As the venerable Voyager 1 spacecraft hurtles ever outward, breaking through the very borders of our solar system at staggering speeds upwards of 35,000 mph, it’s sending back information about the curious region of space where the Sun’s outward flow of energetic particles meets the more intense cosmic radiation beyond — a boundary called the heliosheath.
Voyager 1 has been traveling through this region for the past seven years, all the while its instruments registering gradually increasing levels of cosmic ray particles. But recently the levels have been jumping up and down, indicating something new is going on… perhaps Voyager 1 is finally busting through the breakers of our Sun’s cosmic bay into the open ocean of interstellar space?
 Data sent from Voyager 1 — a trip that currently takes the information nearly 17 hours to make — have shown steadily increasing levels of cosmic radiation as the spacecraft moves farther from the Sun. But on July 28, the levels of high-energy cosmic particles detected by Voyager jumped by 5 percent, with levels of lower-energy radiation from the Sun dropping by nearly half later the same day. Within three days both levels had returned to their previous states.
Data sent from Voyager 1 — a trip that currently takes the information nearly 17 hours to make — have shown steadily increasing levels of cosmic radiation as the spacecraft moves farther from the Sun. But on July 28, the levels of high-energy cosmic particles detected by Voyager jumped by 5 percent, with levels of lower-energy radiation from the Sun dropping by nearly half later the same day. Within three days both levels had returned to their previous states.
The last time such a jump in levels occurred was in May — and that spike took a week to happen.
“The increase and the decrease are sharper than we’ve seen before, but that’s also what we said about the May data,” said Edward Stone, the Voyager project scientist based at the California Institute of Technology. “The data are changing in ways that we didn’t expect, but Voyager has always surprised us with new discoveries.”
The graph below shows the jump in cosmic particles detected starting May 2012.
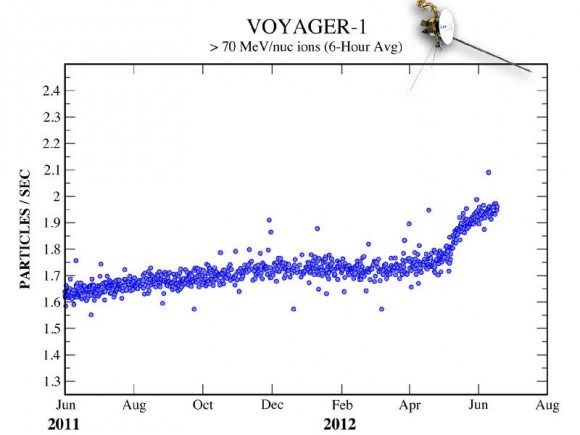
Over 11 billion miles (18 billion km) from home, Voyager 1 has been cruising through space since its launch on September 5, 1977. Its twin, Voyager 2, was launched two weeks earlier and is currently 9.3 billion miles (15 billion km) away. Both spacecraft are healthy and continue to communicate with Earth, and will both eventually break through the borders of our solar system and enter true interstellar space. If they are still operational when that happens — and there’s no reason that they shouldn’t be — we will finally get a sense of what conditions are like “out there”.
Although Voyager 1 is registering intriguing fluctuations in radiation from both inside and outside the Solar System, it’s not quite there yet.
“Our two veteran Voyager spacecraft are hale and healthy as they near the 35th anniversary of their launch,” said Suzanne Dodd, Voyager project manager based at JPL in Pasadena. “We know they will cross into interstellar space. It’s just a question of when.”
Read more about Voyager’s ongoing breakout here.
“We are certainly in a new region at the edge of the solar system where things are changing rapidly. But we are not yet able to say that Voyager 1 has entered interstellar space.”
– Edward Stone, Voyager project scientist, Caltech
Images: NASA/JPL-Caltech





