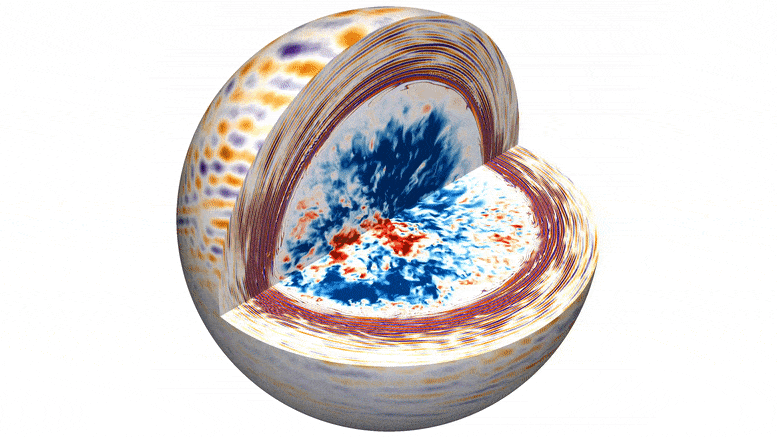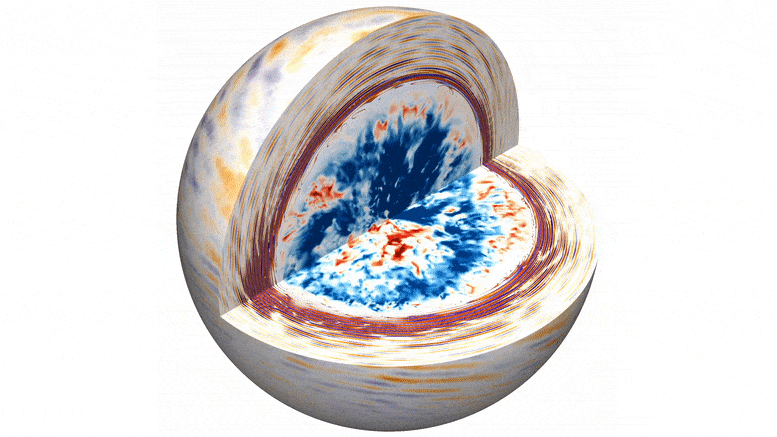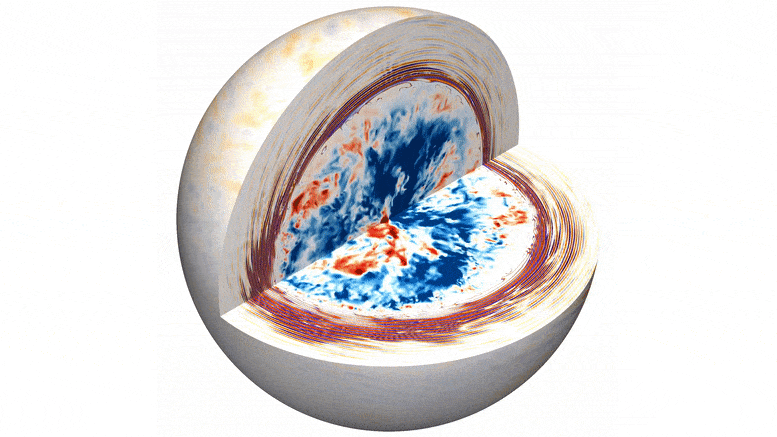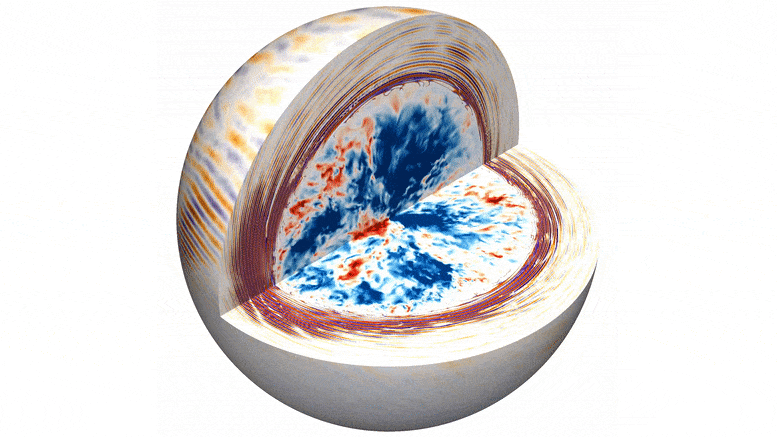
We may be already seeing the makings of next solar cycle, peeking out through the current one.
It’s been a wild ride. Thus far, Solar Cycle Number 25 has been one of the strongest cycles in recent memory, producing several massive sunspot groups. The current large region turned Earthward (Active Region 3780) is now easily visible with eclipse glasses… no magnification needed. Cycle 25 started back in 2019.
Continue reading “The Next Solar Cycle Has Started… But the Current One Hasn’t Finished Yet”