Placing a mass driver on the Moon has long been a dream of space exploration enthusiasts. It would open up so many possibilities for the exploration of our solar system and the possibility of actually living in space. Gerard O’Neill, in his work on the gigantic cylinders that now bear his name, mentioned using a lunar mass driver as the source of the material to build them. So far, we have yet to see such an engineering wonder in the real world, but as more research is done on the topic, more and more feasible paths seem to be opening up to its potential implementation.
Continue reading “Launching Mass From the Moon Helped by Lunar Gravity Anomalies”Finally, an Explanation for the Moon’s Radically Different Hemispheres
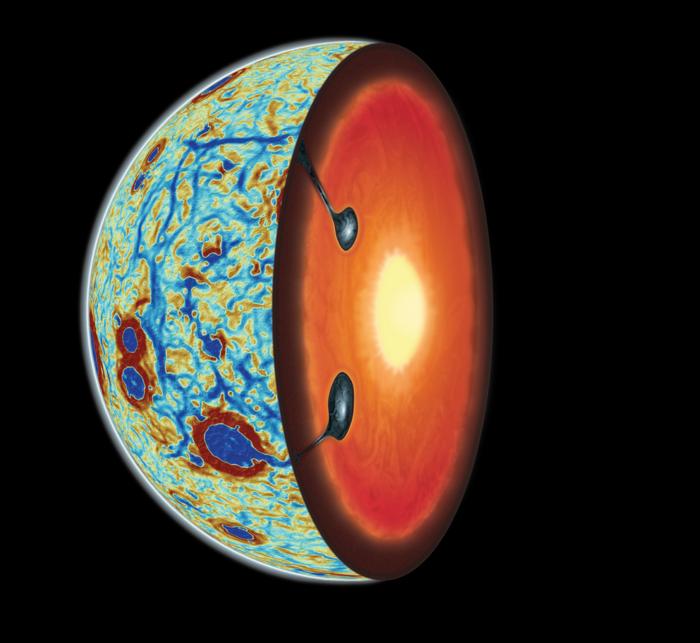
Pink Floyd was wrong, there is no dark side to the Moon. There is however, a far side. The tidal effects between the Earth and Moon have caused this captured or synchronous rotation. The two sides display very different geographical features; the near side with mare and ancient volcanic flows while the far side displaying craters within craters. New research suggests the Moon has turned itself inside out with heavy elements like titanium returning to the surface. It’s now thought that a giant impact on the far side pushed titanium to the surface, creating a thinner more active near side.
Continue reading “Finally, an Explanation for the Moon’s Radically Different Hemispheres”That Explains a Lot. The Moon’s Largest Crater has a Chunk of Metal Embedded in it That’s 5 Times Bigger than the Big Island of Hawaii
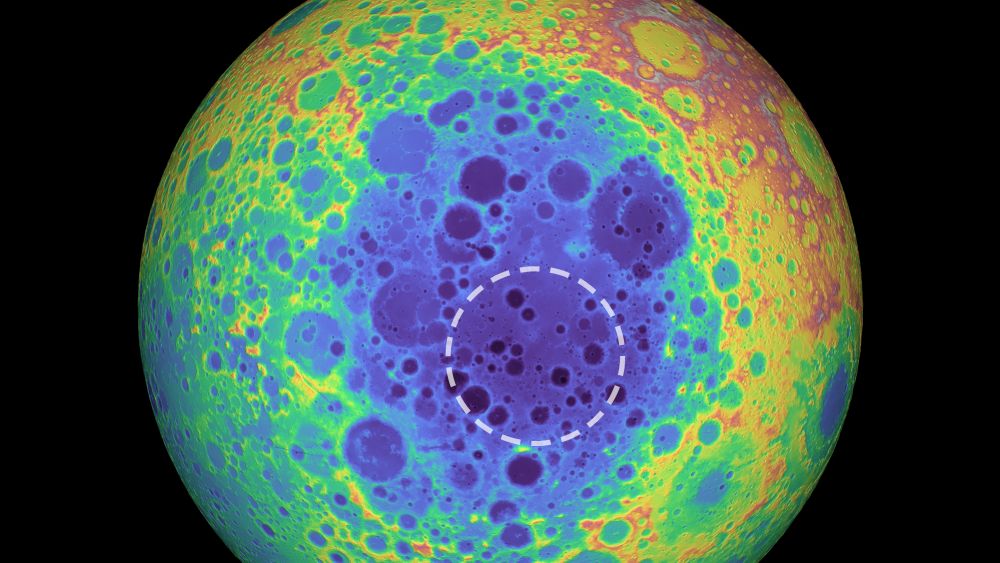
One of the largest craters in the Solar System is on our Moon. It’s called the South Pole-Aitken (SPA) basin and it’s 2,500 km (1,600 mi) in diameter and 13 km (8.1 mi) deep. A new study says that the basin may contain an enormous chunk of metal that’s larger than Hawaii’s Big Island.
Continue reading “That Explains a Lot. The Moon’s Largest Crater has a Chunk of Metal Embedded in it That’s 5 Times Bigger than the Big Island of Hawaii”GRAIL Data Points To Possible Lava Tubes On The Moon
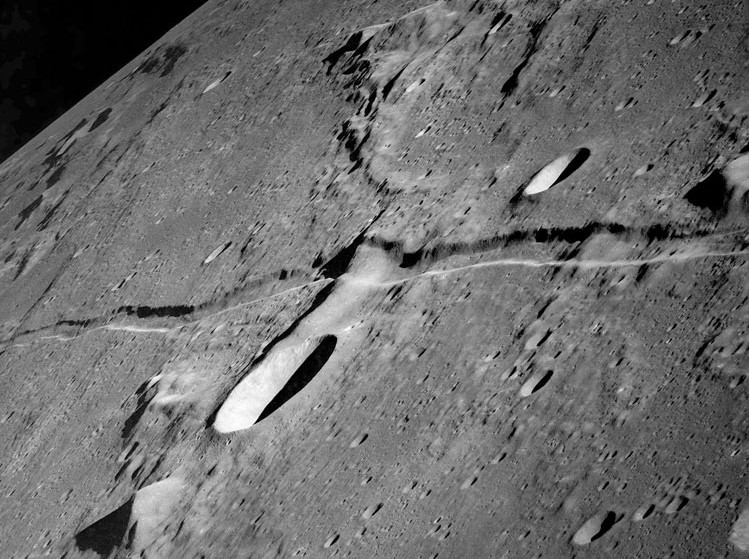
For years, scientists have been hunting for the stable lava tubes that are believed to exist on the Moon. A remnant from the Moon’s past, when it was still volcanically active, these underground channels could very well be an ideal location for lunar colonies someday. Not only would their thick roofs provide naturally shielding from solar radiation, meteoric impacts, and extremes in temperature. They could also be pressurized to create a breathable environment.
But until now, evidence of their existence has been inferred from surface features such as sinuous rilles – channel-like depressions that run along the surface that indicate the presence of subterranean lava flows – and holes in the surface (aka. “skylights”). However, recent evidence presented at the 47th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference (LPSC) in Texas indicates that one such stable lava tube could exist in the once-active region known as Marius Hills.
Continue reading “GRAIL Data Points To Possible Lava Tubes On The Moon”
There Could Be Lava Tubes on the Moon, Large Enough for Whole Cities
Every year since 1970, astronomers, geologists, geophysicists, and a host of other specialists have come together to participate in the Lunar and Planetary Science Conference (LPCS). Jointly sponsored by the Lunar and Planetary Institute (LPI) and NASA’s Johnson Space Center (JSC), this annual event is a chance for scientists from all around the world to share and present the latest planetary research concerning Earth’s only moon.
This year, one of the biggest attention-grabbers was the findings presented on Tuesday, March 17th by a team of students from Purdue University. Led by a graduate student from the university’s Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences, the study they shared indicates that there may be stable lava tubes on the moon, ones large enough to house entire cities.
In addition to being a target for future geological and geophysical studies, the existence of these tubes could also be a boon for future human space exploration. Basically, they argued, such large, stable underground tunnels could provide a home for human settlements, shielding them from harmful cosmic radiation and extremes in temperature.
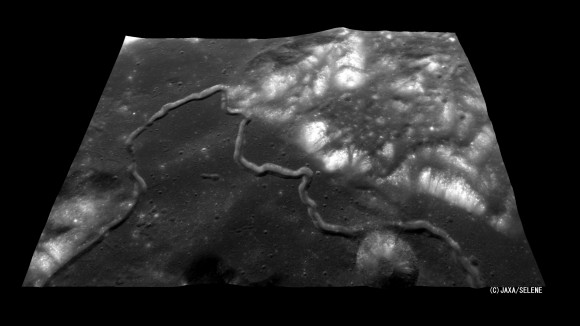
Lava tubes are natural conduits formed by flowing lava that is moving beneath the surface as a result of a volcanic eruption. As the lava moves, the outer edges of it cools, forming a hardened, channel-like crust which is left behind once the lava flow stops. For some time, Lunar scientists have been speculating as to whether or not lava flows happen on the Moon, as evidenced by the presence of sinuous rilles on the surface.
Sinuous rilles are narrow depressions in the lunar surface that resemble channels, and have a curved paths that meanders across the landscape like a river valley. It is currently believed that these rilles are the remains of collapsed lava tubes or extinct lava flows, which is backed up by the fact they usually begin at the site of an extinct volcano.
Those that have been observed on the Moon in the past range in size of up to 10 kilometers in width and hundreds of kilometers in length. At that size, the existence of a stable tube – i.e. one which had not collapsed to form a sinuous rille – would be large enough to accommodate a major city.
For the sake of their study, the Purdue team explored whether lava tubes of the same scale could exist underground. What they found was that the stability of a lava tube depended on a number of variables- including width, roof thickness and the stress state of the cooled lava. he researchers also modeled lava tubes with walls created by lava placed in one thick layer and with lava placed in many thin layers.

David Blair, a graduate student in Purdue’s Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences, led the study that examined whether empty lava tubes more than 1 kilometer wide could remain structurally stable on the moon.
“Our work is somewhat unique in that we’ve combined the talents of people from various Departments at Purdue,” Blair told Universe Today via email. “With guidance from Prof. Bobet (a civil engineering professor) we’ve been able to incorporate a modern understanding of rock mechanics into our computer models of lava tubes to see how they might actually fail and break under lunar gravity.”
For the sake of their research, the team constructed a number of models of lava tubes of different sizes and with different roof thicknesses to test for stability. This consisted of them checking each model to see if it predicted failure anywhere in the lava tube’s roof.
“What we found was surprising,” Blair continued, “in that much larger lava tubes are theoretically possible than what was previously thought. Even with a roof only a few meters thick, lava tubes a kilometer wide may be able to stay standing. The reason why, though, is a little less surprising. The last work we could find on the subject is from the Apollo era, and used a much simpler approximation of lava tube shape – a flat beam for a roof.

The study he refers to, “On the origin of lunar sinuous rilles“, was published in 1969 in the journal Modern Geology. In it, professors Greeley, Oberbeck and Quaide advanced the argument that sinuous rilles formation was tied to the collapse of lava flow tubes, and that stable ones might still exist. Calculating for a flat-beam roof, their work found a maximum lava tube size of just under 400 m.
“Our models use a geometry more similar to what’s seen in lava tubes on Earth,” Blair said, “a sort of half-elliptical shape with an arched roof. The fact that an arched roof lets a larger lava tube stay standing makes sense: humans have known since antiquity that arched roofs allow tunnels or bridges to stay standing with wider spans.”
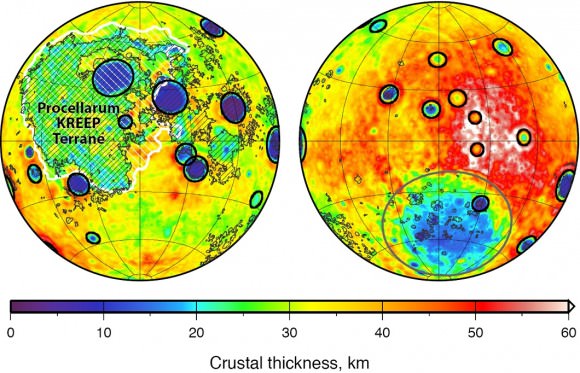
The Purdue study also builds on previous studies conducted by JAXA and NASA where images of “skylights” on the Moon – i.e. holes in the lunar surface – confirmed the presence of caverns at least a few tens of meters across. The data from NASA’s lunar Gravity Recovery And Interior Laboratory (GRAIL) – which showed big variations in the thickness of the Moon’s crust is still being interpreted, but could also be an indication of large subsurface recesses.
As a result, Blair is confident that their work opens up new and feasible explanations for many different types of observations that have been made before. Previously, it was unfathomable that large, stable caverns could exist on the Moon. But thanks to his team’s theoretical study, it is now known that under the proper conditions, it is least possible.
Another exciting aspect that this work is the implications it offers for future exploration and even colonization on the Moon. Already, the issue of protection against radiation is a big one. Given that the Moon has no atmosphere, colonists and agricultural operations will have no natural shielding from cosmic rays.
“Geologically stable lava tubes would absolutely be a boon to human space exploration,” Blair commented. “A cavern like that could be a really ideal place for building a lunar base, and generally for supporting a sustained human presence on the Moon. By going below the surface even a few meters, you suddenly mitigate a lot of the problems with trying to inhabit the lunar surface.”
Basically, in addition to protecting against radiation, a subsurface base would sidestep the problems of micrometeorites and the extreme changes in temperature that are common on the lunar surface. What’s more, stable, subsurface lava tubes could also make the task of pressurizing a base for human habitation easier.
“People have studied and talked about all of these things before,” Blair added, “but our work shows that those kinds of opportunities could potentially exist – now we just have to find them. Humans have been living in caves since the beginning, and it might make sense on the Moon, too!”
In addition to Melosh, Blair and Bobet, team members include Loic Chappaz and Rohan Sood, graduate students in the School of Aeronautics and Astronautics; Kathleen Howell, Purdue’s Hsu Lo Professor of Aeronautical and Astronautical Engineering; Andy M. Freed, an associate professor of earth, atmospheric and planetary sciences; and Colleen Milbury, a postdoctoral research associate in the Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences.
Further Reading: Purdue News
You Can Vote to Name America’s New Rocket from ULA
Help ULA name America’s next rocket to space. Credit: ULA
Voting Details below
Watch ULA’s March 25 Delta Launch Live – details below
Update 3/26: 2 new names have been added to the voting list – Zeus and Vulcan ![/caption]
United Launch Alliance (ULA) is asking the public for your help in naming their new American made rocket, now under development that “represents the future of space”- and will replace the firms current historic lines of Atlas and Delta rocket families that began launching back near the dawn of the space age.
Eagle, Freedom or GalaxyOne – those are the names to choose from for the next two weeks, from now until April 6.
UPDATE 3/26: 2 new names have been added to the voting list – Zeus and Vulcan !
ULA says the names were selected from a list of over 400 names submitted earlier this year by ULA’s 3400 employees and many space enthusiasts.
ULA has set up a simple voting system whereby you can vote for your favorite name via text or an online webpage.
Currently dubbed the “Next Generation Launch System,” or NGLS, ULA’s new president and CEO Tory Bruno is set to unveil the next generation rockets design and name at the National Space Symposium on April 13 in Colorado Springs, Colorado.
“ULA’s new rocket represents the future of space – innovative, affordable and reliable,” said Bruno, in a statement.
“More possibilities in space means more possibilities here on earth. This is such a critical time for space travel and exploration and we’re excited to bring all of America with us on this journey into the future.”
The NGLS is ULA’s response to what’s shaping up as a no holds barred competition with SpaceX for future launch contracts where only the innovative and those who dramatically cut the cost of access to space will survive.
The first flight of the NGLS is slated for 2019.
Here’s how you can cast your vote for America’s next rocket to April 6, 2015:
Visit the website: http://bit.ly/rocketvote
OR
Voters can text 22333 to submit a vote for their favorite name. The following key can be used to text a vote:
• ULA1 for “Eagle”
• ULA2 for “Freedom”
• ULA3 for “GalaxyOne”
3/26 Update: Zeus and Vulcan have been added to the voting list

“Name America’s next ride to space. Vote early, vote often … ” says Bruno.
I have already voted – early and often.
Over 11,000 votes were tallied in just the first day.
Currently ULA is the nation’s premier launch provider, launching at a rate of about once per month. 13 launches are planned for 2015- as outlined in my earlier article here.
But ULA faces stiff and relentless pricing and innovative competition from NewSpace upstart SpaceX, founded by billionaire Elon Musk.
NGLS is ULA’s answer to SpaceX – they must compete in order to survive.
To date ULA has accomplished a 100 percent mission success for 94 launches since the firms founding in 2006 as a joint venture between Boeing and Lockheed Martin. They have successfully launched numerous NASA, national security and commercial payloads into orbit and beyond.
Planetary missions launched for NASA include the Mars rovers and landers Phoenix and Curiosity, Pluto/New Horizons, Juno, GRAIL, LRO and LCROSS.
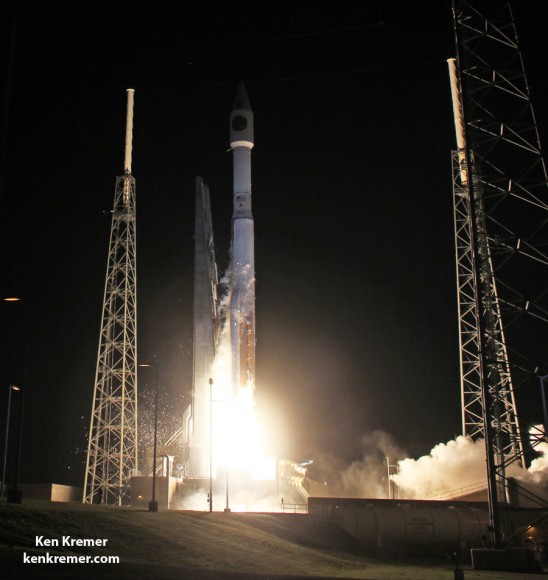

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with NASA’s Magnetospheric Multiscale (MMS) spacecraft onboard launches from the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station Space Launch Complex 41, Thursday, March 12, 2015, Florida. Credit: Ken Kremer- kenkremer.com
ULA’s most recent launch for NASA involved the $1.1 Billion Magnetospheric Multiscale (MMS) mission comprised of four formation flying satellites which blasted to Earth orbit atop an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida, during a spectacular nighttime blastoff on March 12, 2015. Read my onsite reports – here and here.
“Space launch affects everyone, every day, and our goal in letting America name its next rocket is to help all Americans imagine the future of endless possibilities created by affordable space launch,” Bruno added.
NGLS will include some heritage design from the Atlas V and Delta IV rockets, but will feature many new systems and potentially some reusable systems – to be outlined by Bruno on April 13.
ULA plans to phase out the Delta IV around 2019 when the current contracts are concluded. The Atlas V will continue for a transitional period.
The Atlas V is also the launcher for Boeing’s CST-100 manned space taxi due to first launch in 2017.
NGLS will launch from Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida, the same pad as for the Atlas V, as well as from Vandenberg AFB, Calif.
ULA’s next Delta IV launch with GPS IIF-9 is scheduled shortly for Wednesday, March 25, with liftoff at 2:36 p.m. EDT from Cape Canaveral.
Live webcast begins at 2:06 p.m. Live link here – http://www.ulalaunch.com/webcast.aspx
Vote now!
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.

Astronomy Cast Ep. 361: Modern Women: Maria Zuber
Maria Zuber is one of the hardest working scientists in planetary science, being a part of six different space missions to explore the Solar System. Currently, she’s the lead investigator for NASA’s GRAIL mission.
Visit the Astronomy Cast Page to subscribe to the audio podcast!
We record Astronomy Cast as a live Google+ Hangout on Air every Monday at 12:00 pm Pacific / 3:00 pm Eastern. You can watch here on Universe Today or from the Astronomy Cast Google+ page.
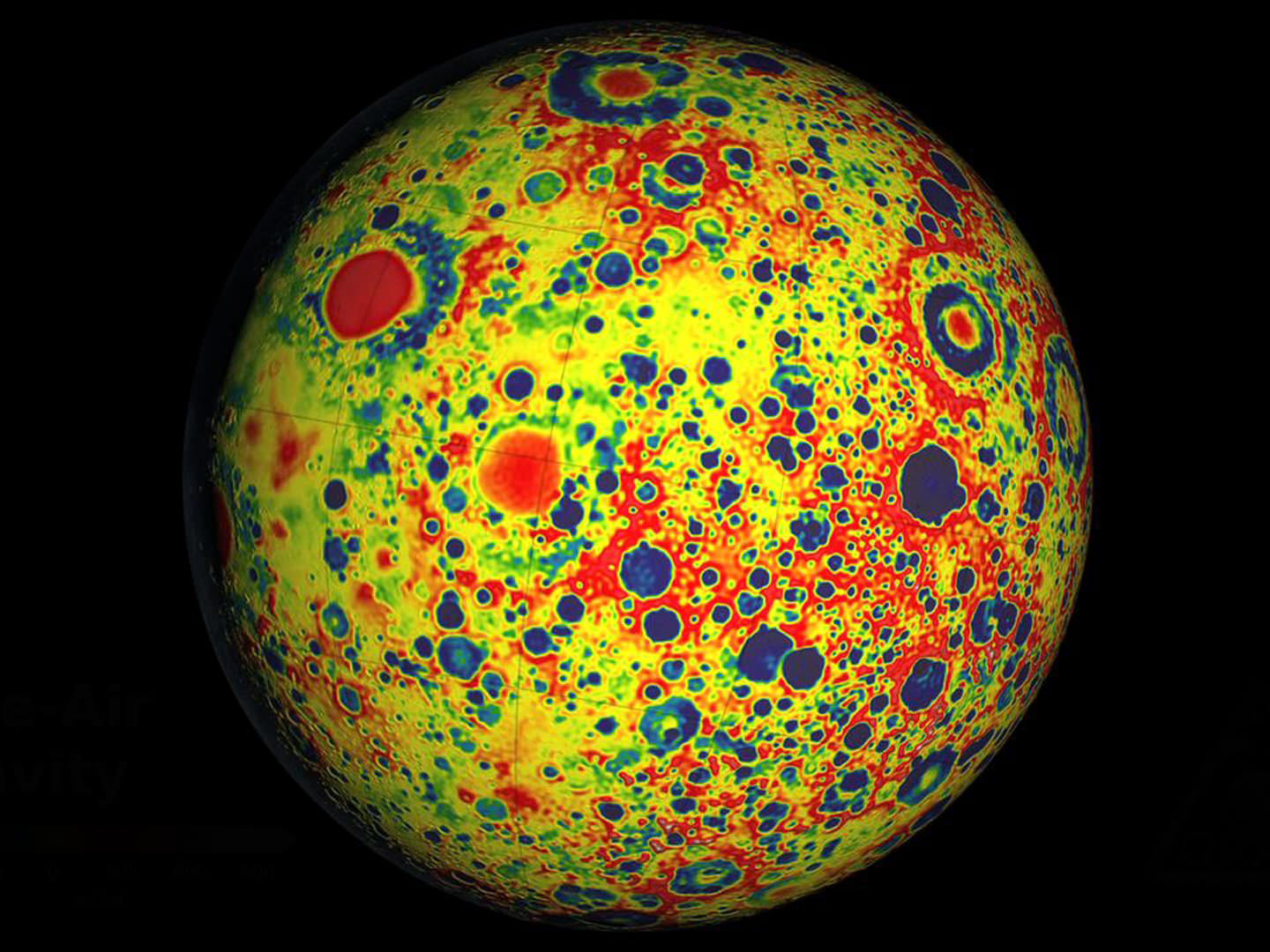
Moon’s Blotchy Near Side Has Bigger Craters Than Expected
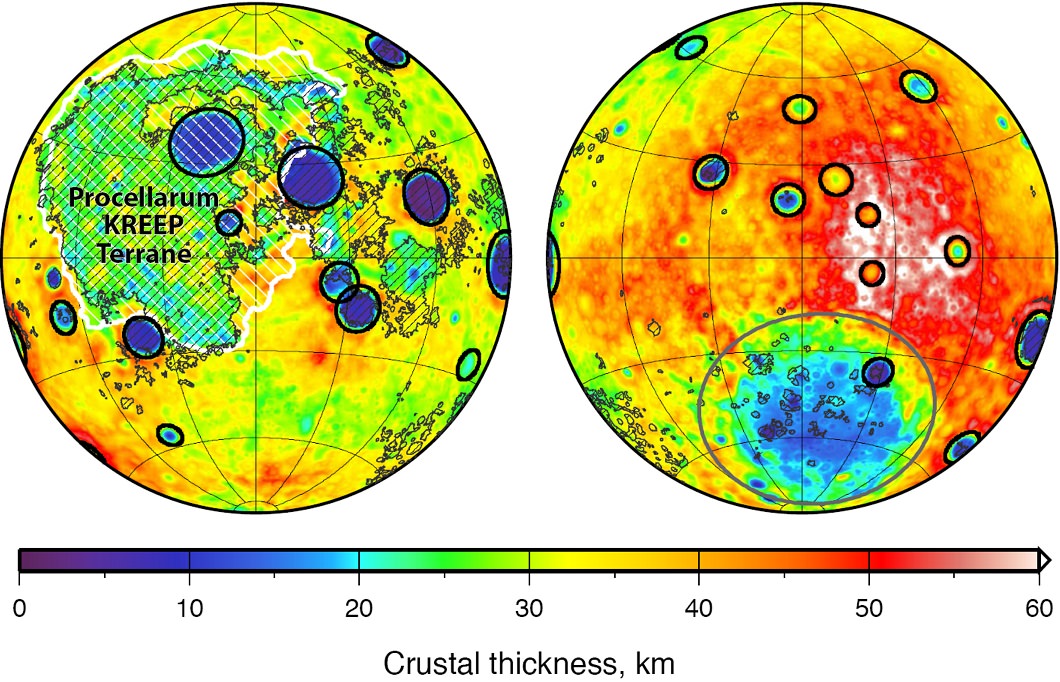
The familiar blotches that make up “the man in the moon”, from the vantage point of Earth, happened because the moon’s crust is thinner on the near side than the far side to our planet, new research reveals.
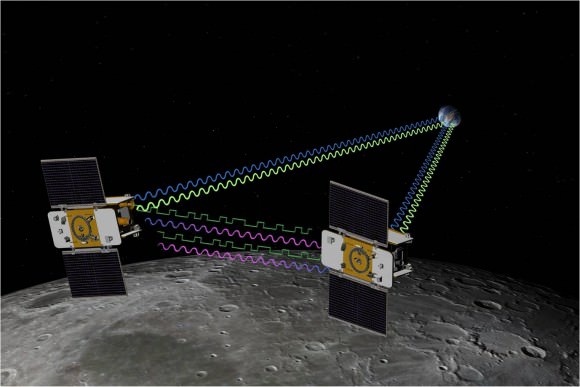
The twin GRAIL spacecraft provided the most accurate sizes yet of lunar impact craters on the moon, providing more insight into what happened when Earth’s closest large neighbor was hammered with meteorites over billions of years.
“Since time immemorial, humanity has looked up and wondered what made the man in the moon,” stated Maria Zuber, GRAIL principal investigator from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in Cambridge.
“We know the dark splotches are large, lava-filled, impact basins that were created by asteroid impacts about four billion years ago. GRAIL data indicate that both the near side and the far side of the moon were bombarded by similarly large impactors, but they reacted to them much differently.”
The moon’s near side is easily visible in a telescope, but it’s hard to measure the size of the impacts because lava is obscuring their dimensions. The GRAIL spacecraft, however, peered at the internal structure of the moon and also produced information showing how thick the crust is. This showed that there are more, bigger craters on the closer side of the moon to us than the further side.

“Impact simulations indicate that impacts into a hot, thin crust representative of the early moon’s near-side hemisphere would have produced basins with as much as twice the diameter as similar impacts into cooler crust, which is indicative of early conditions on the moon’s far-side hemisphere,” stated lead author Katarina Miljkovic of the Paris Institute of Earth Physics (Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris).
As is common with research projects, learning more about the moon is revealing a new mystery that needs to be examined. It’s commonly cited that the moon was walloped during something called the late heavy bombardment, a period four billion years ago when it was believed that more meteorites impacted the moon.
“The late heavy bombardment is based largely on the ages of large near-side impact basins that are either within, or adjacent to the dark, lava-filled basins, or lunar maria, named Oceanus Procellarum and Mare Imbrium,” NASA stated.
“However, the special composition of the material on and below the surface of the near side implies that the temperatures beneath this region were not representative of the moon as a whole at the time of the late heavy bombardment. The difference in the temperature profiles would have caused scientists to overestimate the magnitude of the basin-forming impact bombardment.”
A research paper on the topic recently appeared in Science. GRAIL successfully concluded its mission last year after nine months of operations, flying into the side of a mountain as planned.
Source: NASA
Moon’s Variable Gravity Came From Ancient Impacts
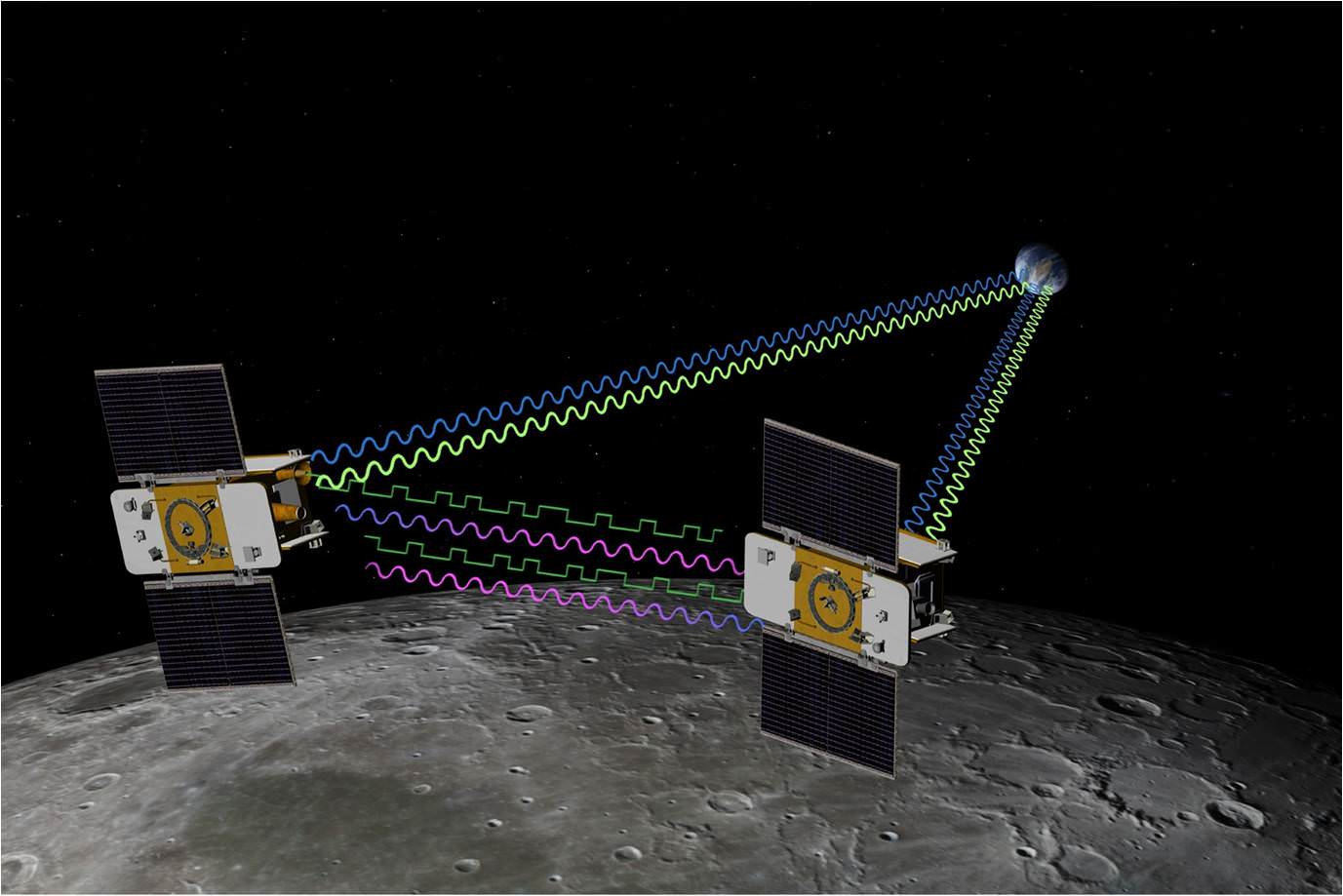
The moon’s gravity has been a headache ever since the Apollo era. Areas of “mass concentration” or mascons, discovered in 1968, affected spacecraft orbits and made landing on Earth’s neighbor a tricky challenge.
The phenomenon has puzzled scientists, but new data shows that mascons might have come to be after asteroids or comets hit the moon a long time ago.
For nine months last year, until their mission ended with a deliberate crash on a moon mountain, twin washing-machine sized spacecraft Ebb and Flow circled the planet. Their work was known as the GRAIL mission (also known as Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory.) As they orbited together, gravity changes in the moon below them slightly changed their distances to each other — sometimes closer, sometimes further.
This allowed scientists to map out the mascons to high precision once they combined that information with computer models of big asteroid impacts as well as how craters on the moon evolved.

Mascons, which are invisible on the surface but appear in gravity maps as a sort of bulls-eye, arise “as a natural consequence of crater excavation, collapse and cooling following an impact,” NASA stated.
The center of the bulls-eye has stronger gravity, with a ring of weaker gravity surrounding the bulls-eye, and then another ring of strong gravity surrounding the bulls-eye and inner ring.
“GRAIL data confirm that lunar mascons were generated when large asteroids or comets impacted the ancient moon, when its interior was much hotter than it is now,” stated Jay Melosh, lead researcher and a GRAIL co-investigator at Purdue University.
“We believe the data from GRAIL show how the moon’s light crust and dense mantle combined with the shock of a large impact to create the distinctive pattern of density anomalies that we recognize as mascons.”
What’s more, researchers expect they’ll be able to apply that understanding to Mercury and Mars, as mascons were also discovered on those terrestrial planets.
The findings appeared in the May 30 edition of Science. You can read the entire article here.
Source: NASA
NASA: Reaches for New Heights – Greatest Hits Video
Video Caption: At NASA, we’ve been a little busy: landing on Mars, developing new human spacecraft, going to the space station, working with commercial partners, observing the Earth and the Sun, exploring our solar system and understanding our universe. And that’s not even everything.Credit: NASA
Check out this cool action packed video titled “NASA: Reaching for New Heights” – to see NASA’s ‘Greatest Hits’ from the past year
The 4 minute film is a compilation of NASA’s gamut of Robotic Science and Human Spaceflight achievements to explore and understand Planet Earth here at home and the heavens above- ranging from our Solar System and beyond to the Galaxy and the vast expanse of the Universe.
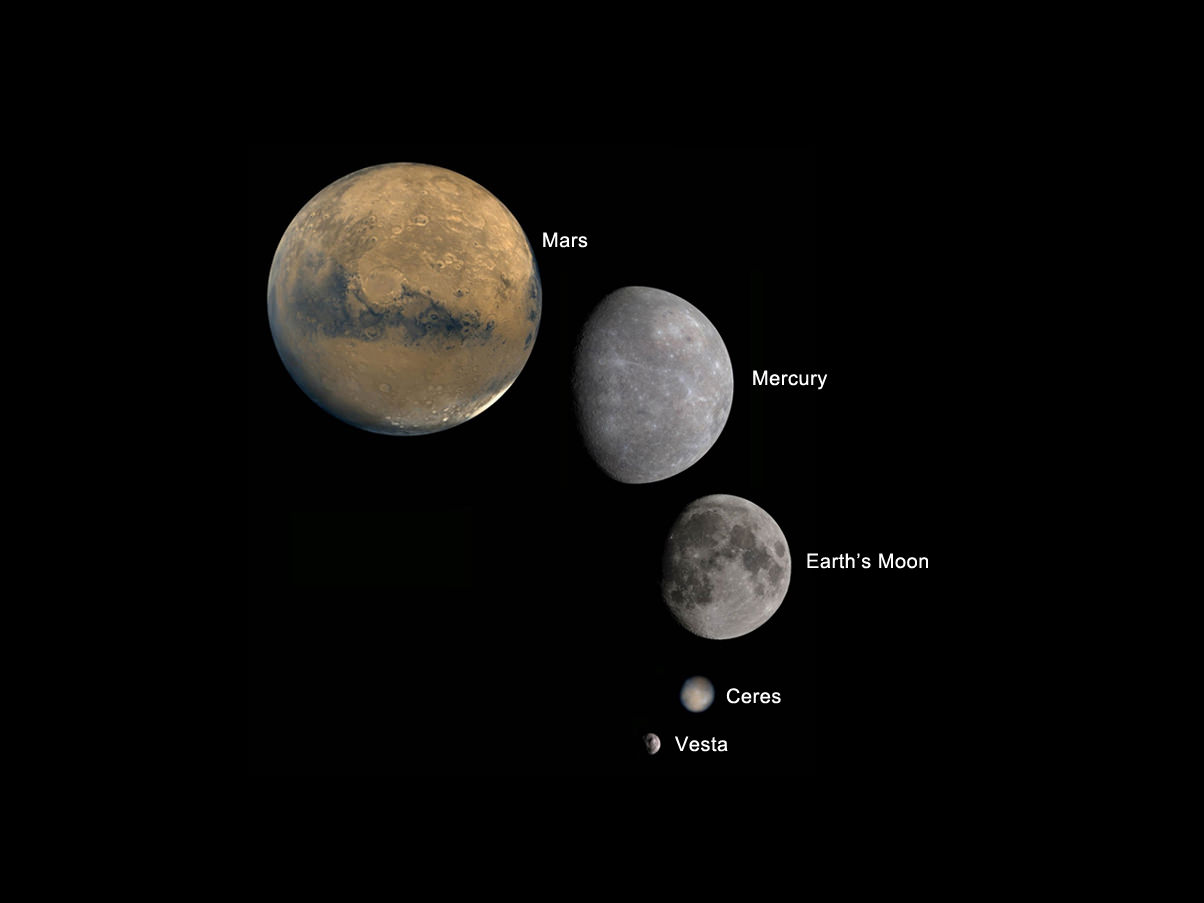
Image caption: Planets and Moons in perspective. Credit: NASA
The missions and programs featured include inspiringly beautiful imagery from : Curiosity, Landsat, Aquarius, GRACE, NuSTAR, GRAIL, Dawn at Asteroid Vesta, SDO, X-48C Amelia, Orion, SLS, Apollo, SpaceX, Sierra Nevada Dream Chaser, Boeing CST-100, Commercial Crew, Hurricane Sandy from the ISS, Robonaut and more !
And even more space exploration thrills are coming in 2013 !
Image caption: SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket blasts off on May 22, 2012 with Dragon cargo capsule from Space Launch Complex-40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla., on the first commercial mission to the International Space Station. The next launch is set for March 1, 2013. Credit: Ken Kremer





