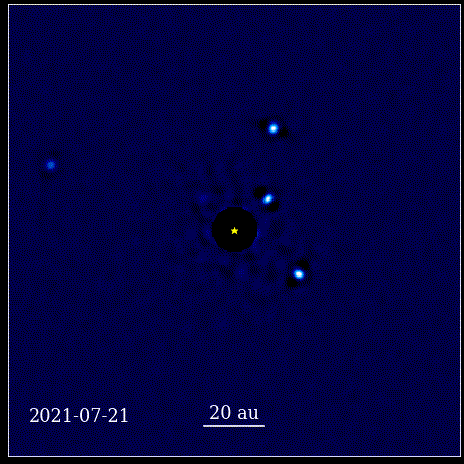
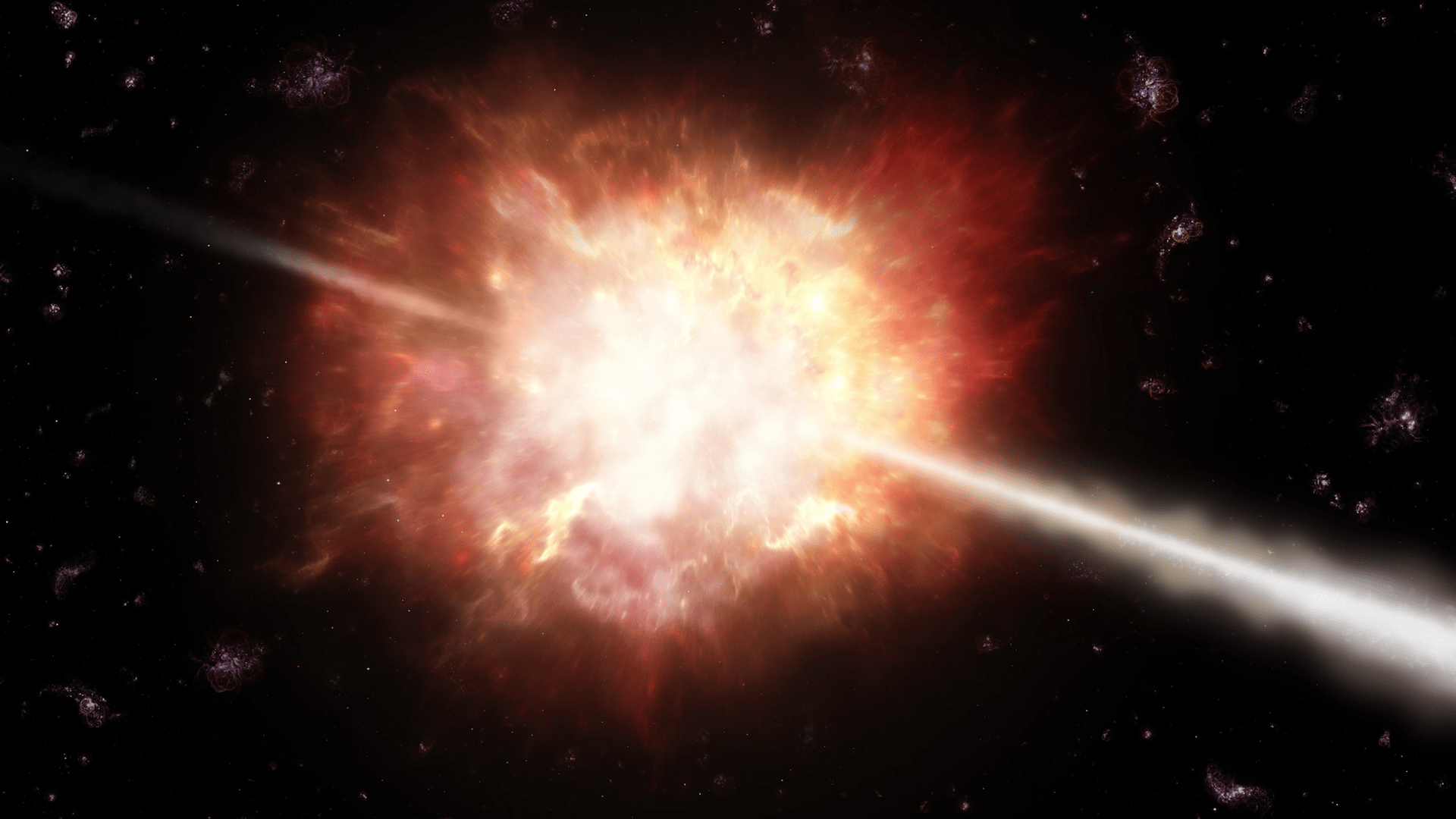
The theory goes that black holes accrete material, often from nearby stars. However the theory also suggests there is a limit to how big a black hole can grow due to accretion and certainly shouldn’t be as large as they are seen to be in the early Universe. Black holes it seems, are fighting back and don’t care about those limits! A recent study shows that supermassive black holes are growing at rates that defy the limits of current theory. Astronomers just need to figure out how they’re doing it!
Continue reading “Early Black Holes Fed 40x Faster than Should Be Possible”Early Black Holes Fed 40x Faster than Should Be Possible