Getting a mission to the point of officially being accepted for launch is an ordeal. However, even when they aren’t selected for implementation, their ideas, and in some cases, their technologies, can live on in other missions. That was the case for the Oversize Kite-craft for Exploration and AstroNautics in the Outer Solar system (OKEANOS) project, originally planned as a Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) mission. Despite not receiving funding to complete its entire mission, the project team released a paper that details the original plan for the mission, and some of those plans were incorporated into other missions that are still under development.
Continue reading “OKEANOS – A Mission That Would Have Retrurned Samples From the Trojan Asteroids”Asteroid Ryugu Might Actually Be a Dead Comet
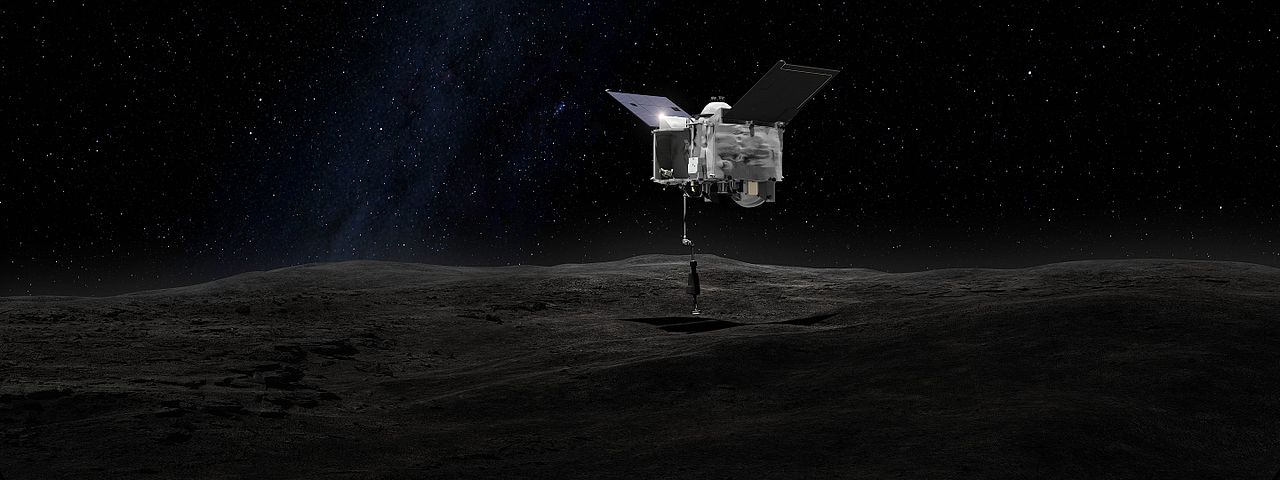
In 2014, the Japanese Space Agency JAXA launched the Hayabusa 2 spacecraft to visit asteroid Ryugu. It arrived at the asteroid in June 2018 and studied it from orbit for over a year. Hayabusa 2 even dispatched four rovers to the asteroid’s surface. After departing, it flew past Earth in December 2020, dropping off a sample of Ryugu.
Of all the scientific results from that impressive mission, the most interesting one might be this: Asteroid Ryugu might not be an asteroid. It might be the remnant of a comet.
Continue reading “Asteroid Ryugu Might Actually Be a Dead Comet”Why are Rubble Pile Asteroids Shaped Like Diamonds?
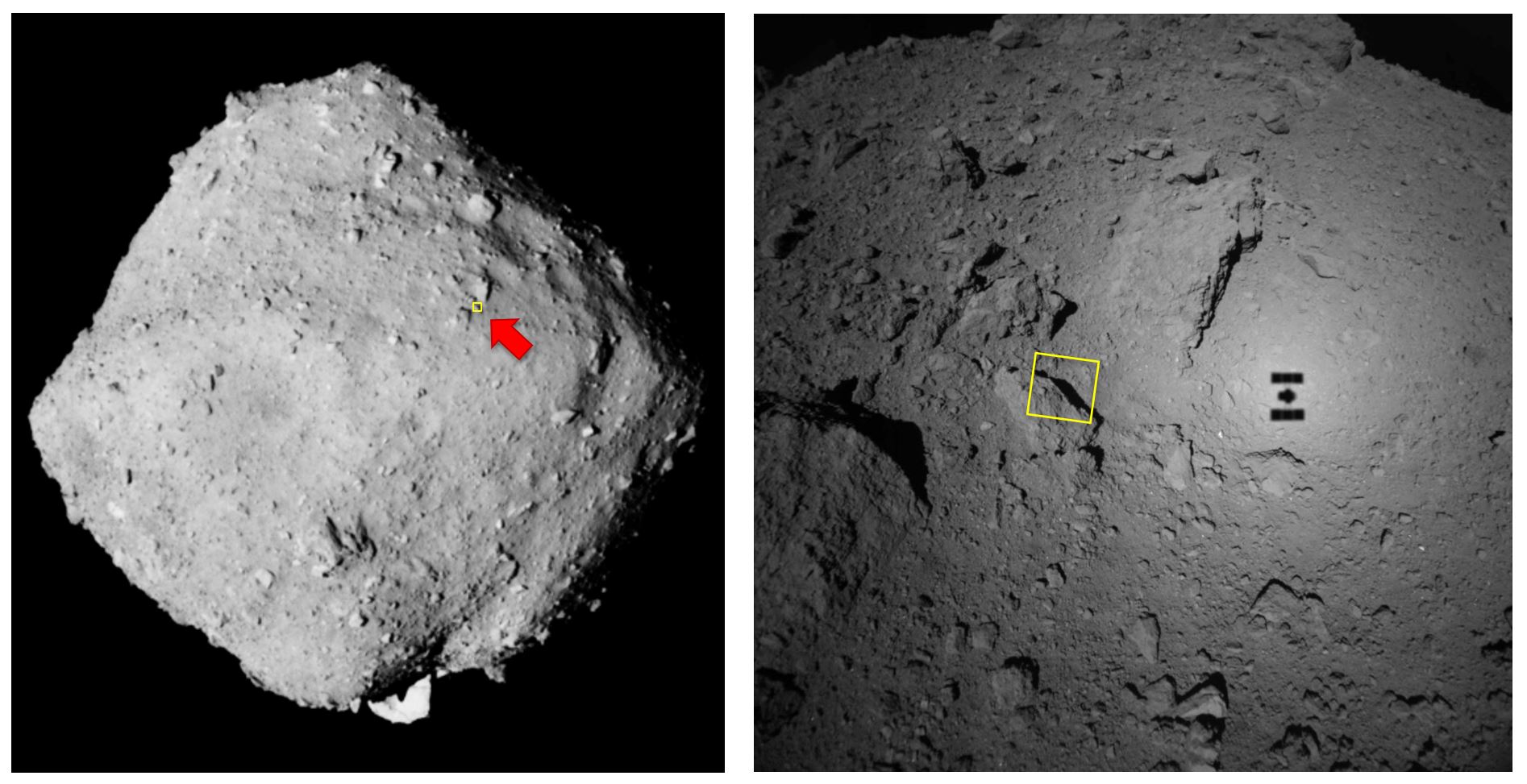
Scientists are fortunate enough to have detailed, close-up views of the near-Earth asteroids Bennu and Ryugu. Both asteroids have a diamond shape, for some reason. Why? Up until now, it’s been a puzzle.
Now a team of scientists has tackled the question and may have come up with the answer.
Continue reading “Why are Rubble Pile Asteroids Shaped Like Diamonds?”OSIRIS-REx Did One Last Close Flyby of Asteroid Bennu. It’s Almost Time to Come Home
After more than two years in orbit around asteroid Bennu, NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft is ready to come home. It’s bringing with it a pristine sample of space rocks that geologists here on Earth are eager to study up close. The sample will arrive in September 2023, but we won’t have to wait nearly that long for new data from OSIRIS-REx. Last week, the probe carried out one final flyby of Bennu, in an effort to photograph the sample collection site. The photographs are being downlinked now, and should be here by midweek.
If you’ve been following the OSIRIS-REx mission, you probably already know why scientists are keen to see these photographs, but if you haven’t, hold on to your hats – it’s a wild story.
Continue reading “OSIRIS-REx Did One Last Close Flyby of Asteroid Bennu. It’s Almost Time to Come Home”Japan’s Hayabusa 2 Probe Drops Off Bits of an Asteroid and Heads for Its Next Target
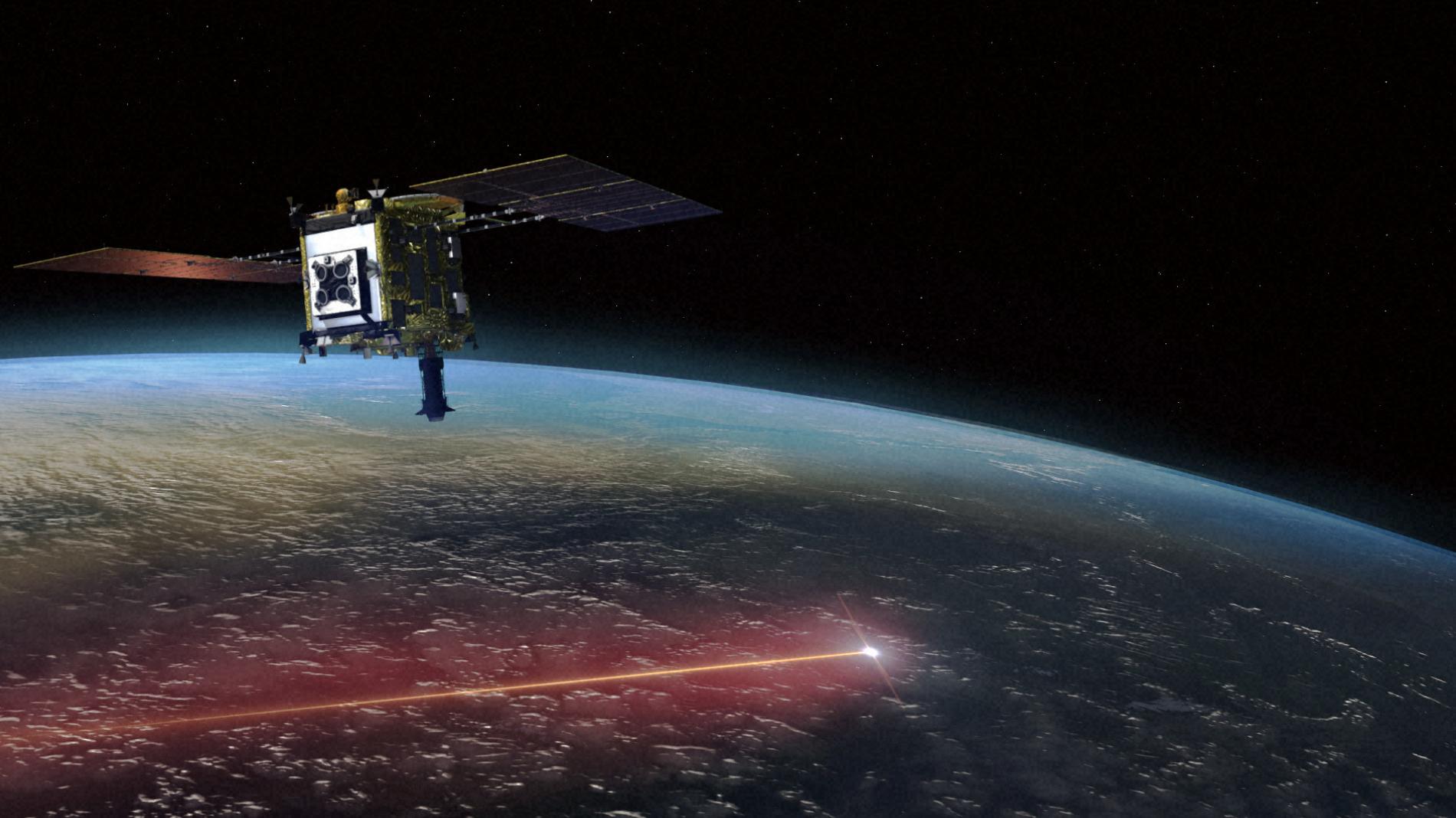

Japan’s Hayabusa 2 probe zoomed past Earth on December 5th and dropped off a capsule containing bits of an asteroid, finishing a six-year round trip.
But the mission is far from over: While Hayabusa 2’s parachute-equipped sample capsule descended to the Australian Outback, its mothership set a new course for an encounter with yet another asteroid in 2031.
Hayabusa 2’s prime objective was to deliver bits of Ryugu, an asteroid that’s currently 11.6 million kilometers from Earth. Mission controllers at the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency, or JAXA, cheered and laughed when word came that the capsule had survived atmospheric re-entry.
Imagery captured by tracking cameras — and from the International Space Station — showed the capsule streaking like a fireball across the sky as it decelerated from an initial speed of 43,000 kilometers per hour.
Continue reading “Japan’s Hayabusa 2 Probe Drops Off Bits of an Asteroid and Heads for Its Next Target”Hayabusa 2’s Sample is Landing on Earth December 6th
Japan’s Hayabusa 2 spacecraft is nearly back home, with precious cargo aboard! The sample-return mission departed asteroid Ryugu (162173 Ryugu) a little over a year ago, with soil samples and data that could provide clues to the early days of our Solar System. On December 6, 2020, the sample return container is set to land in the Australian outback.
Continue reading “Hayabusa 2’s Sample is Landing on Earth December 6th”It’s Time for Hayabusa-2 to Come Home
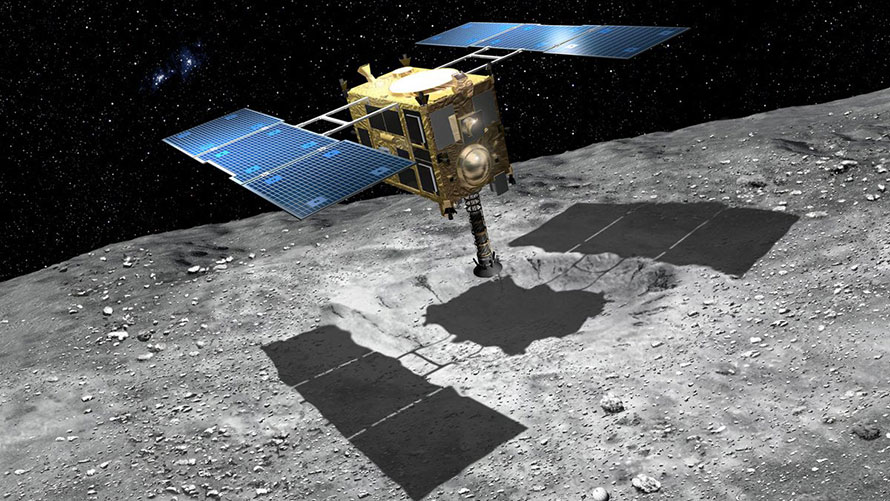

Japan’s Hayabusa 2 spacecraft is on its way home. The asteroid-visiting, sample-return mission departed asteroid Ryugu (162173 Ryugu) on Wednesday, beginning its year-long journey back to Earth. And it’s carrying some precious cargo.
Continue reading “It’s Time for Hayabusa-2 to Come Home”Watch this Amazing Video of Hayabusa 2 Picking Up a Sample from the Surface of Ryugu
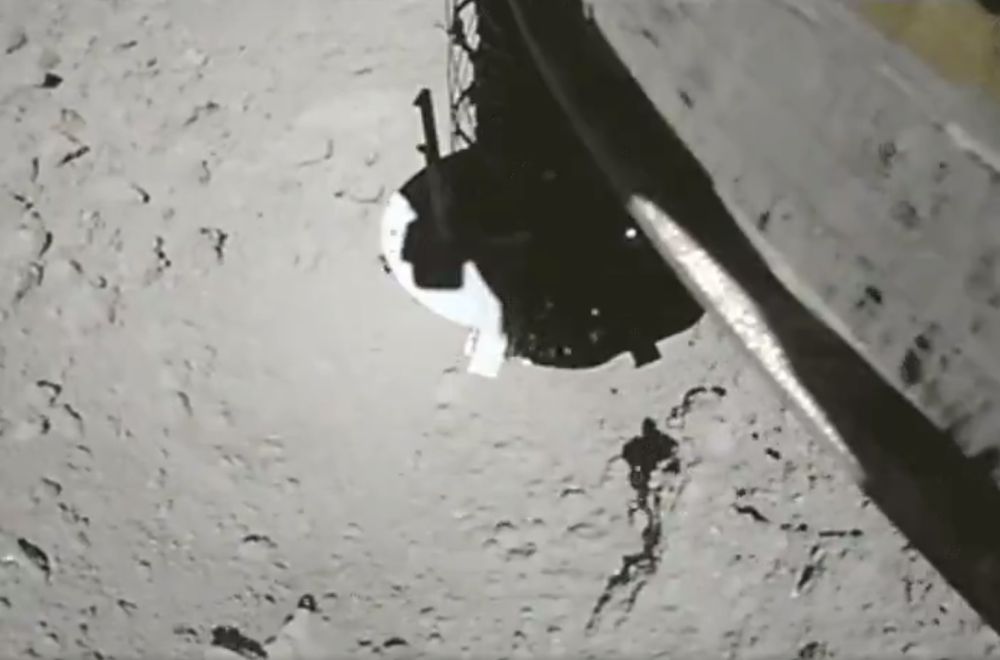

A new video shows Japan’s Hayabusa 2 sample return spacecraft collecting samples from asteroid Ryugu. The spacecraft has been at Ryugu for months now, and it’s all been leading up to this. In the video, you can clearly see airborne asteroid dust and particles swirling around in the low gravity.
Continue reading “Watch this Amazing Video of Hayabusa 2 Picking Up a Sample from the Surface of Ryugu”Hayabusa 2 is the First Spacecraft to Sample the Inside of an Asteroid
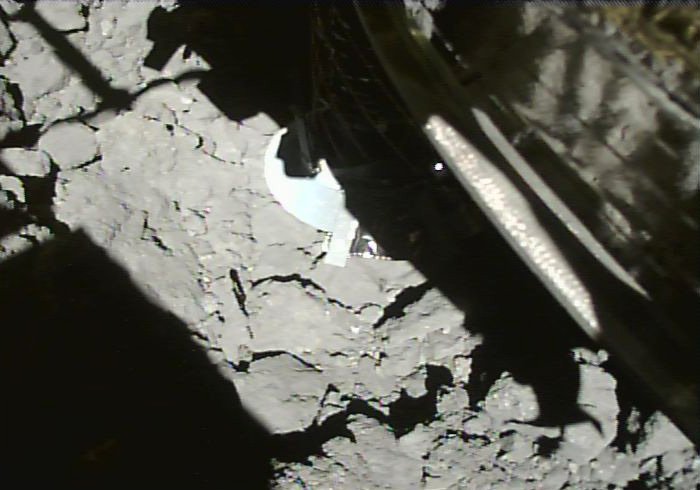
Japan’s Hayabusa 2 spacecraft is now the first spacecraft to retrieve a subsurface sample from an asteroid. On July 11th, the spacecraft touched down for a second time on asteroid 162173 Ryugu. This time, the probe retrieved a sample from a crater it excavated with its impactor.
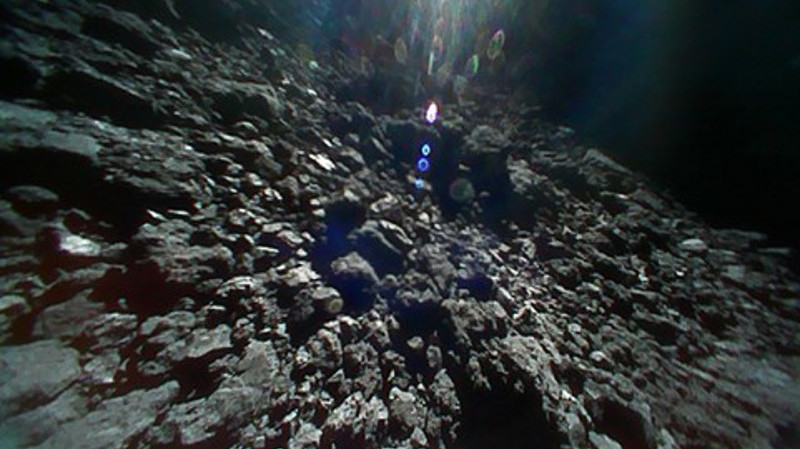
Continue reading “Hayabusa 2 is the First Spacecraft to Sample the Inside of an Asteroid”Japanese Rovers are Now on the Surface of an Asteroid, Sending Back Amazing Pictures
In December of 2014, the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) launched the Hayabusa2 mission. As the second spacecraft to bear this name, Hayabusa2 was deployed by JAXA to conduct a sample-return mission with an asteroid. By studying samples of the near-Earth asteroid 162173 Ryugu, scientists hope to shed new light on the history of the early Solar System
The spacecraft arrived in orbit around Ryugu in July of 2018, where it will spend a total of a year and a half surveying the asteroid before returning to Earth. On September 23rd, the satellite deployed its onboard MINERVA-II rovers onto the surface of Ryugu. According to the latest updates from JAXA, both rovers are in good condition and have recently sent back photographs and a video of the asteroid’s surface.






