In about five billion years, our Sun will exit its main sequence phase and transition to its red giant phase. At this point, the Sun will expand and consume the planets of the inner Solar System, including Mercury and Venus. What will become of Earth when this happens has been the subject of debate for many decades. But with the recent explosion in exoplanet discoveries, 5,759 confirmed in 4,305 systems so far, astronomers hope to learn more about how planets fare as their stars near the end of their life cycle.
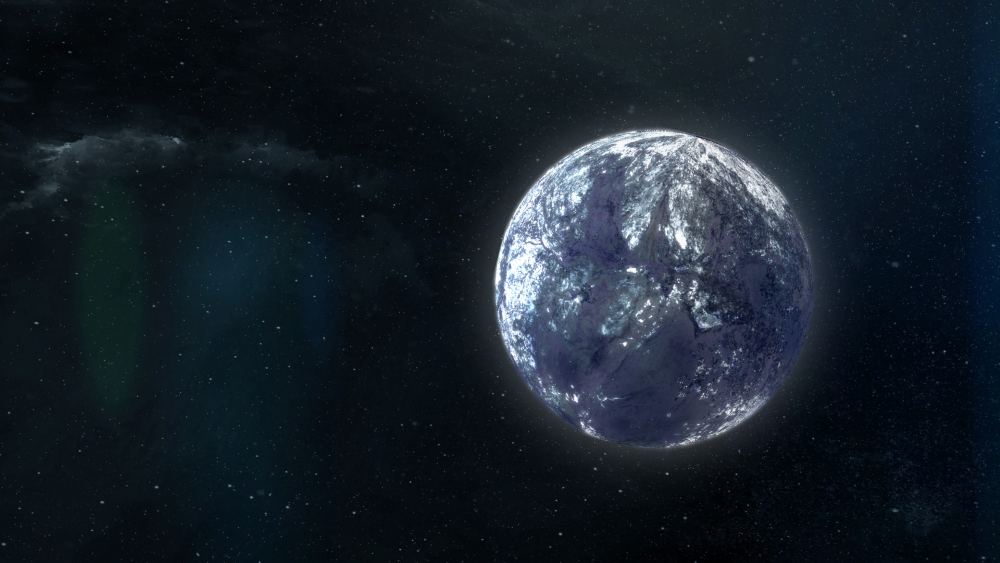
Using the 10-meter telescope at the Keck Observatory in Hawaii, an international team of astronomers discovered an Earth-like planet orbiting a white dwarf star 4,000 light-years from Earth. This planet orbits its star, about half the mass of our Sun, at a distance roughly twice that of the Earth today. The system resembles what is expected to become of our system once the Sun has exhausted the last of its fuel and sheds its outer layers. It also offers some assurances that Earth will survive the Sun becoming a red giant and exploding in a supernova.
Continue reading “An Earth-like Planet Around a Dead Sun Provides Some Reassurance About the Future of Earth”