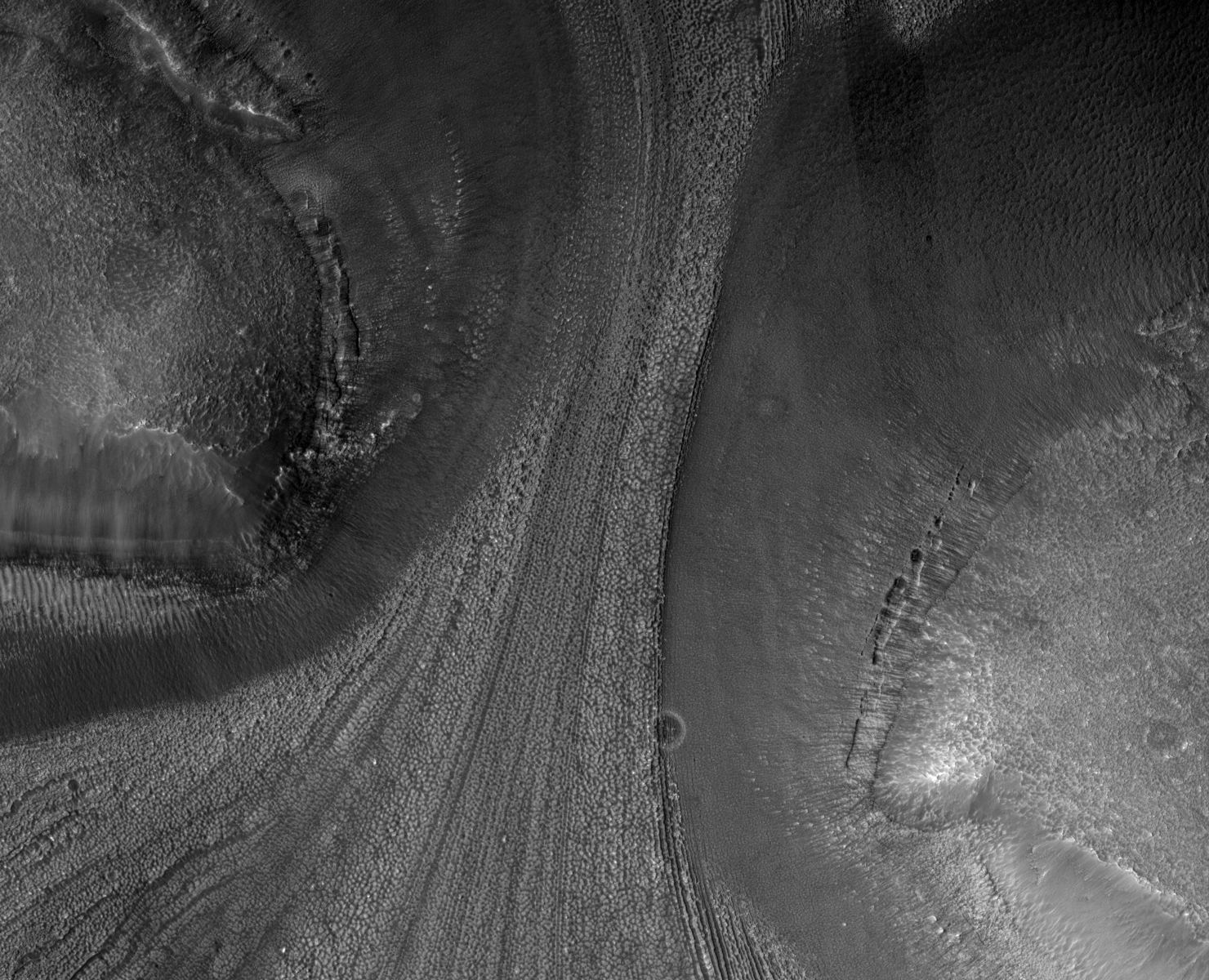
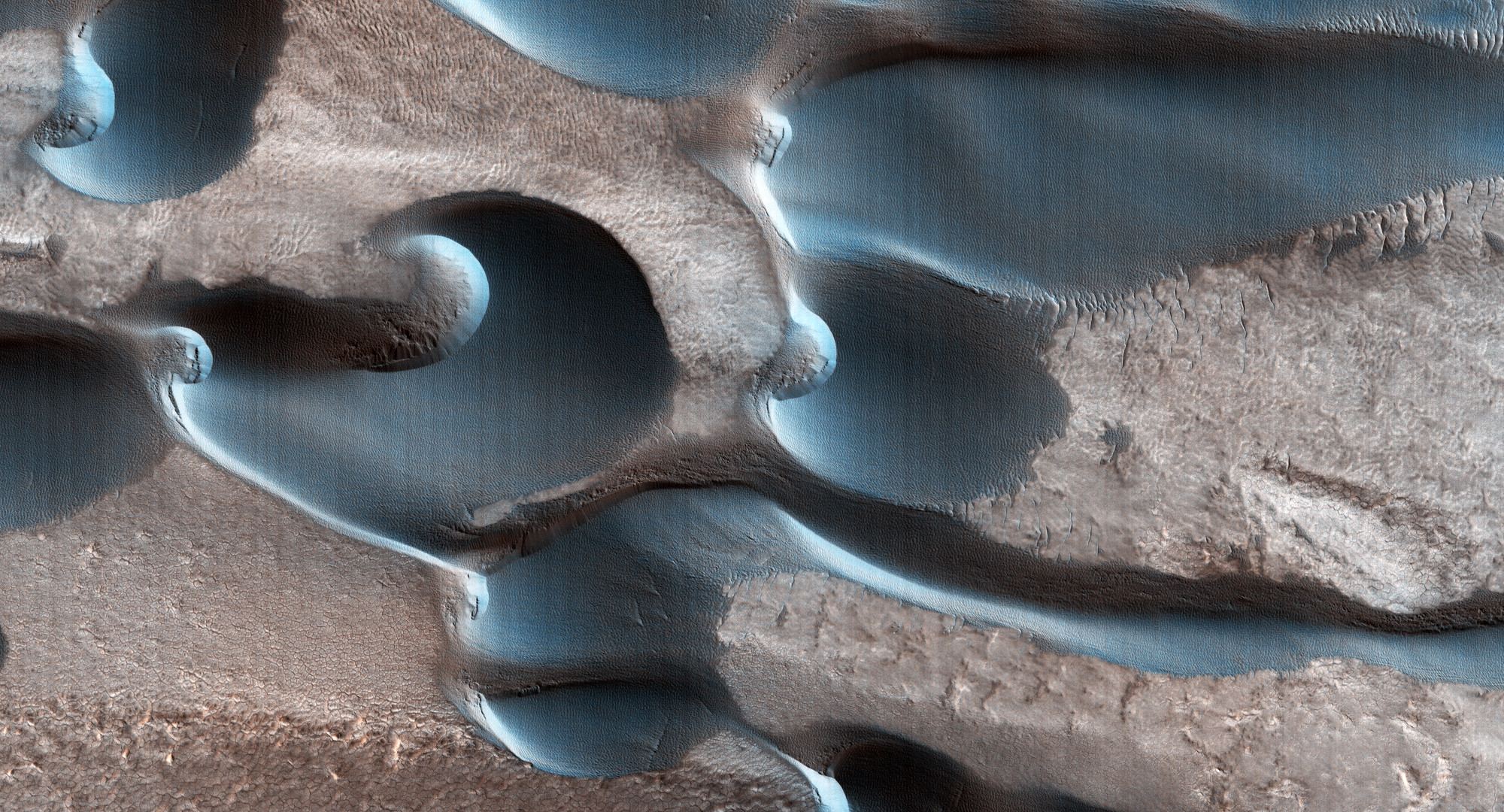
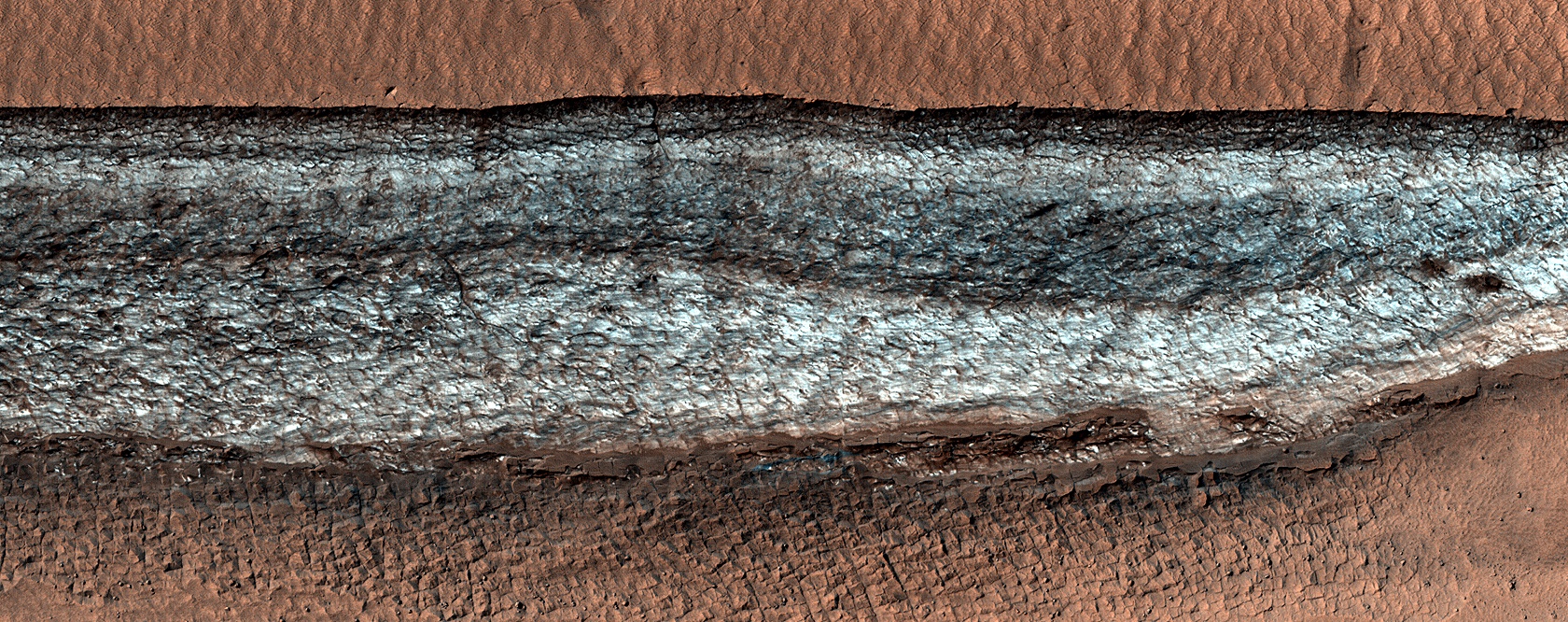
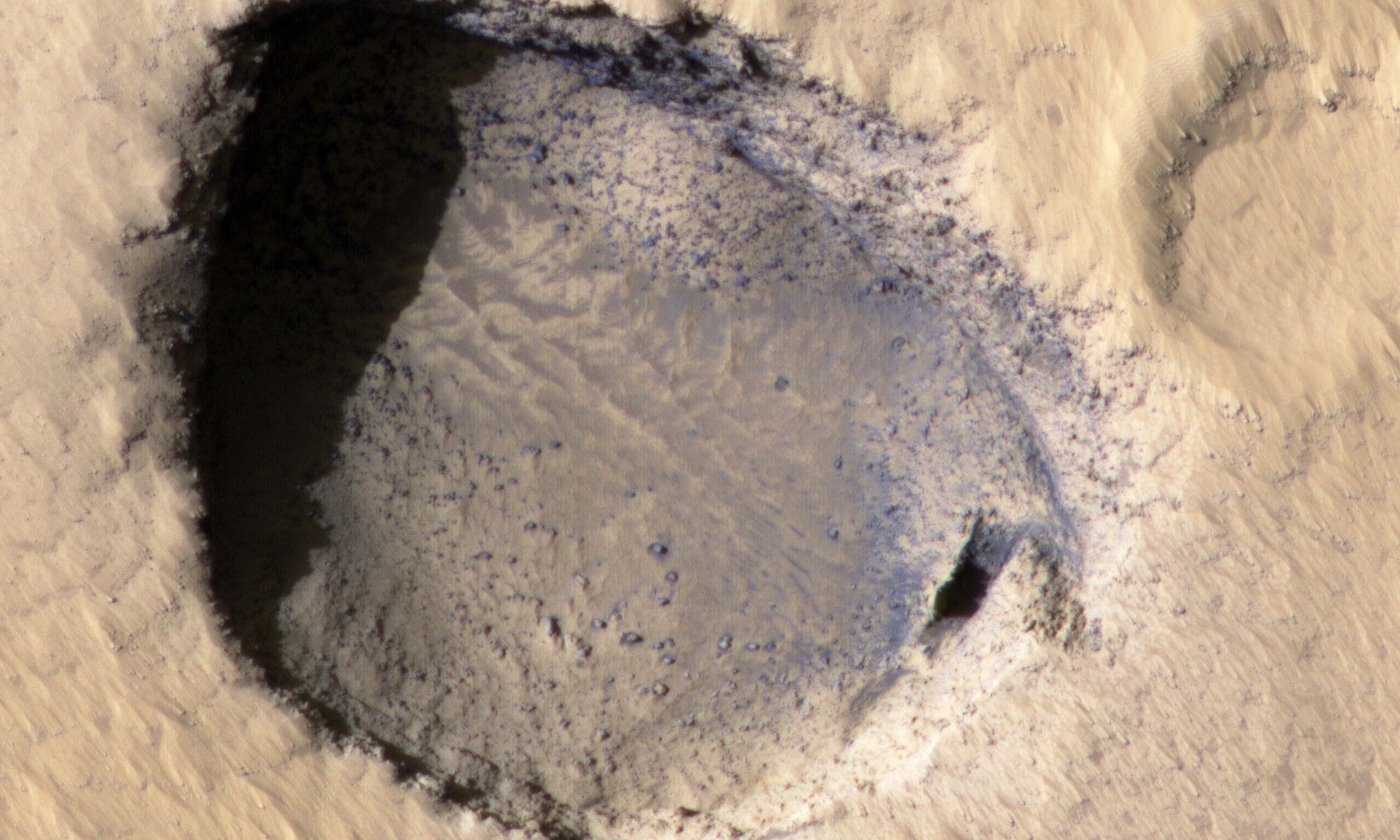
In the 17th century, astronomers Giovanni Domenica Cassini and Christian Huygens noted the presence of hazy white caps while studying the Martian polar regions. These findings confirmed that Mars had ice caps in both polar regions, similar to Earth. By the 18th century, astronomers began to notice how the size of these poles varied depending on where Mars was in its orbital cycle. Along with discovering that Mars’ axis was tilted like Earth’s, astronomers realized that Mars’ polar ice caps underwent seasonal changes, much like Earth’s.
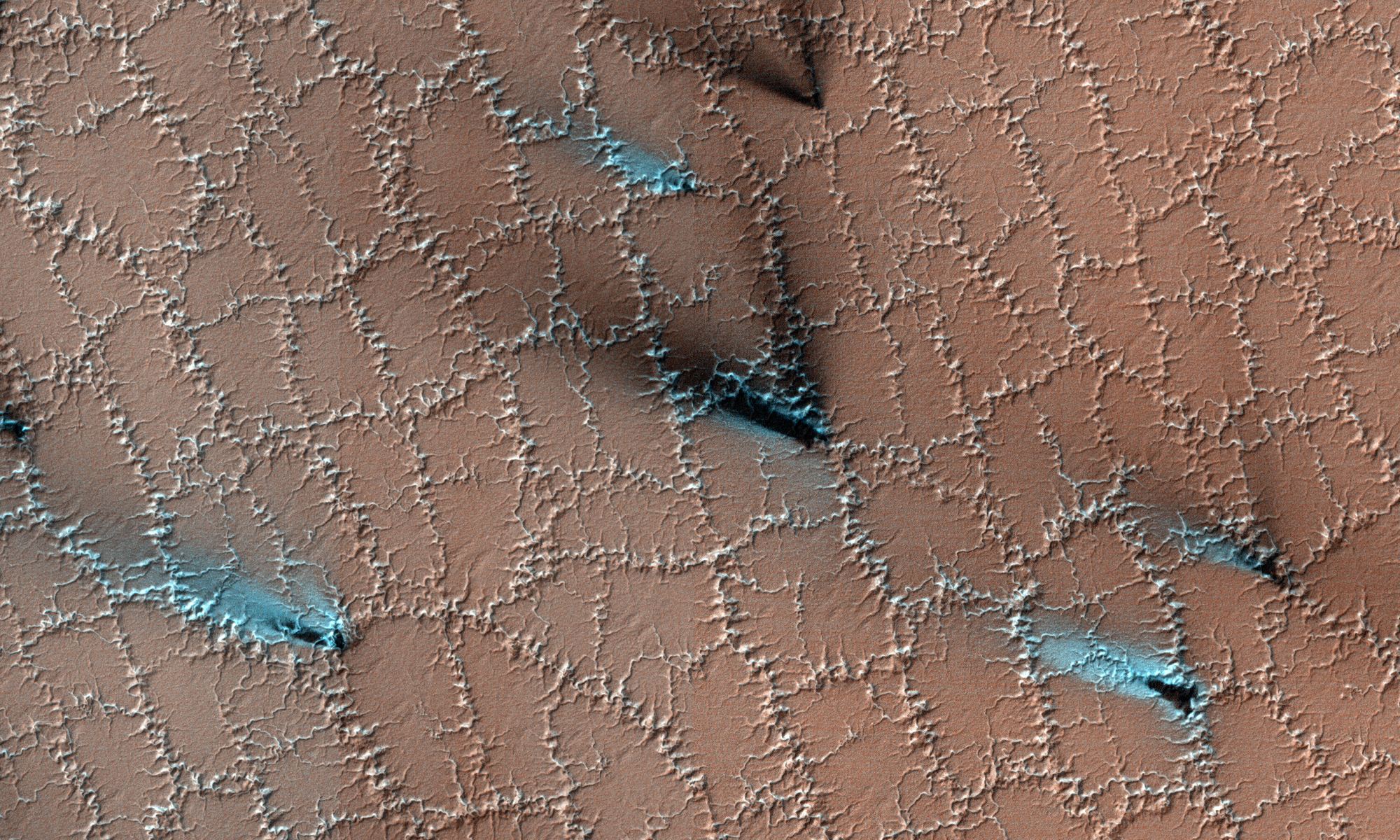
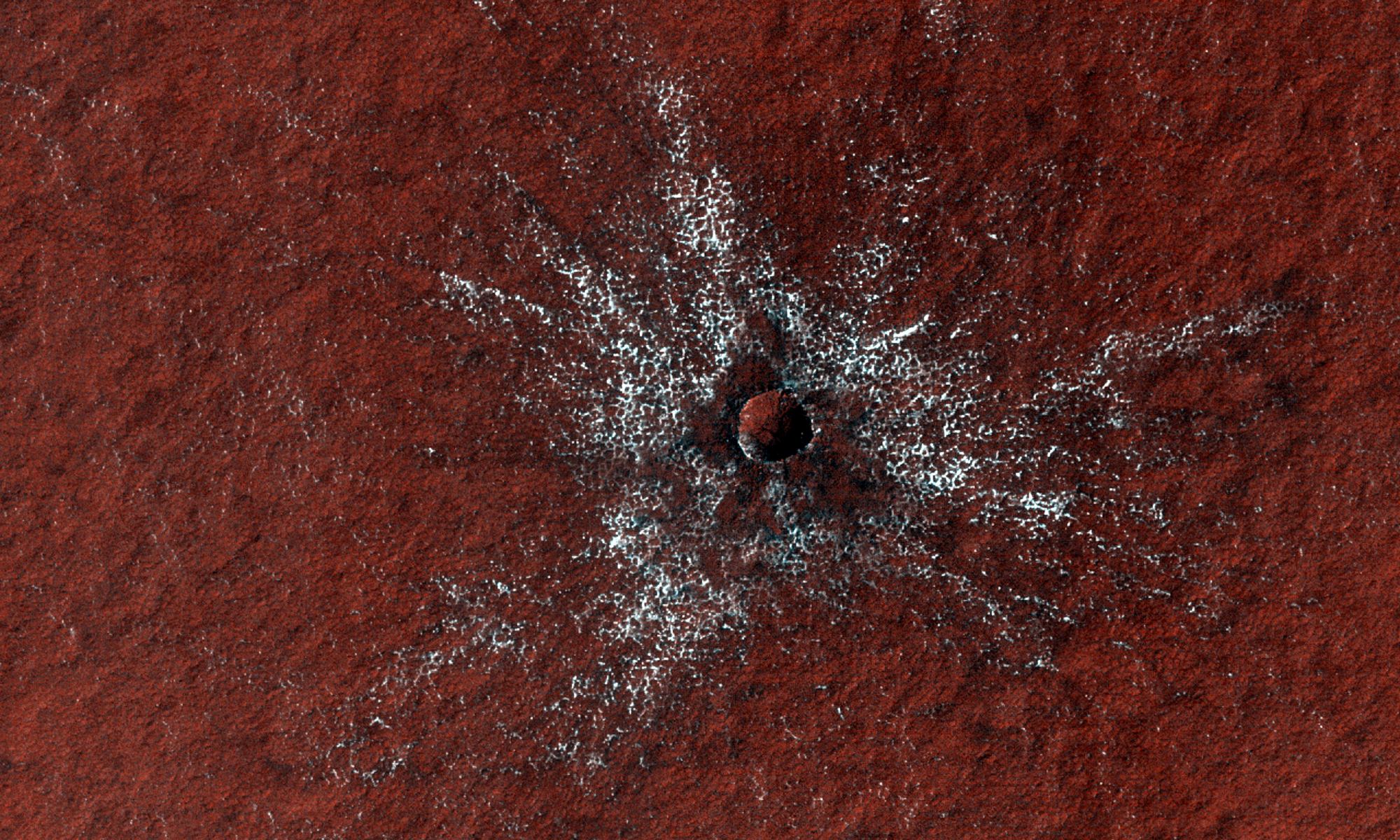
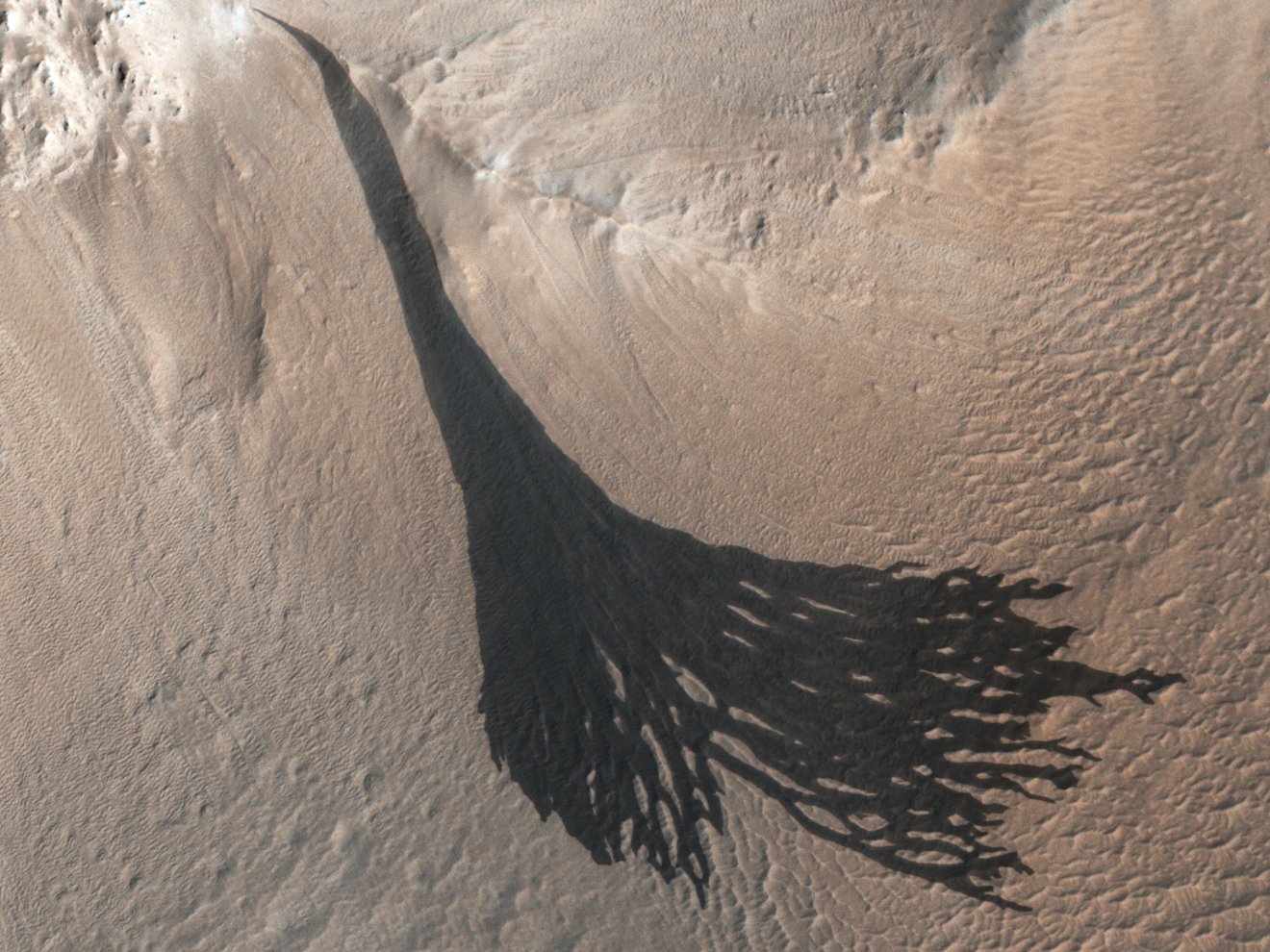
While scientists have been aware that Mars’ polar ice caps change with the seasons, it has only been within the last 50 years that they have realized that they are largely composed of frozen carbon dioxide (aka. “dry ice”) that cycles in and out of the atmosphere – and questions as to how this happens remain. In a recent study, a team of researchers led by the Planetary Science Institute (PSI) synthesized decades of research with more recent observations of the poles. From this, they determined how the Martian poles differ in terms of their seasonal accumulation and release of atmospheric carbon dioxide.
Continue reading “There are Important Differences Between the Ice Caps on Mars”