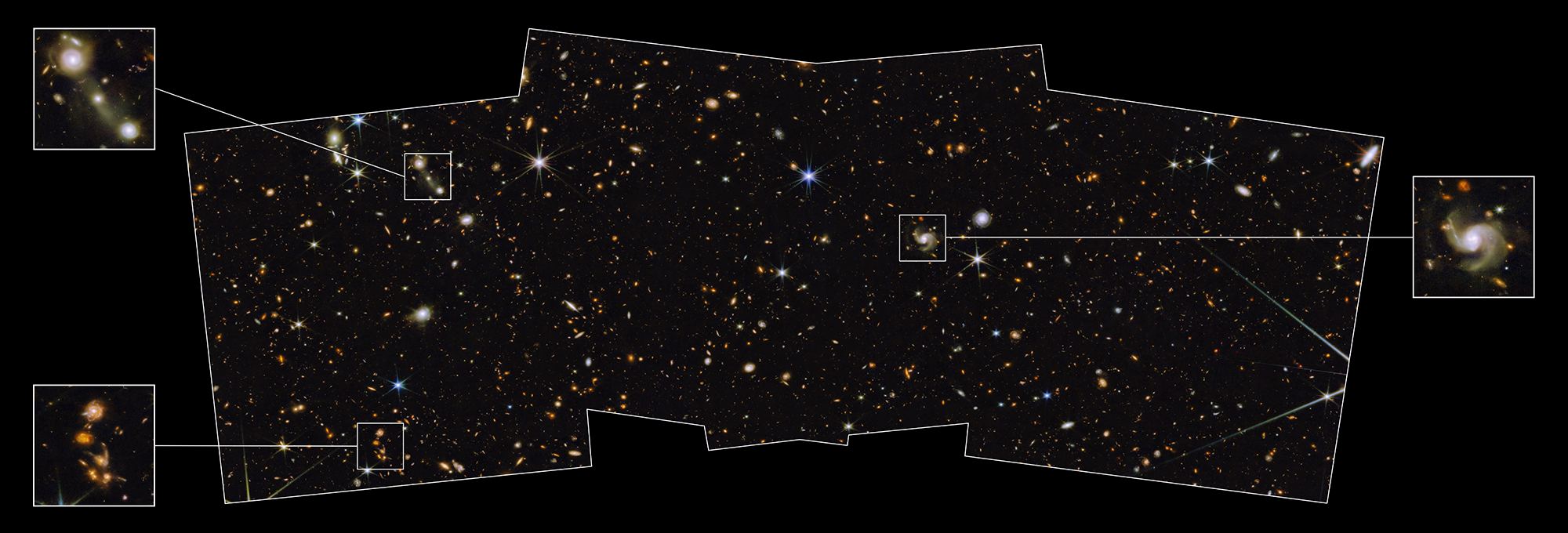
A star that sounds as if it came from “The Lord of the Rings” now marks one of the Hubble Space Telescope’s farthest frontiers: The fuzzy point of light, known as Earendel, has been dated to a mere 900 million years after the Big Bang and appears to represent the farthest-out individual star seen to date.
Based on its redshift value of 6.2, Earendel’s light has taken 12.9 billion years to reach Earth, astronomers report in this week’s issue of the journal Nature. That distance mark outshines Hubble’s previous record-holder for a single star, which registered a redshift of 1.5 and is thought to have existed when the universe was 4 billion years old.
The newly reported record comes with caveats. First of all, we’re talking here about a single star rather than star clusters or galaxies. Hubble has seen agglomerations of stars that go back farther in time.
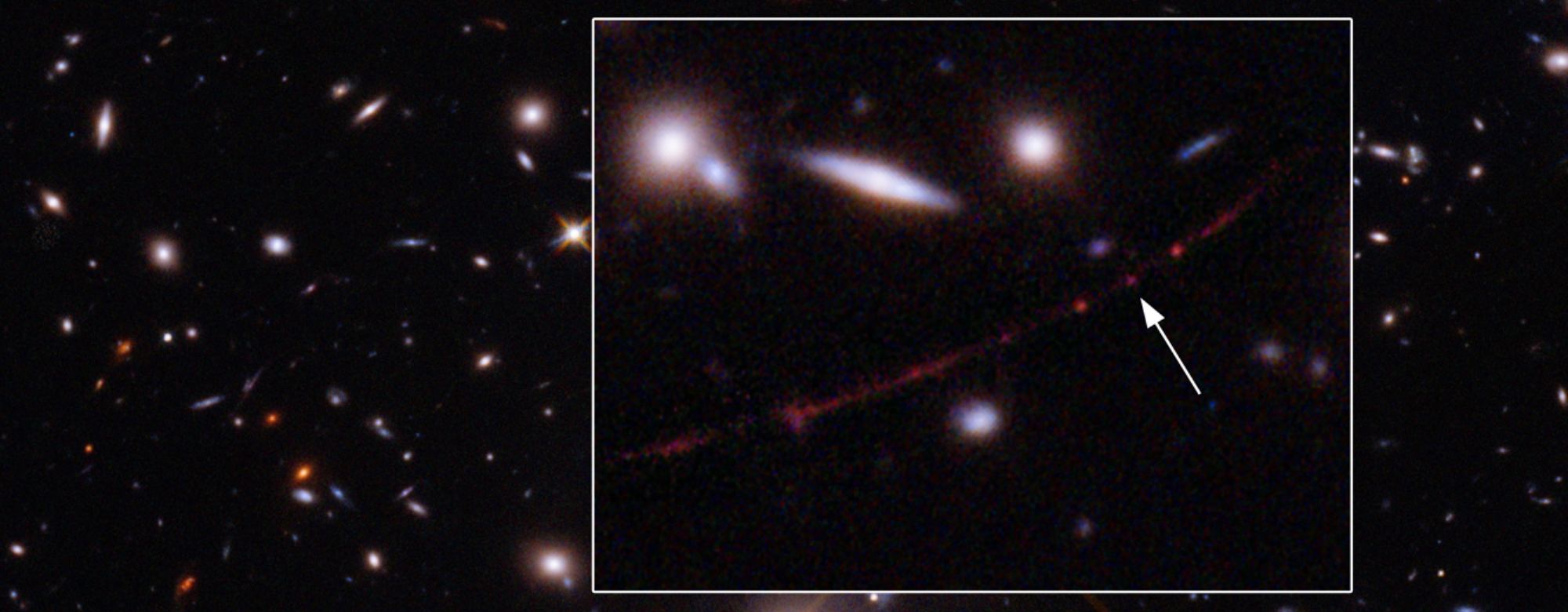
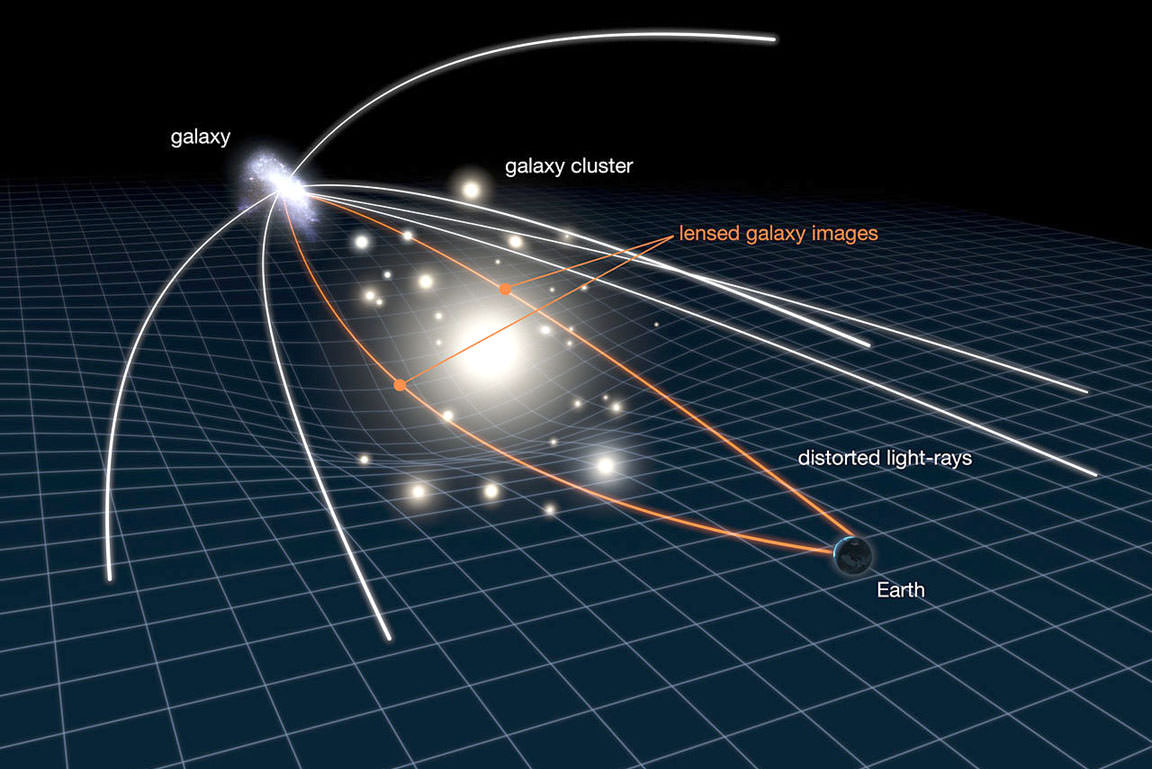
“Normally at these distances, entire galaxies look like small smudges, with the light from millions of stars blending together,” lead author Brian Welch, an astronomer at Johns Hopkins University, said today in a news release. “The galaxy hosting this star has been magnified and distorted by gravitational lensing into a long crescent that we named the Sunrise Arc.”
A close look at the arc turned up several bright spots, but the characteristics of the light coming from Earendel pointed to a high redshift, which translates into extreme distance. The higher the redshift, the faster the source of the light is receding from us in an ever-more-quickly expanding universe.
Continue reading “A New Record! Hubble Detects an Individual Star From a Time When the Universe Was Less Than a Billion Years Old”