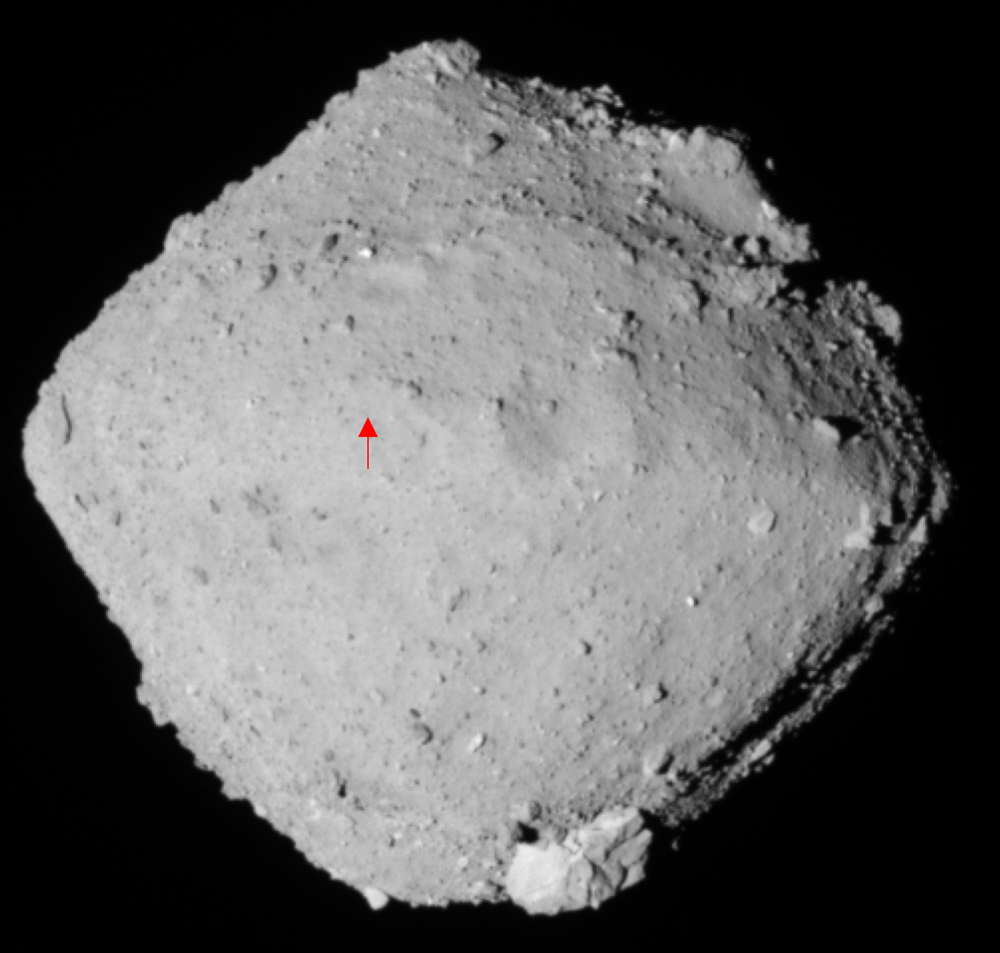
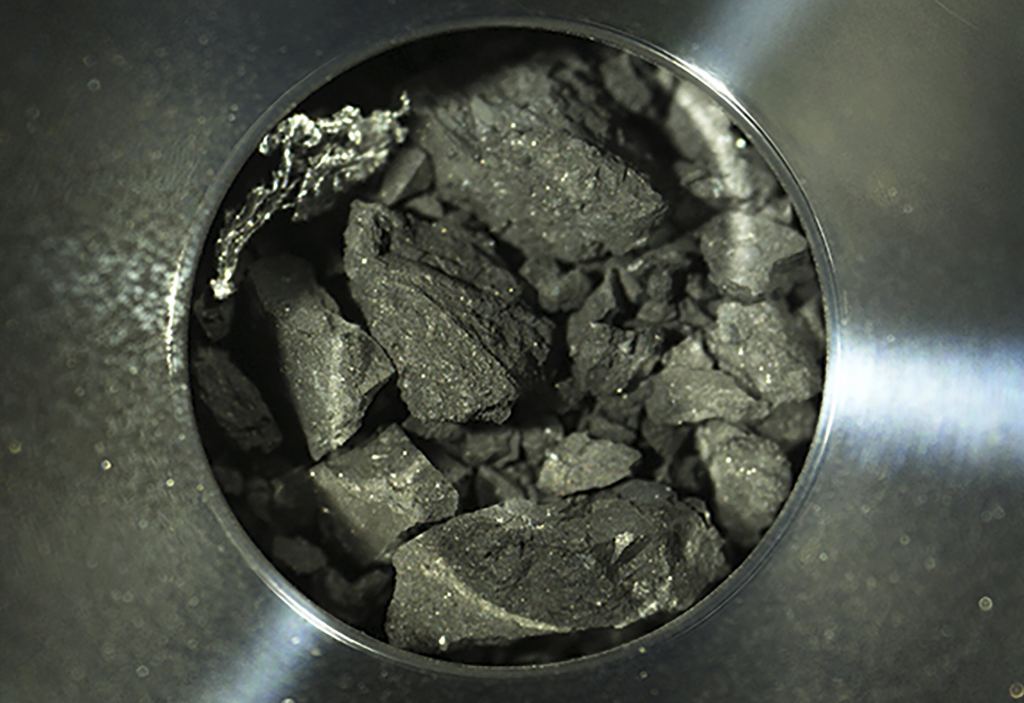
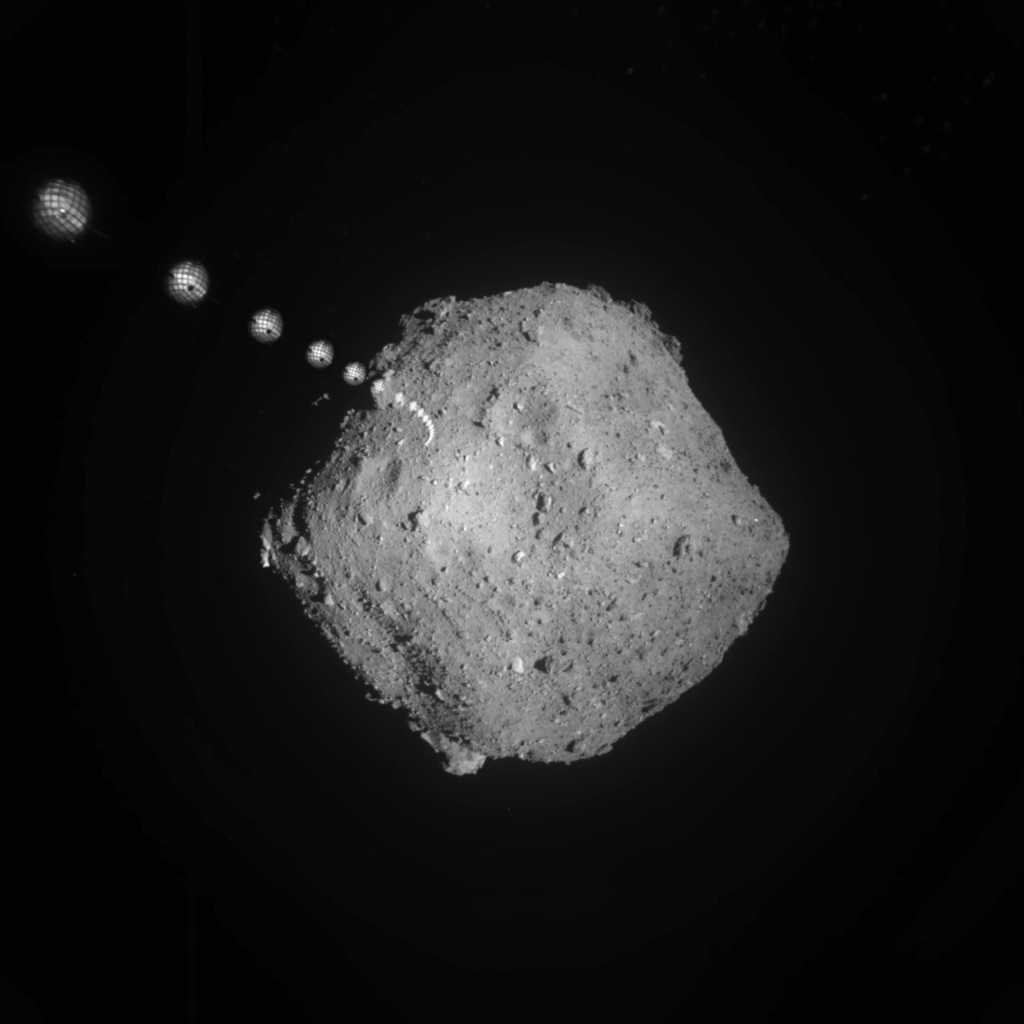
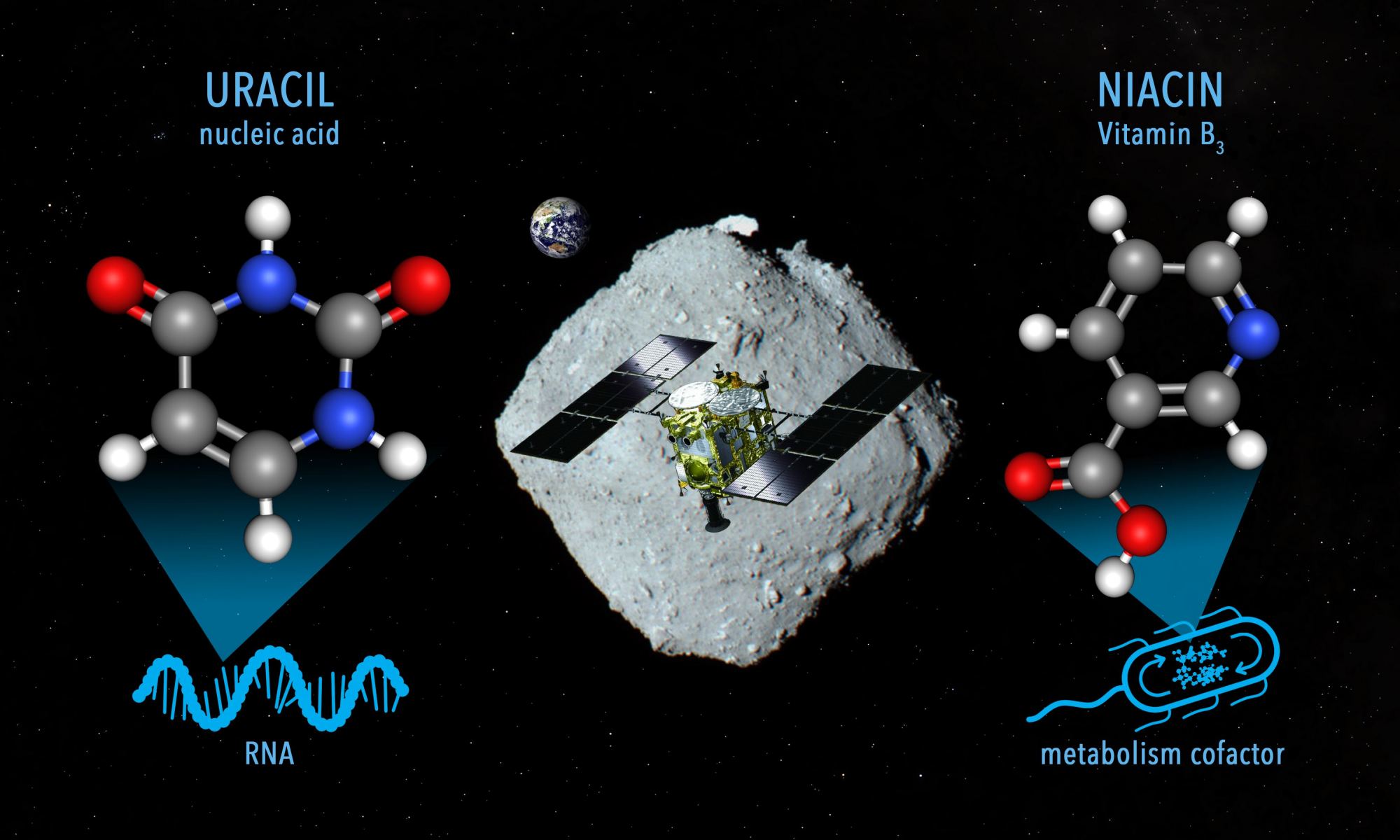
On December 5th, 2020, Japan’s Hayabusa2 mission successfully returned samples it had collected from the Near-Earth Asteroid (NEA) 162173 Ryugu home. Since asteroids are basically leftover material from the formation of the Solar System, analysis of these samples will provide insight into what conditions were like back then. In particular, scientists are interested in determining how organic molecules were delivered throughout the Solar System shortly after its formation (ca. 4.6 billion years ago), possibly offering clues as to how (and where) life emerged.
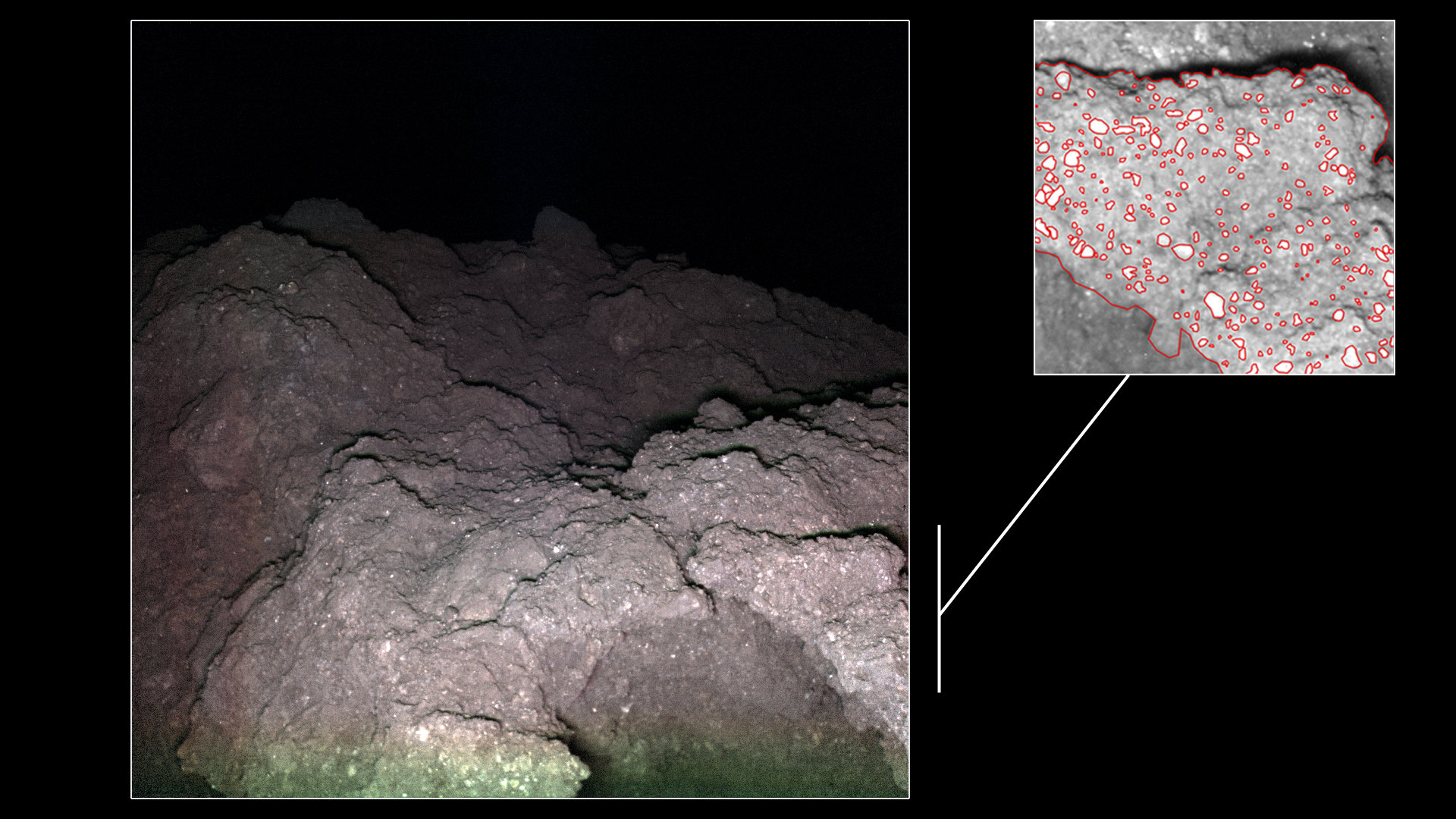
The samples have already provided a wealth of information, including more than 20 amino acids, vitamin B3 (niacine), and interstellar dust. According to a recent study by a team of Earth scientists from Tohoku University, the Ryugu samples also showed evidence of micrometeoroid impacts that left patches of melted glass and minerals. According to their findings, these micrometeoroids likely came from other comets and contained carbonaceous materials similar to primitive organic matter typically found in ancient cometary dust.
Continue reading “Asteroid Ryugu Contained Bonus Comet Particles”